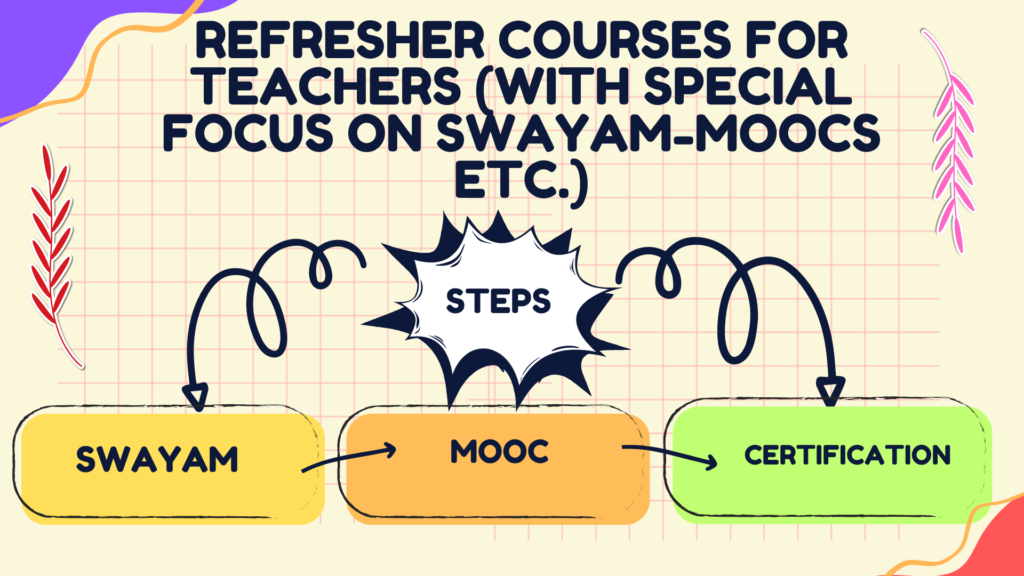
Refresher courses for teachers play a crucial role in keeping educators updated with the latest advancements in their respective fields and enhancing their teaching skills. The SWAYAM platform in India, which stands for Study Webs of Active-Learning for Young Aspiring Minds, offers Massive Open Online Courses (MOOCs) that can serve as valuable refresher courses for teachers. Here’s an overview:
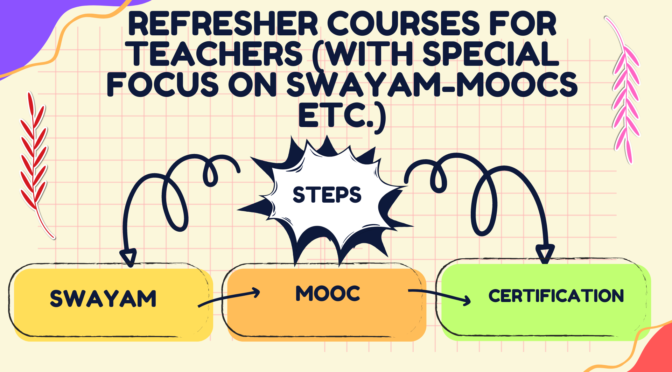
SWAYAM (Study Webs of Active Learning for Young Aspiring Minds)
- Platform: SWAYAM is an online learning platform initiated by the Government of India, providing a wide range of courses across various subjects and levels.
- MOOCs: Massive Open Online Courses on SWAYAM cover diverse topics, including education, science, technology, humanities, and social sciences.
- Accessibility: SWAYAM courses are open to all, including teachers, and they offer flexible learning schedules.
Refresher Courses for Teachers on SWAYAM:
- Professional Development: Teachers can find refresher courses on pedagogy, educational technology, subject-specific methodologies, and other aspects of teaching and learning.
- Certification: Many courses on SWAYAM provide certification upon completion, allowing teachers to showcase their commitment to continuous learning.
- Convenience: SWAYAM MOOCs provide a convenient way for teachers to access high-quality content and update their knowledge without the need for physical attendance.
Other Platforms and Initiatives:
- Apart from SWAYAM, teachers can explore other MOOC platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udacity for a broader range of courses from international institutions.
- Local educational bodies and universities may offer refresher courses or workshops for teachers. These could be conducted in person or through online platforms.
Government Initiatives:
Governments often launch initiatives and programs to support the professional development of teachers. Teachers should check with their local education departments or educational institutions for information on available refresher courses.
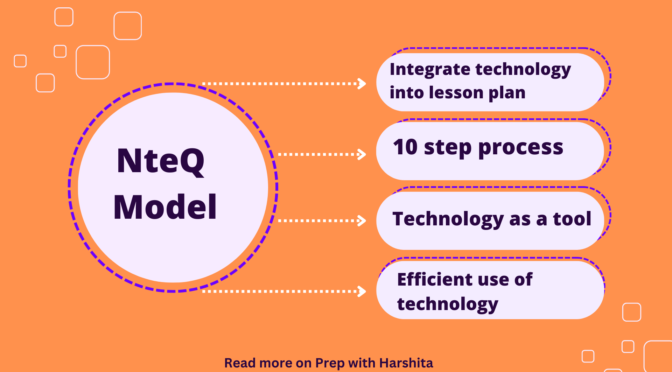
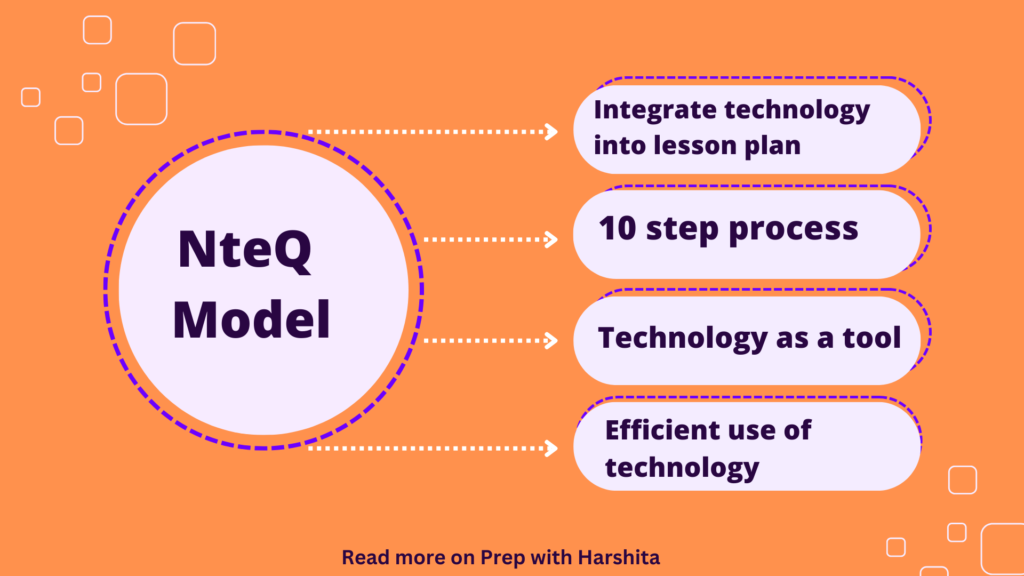
Also Read: NteQ Model
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita