Language serves a variety of functions, and its primary purpose is communication. The functions of language can be broadly categorized into several types, each contributing to the effectiveness of human communication.
Here are some key functions of language:
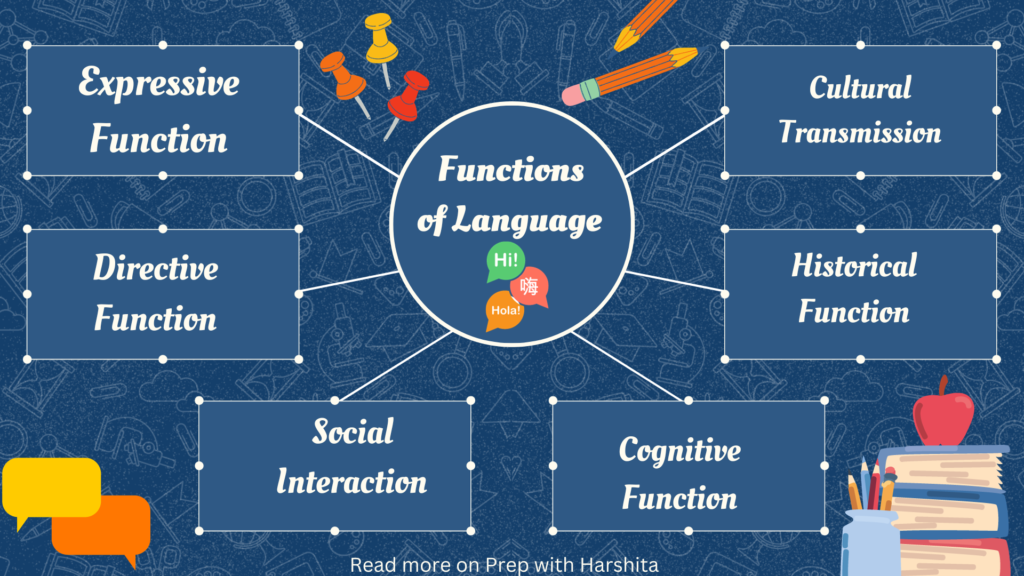
Expressive Function:
Language allows individuals to express their thoughts, feelings, and experiences, describing their internal states or external events.
Directive Function:
Language can be used to give instructions, commands, or requests. This function is directive, influencing the behavior of others.
Referential Function:
Language is used to refer to and denote objects, people, events, or concepts in the external world. It provides a means for sharing information about the surrounding environment.
Also Read : Features of Language
Social Interaction:
Language is used for social purposes, maintaining social contact and establishing or reinforcing social relationships. Small talk and greetings are examples of phatic communication.
Poetic Function:
Language is used to refer to and denote objects, people, events, or concepts in the external world. It provides a means for sharing information about the surrounding environment.
Cognitive Function:
Language is crucial for cognitive processes, such as problem-solving, reasoning, and organizing thoughts. It serves as a tool for mental representation and understanding.
Cultural Transmission:
Language plays a crucial role in transmitting cultural values, traditions, and knowledge from one generation to another.
Historical Function:
Language serves as a tool for documenting and preserving historical events, cultural practices, and societal changes.
Also visit : Prep with Harshita

16 thoughts on “Functions of Language”