UNESCO define vocational education as “Education action to prepare for work & active life”
More in Video
Also Read : Need and Importance of Institutional Planning | Institutional Planning & Management | M.Ed
UNESCO define vocational education as “Education action to prepare for work & active life”
More in Video
Also Read : Need and Importance of Institutional Planning | Institutional Planning & Management | M.Ed
Each school is headed by one head or principal & is solely responsible for institutional planning & management.
More in Video…
Also Read : Social Demand Approach | Institutional Planning & Management | M.Ed
The social demand approach is based on an assessment of society’s requirement & need for education.
More In Video…
Also Read : Defence Mechanism in Psychology | Psychology of Learning and Development | M.Ed
Freud’s Psychoanalytical Theory was developed by Sigmund Freud. He is the founder of psychoanalysis, a method of treating mental illness and understanding the human psyche. His theory is based on the idea that the unconscious mind contains repressed thoughts, memories, and desires that shape our behavior.
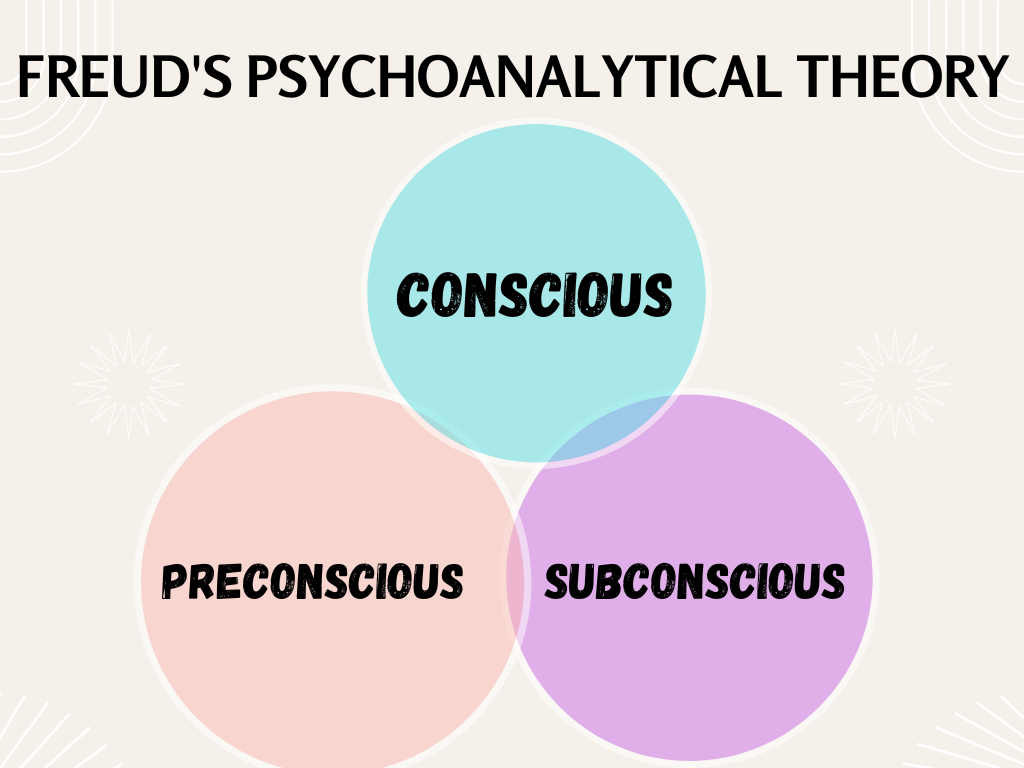
According to Freud’s theory, the mind is divided into three parts: the conscious mind, the preconscious mind, and the unconscious mind. The conscious mind is what we are aware of at any given moment, while the preconscious mind contains thoughts and memories that can be brought into consciousness with ease. The unconscious mind contains thoughts, memories, and desires that are hidden from consciousness and can only be accessed through psychoanalytic techniques.
Freud believed that the unconscious mind has a powerful influence on behavior and that much of our behavior is motivated by unconscious desires and conflicts. He developed a model of personality consisting of three parts: the id, the ego, and the superego. The id represents our primitive instincts and desires, the ego is the rational part of the mind that mediates between the id and the external world, and the superego is the moral and ethical component that represents societal values and norms.
One of the key concepts in Freud’s theory is the Oedipus complex, which describes a child’s sexual desire for their opposite-sex parent and hostility towards their same-sex parent. This complex is believed to be resolved through identification with the same-sex parent, leading to the development of gender identity and the superego.
Freud’s psychoanalytic theory has been widely debated and criticized, but it remains an important influence on psychology and popular culture. Its influence can be seen in fields such as literary criticism, film studies, and art history, where psychoanalytic techniques are used to interpret works of art and literature.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita
Also Read : Group Guidance
To protect ourselves from problems like anxiety & stress, our body sets up mechanisms known as defence mechanisms.
More in Video…
Also Read : Scope of Educational Psychology | Psychology of Learning and Development | M.Ed