Evaluation is the process of assessing or measuring the effectiveness, impact, or value of something, such as a program, project, product, or service. There are many types of Evaluation method. It involves collecting and analyzing data to determine whether the goals and objectives of the thing being evaluated have been achieved, and to identify strengths and weaknesses in the implementation.
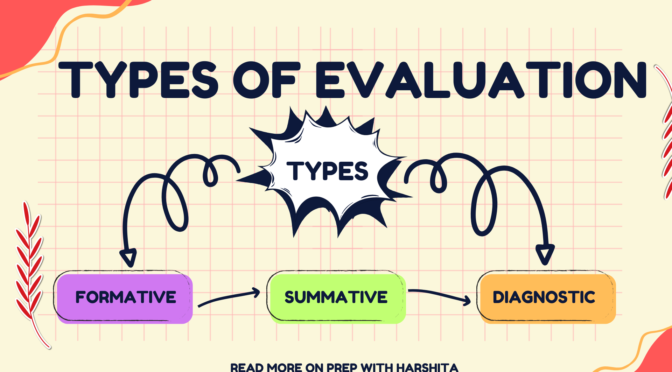
Here are more details about the three types of evaluation:
- Formative Evaluation: It is a type of evaluation that is conducted during the development and implementation of a program or project. Its purpose is to assess progress and identify areas for improvement. It involves ongoing feedback and monitoring to ensure that the program is on track to meet its goals. It can be used to identify strengths and weaknesses in a program, to assess the quality of the program’s implementation, and to make adjustments to the program to ensure its success. This type of evaluation is usually qualitative and can involve surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
- Diagnostic Evaluation: Diagnostic evaluation is used to identify the root cause of a problem or issue. It is used to determine why a program is not working as intended and what changes need to be made to improve its effectiveness. Diagnostic evaluation involves collecting data on the problem or issue, analyzing the data, and making recommendations for improvement. This type of evaluation is usually qualitative and can involve surveys, interviews, and focus groups.
- Summative Evaluation: It is a type of evaluation that is conducted at the end of a program or project to measure its overall impact and effectiveness. Its purpose is to determine whether the program achieved its goals and objectives. It involves collecting data on the outcomes of the program, analyzing the data, and making conclusions about the program’s success or failure. This type of evaluation is usually quantitative and can involve surveys, tests, and other standardized assessments.
Also Read : Socio Metric Technique
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita