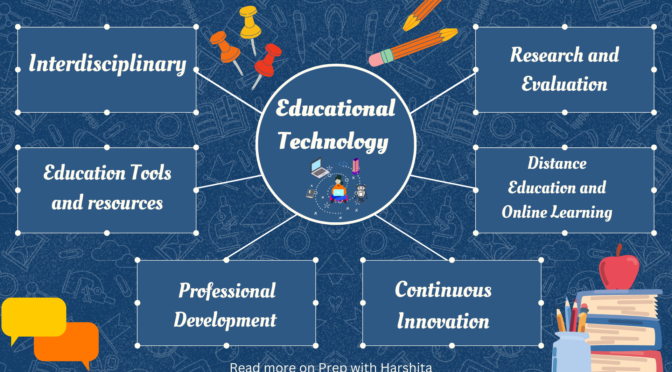
Educational technology is a multidisciplinary field of study that involves the integration of technology into educational processes to enhance learning and teaching. As a discipline, educational technology focuses on understanding how technology can be effectively used to support and improve education. Here are key aspects of the concept of educational technology as a discipline:
Interdisciplinary Nature:
Educational technology draws from various disciplines, including education, psychology, communication, computer science, and instructional design. It brings together insights from these fields to create effective educational tools and strategies.
Design and Development:
The discipline involves the design, development, and implementation of educational tools and resources. This includes the creation of software, multimedia materials, online courses, and other technology-enhanced learning environments.
Read more on next page..
Also Read : E portfolio