The role of guidance and participation in inclusive education is crucial for creating a supportive and empowering learning environment for all students, regardless of their abilities, backgrounds, or diverse needs.
Here is a detailed explanation of the role of guidance and participation in inclusive education:
- Guidance for Teachers and Educators: Inclusive education requires guidance and support for teachers and educators to develop the necessary knowledge, skills, and attitudes to meet the diverse needs of students. This guidance includes:
a) Professional Development: Providing ongoing professional development opportunities to enhance teachers’ understanding of inclusive practices, differentiated instruction, assessment strategies, and classroom management techniques.
b) Collaboration and Networking: Facilitating collaboration among teachers, special educators, support staff, and specialists to share expertise, exchange ideas, and develop effective teaching strategies for diverse learners.
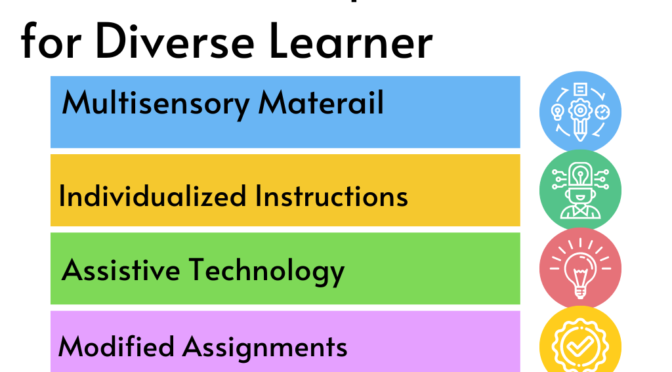
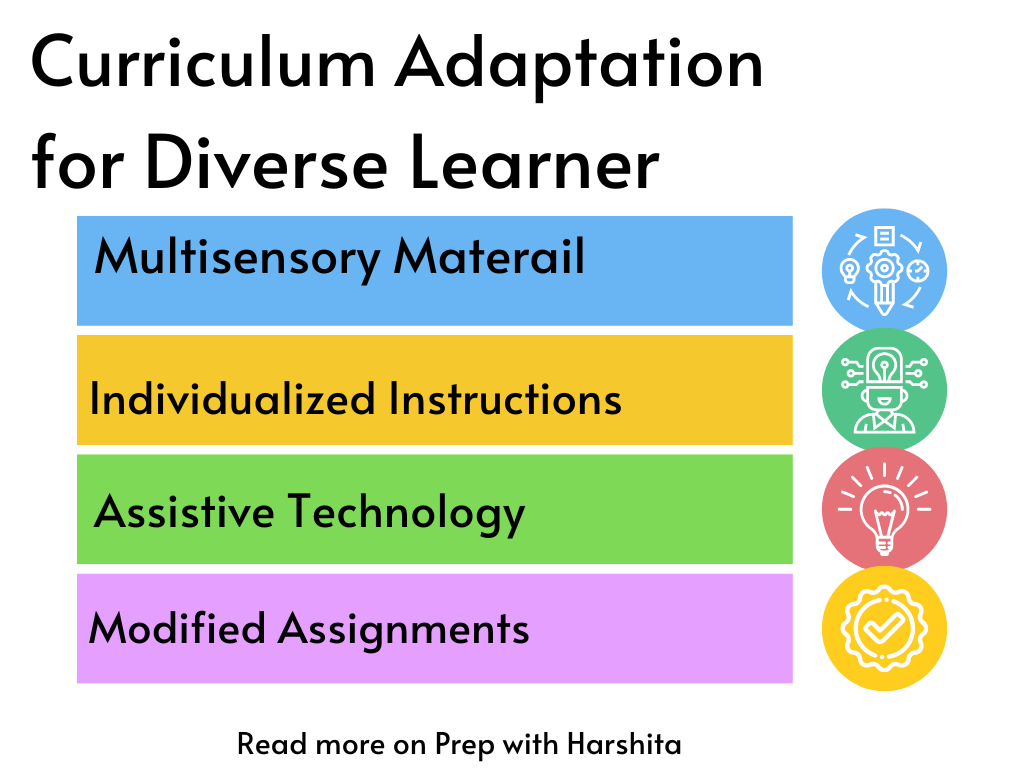
c) Access to Resources: Ensuring teachers have access to appropriate resources, including instructional materials, assistive technologies, and specialized equipment, to meet the individual learning needs of students.
- Individualized Support for Students: Guidance and participation in inclusive education involve providing individualized support to students to help them succeed in the classroom. This support includes:
a) Individual Education Plans (IEPs): Developing and implementing IEPs for students with special educational needs, outlining specific goals, accommodations, and support services tailored to their individual requirements.
b) Differentiated Instruction: Adapting teaching methods, materials, and assessments to accommodate students’ diverse learning styles, abilities, and interests. This ensures that all students can actively engage and access the curriculum.
c) Personalized Learning: Recognizing and addressing the unique strengths and challenges of each student, promoting self-directed learning, and setting achievable goals that promote their academic, social, emotional, and behavioral development.
- Collaboration with Families and Communities: Guidance and participation in inclusive education involve actively involving families and communities in the education process. This collaboration includes:
a) Parental Involvement: Encouraging parents to actively participate in their child’s education, seeking their input and involving them in decision-making processes related to their child’s educational journey.
b) Open Communication: Establishing effective channels of communication between schools, teachers, and parents, ensuring regular updates, sharing progress reports, and discussing strategies to support students’ learning and well-being.
c) Community Engagement: Creating opportunities for students to connect with their local communities, engaging in inclusive practices and fostering a sense of belonging, respect, and understanding for all individuals.
- Advocacy and Policy Development: Guidance and participation in inclusive education extend to advocating for inclusive policies, promoting awareness, and actively contributing to the development of inclusive practices. This involves:
a) Advocacy for Inclusive Policies: Collaborating with stakeholders, policymakers, and educational authorities to advocate for inclusive policies and legislation that support the rights and equitable access to education for all students.
b) Creating Inclusive School Culture: Promoting a positive and inclusive school culture that celebrates diversity, fosters tolerance, and embraces the principles of inclusivity, respect, and equality.
c) Addressing Barriers and Challenges: Identifying and addressing systemic barriers and challenges that hinder inclusive education, such as physical accessibility, social stigmas, discriminatory practices, and lack of resources.
In conclusion, guidance and participation play a crucial role in creating an inclusive education system. By providing guidance and support to teachers, individualized assistance to students, collaborating with families and communities, and advocating for inclusive policies, inclusive education can be effectively implemented to ensure equitable access, participation, and success for all learners.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita

Also Read : Person with Disabilities act