The theory was first developed by B.F. Skinner in the mid-20th century and has been influential in shaping our understanding of learning and behavior. Behaviorism is a psychological theory that views behavior as a response to stimuli in the environment. It is based on the idea that all behavior can be explained by the relationship between stimuli and responses, and that learning occurs through the formation of associations between stimuli and responses.
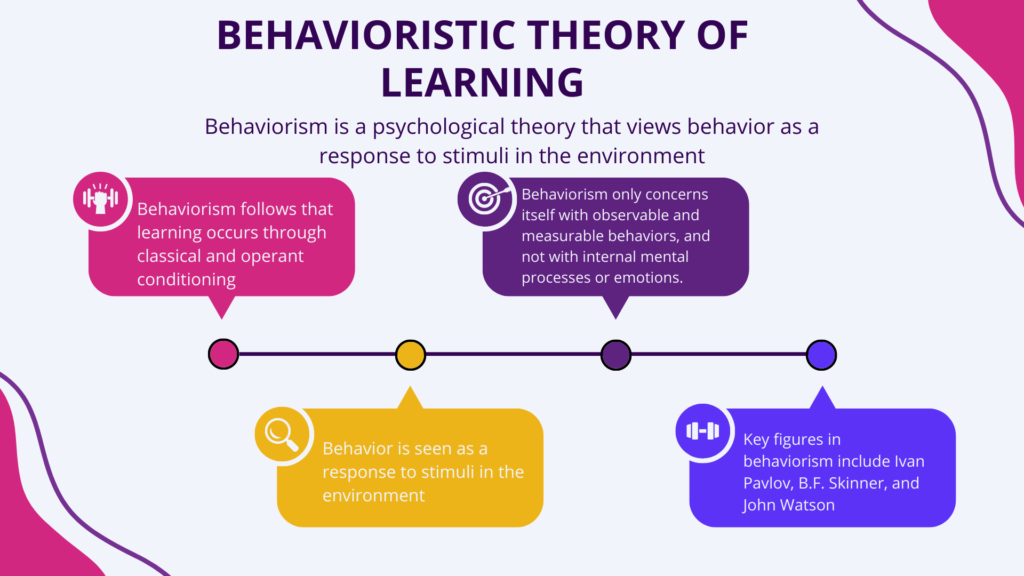
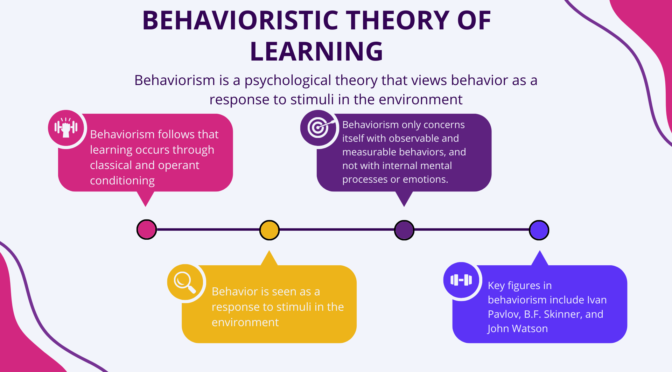
It emphasizes the role of environmental stimuli and rewards/punishments in shaping and modifying behavior. Key figures in behaviorism include Ivan Pavlov, B.F. Skinner, and John Watson. This theory has been applied in fields such as education , and has also influenced the development of behavior modification techniques and therapies.
Key features of behaviorism include:
- Emphasis on observable behavior: Behaviorism only concerns itself with observable, measurable behavior and disregards internal processes such as thoughts and feelings.
- Conditioning: Behaviorism follows that learning occurs through classical and operant conditioning, where behavior is shaped through reinforcement or punishment.
- Stimulus-Response Relationships: Behavior is seen as a response to stimuli in the environment, and the goal of behaviorism is to identify the specific relationships between stimuli and responses.
- Use of Reinforcement and Punishment: Reinforcement is used to increase the frequency of desired behaviors, while punishment is used to decrease the frequency of undesired behaviors.
- Focus on the Environment: Behaviorism places a strong emphasis on the role of the environment in shaping behavior, and views behavior as largely determined by environmental factors.
- Scientific approach: Behaviorism uses a scientific, empirical approach to understanding behavior, relying on systematic observation and experimentation to develop theories and principles.
- Limited focus: Behaviorism has a limited focus on human behavior, neglecting the internal mental processes that may play a role in shaping behavior.
Also Read : Sigmund Freud Theory
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita

I’d incessantly want to be update on new posts on this internet site, saved to favorites! .
Sweet blog! I found it while surfing around on Yahoo News. Do you have any tips on how to get listed in Yahoo News? I’ve been trying for a while but I never seem to get there! Appreciate it
Amazing! This blog looks just like my old one! It’s on a totally different topic but it has pretty much the same layout and design. Wonderful choice of colors!
vibracion de motor
Sistemas de ajuste: esencial para el rendimiento estable y óptimo de las maquinarias.
En el ámbito de la innovación moderna, donde la efectividad y la confiabilidad del equipo son de suma trascendencia, los dispositivos de calibración cumplen un papel fundamental. Estos dispositivos específicos están desarrollados para equilibrar y estabilizar elementos giratorias, ya sea en herramientas productiva, transportes de movilidad o incluso en aparatos domésticos.
Para los profesionales en conservación de sistemas y los técnicos, trabajar con dispositivos de balanceo es importante para promover el operación fluido y seguro de cualquier aparato rotativo. Gracias a estas opciones innovadoras avanzadas, es posible disminuir notablemente las oscilaciones, el ruido y la carga sobre los cojinetes, aumentando la tiempo de servicio de elementos costosos.
Igualmente relevante es el rol que juegan los sistemas de equilibrado en la servicio al cliente. El asistencia técnico y el mantenimiento continuo empleando estos equipos facilitan dar asistencias de excelente calidad, aumentando la contento de los consumidores.
Para los responsables de empresas, la financiamiento en sistemas de balanceo y detectores puede ser fundamental para aumentar la rendimiento y desempeño de sus sistemas. Esto es particularmente significativo para los dueños de negocios que manejan modestas y medianas organizaciones, donde cada detalle importa.
También, los sistemas de balanceo tienen una extensa aplicación en el sector de la prevención y el control de calidad. Permiten detectar probables errores, previniendo mantenimientos elevadas y problemas a los dispositivos. También, los información generados de estos equipos pueden aplicarse para perfeccionar procedimientos y potenciar la exposición en sistemas de investigación.
Las zonas de aplicación de los sistemas de balanceo incluyen variadas industrias, desde la producción de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el control ecológico. No interesa si se considera de grandes elaboraciones manufactureras o pequeños establecimientos domésticos, los sistemas de equilibrado son fundamentales para promover un funcionamiento óptimo y libre de detenciones.
Comercializamos máquinas para balanceo!
Somos fabricantes, elaborando en tres ubicaciones al mismo tiempo: Argentina, España y Portugal.
✨Ofrecemos equipos altamente calificados y debido a que somos productores directos, nuestros costos superan en competitividad.
Disponemos de distribución global en cualquier lugar del planeta, lea la descripción de nuestros equipos de equilibrio en nuestro sitio web.
El equipo de equilibrio es transportable, de bajo peso, lo que le permite ajustar cualquier elemento giratorio en todas las circunstancias.
Vipertoto alternatif
Your posts feel like a breath of fresh air — honest, insightful, and always written with intention.
[b]Eliminate Vibration Issues and Improve Equipment Performance[/b]
Vibration is a silent killer of industrial machines. Imbalance leads to worn-out bearings, misalignment, and costly breakdowns. [b]Balanset-1A[/b] is the ultimate tool for detecting and correcting vibration problems in electric motors, pumps, and turbines.
[b]What Makes Balanset-1A Stand Out?[/b]
– Precise vibration measurement & balancing
– Compact, lightweight, and easy to use
– Two kit options:
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT]Full Kit on Amazon[/url] – Advanced sensors & accessories, Software for real-time data analysis, Hard carrying case
Price: [b]2250 EUR[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT][img]https://i.postimg.cc/SXSZy3PV/4.jpg[/img][/url]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR]OEM Kit on Amazon[/url] – Includes core balancing components, Same high-quality device
Price: [b]1978 EUR[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR][img]https://i.postimg.cc/cvM9G0Fr/2.jpg[/img][/url]
Prevent unexpected breakdowns – Invest in [b]Balanset-1A[/b] today!