Inclusive education is a philosophy that advocates for the integration of children with special needs and disabilities into mainstream schools and classrooms. The goal of inclusive education is to create an environment where all students, regardless of their abilities, can learn and thrive together. However, implementing inclusive education can be challenging due to a number of barriers that exist in the education system. In this response, we will discuss the barriers and facilitators of inclusive education in detail.
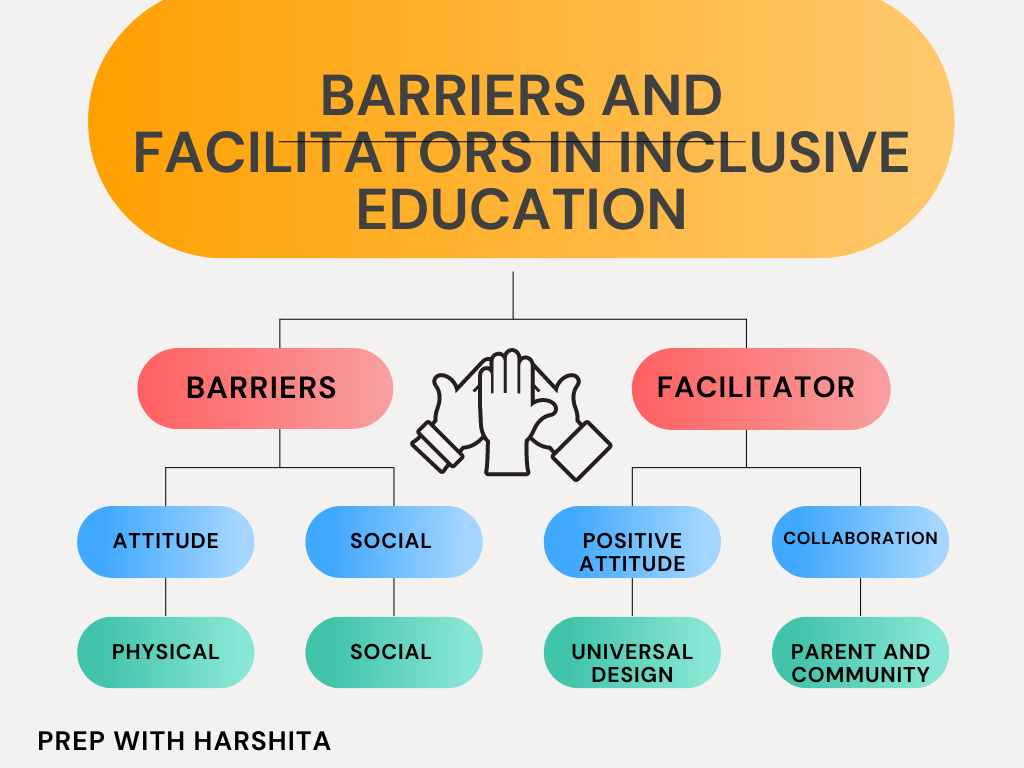
Barriers to Inclusive Education:
- Lack of resources: One of the biggest barriers to inclusive education is the lack of resources, including funding, staff, and materials. Schools often struggle to provide the necessary support and accommodations for students with special needs and disabilities, which can result in these students being excluded from mainstream classrooms.
- Attitudes and beliefs: Attitudes and beliefs about disability can also be a significant barrier to inclusive education. Negative attitudes and stereotypes about students with disabilities can lead to exclusion, discrimination, and a lack of support. Teachers and other education professionals may also hold beliefs that certain students are not capable of learning and, as a result, may not put forth the necessary effort to help these students succeed.
- Limited teacher training: Another barrier to inclusive education is the lack of training that teachers and other education professionals receive in working with students with disabilities. Many teachers may not feel prepared or equipped to handle the needs of students with special needs, which can lead to a lack of support and accommodations.
- Physical barriers: Physical barriers can also make it difficult for students with disabilities to access mainstream classrooms. For example, if a school building is not accessible to students who use wheelchairs, these students may be unable to attend mainstream classes.
- Assessment and testing: Standardized assessments and testing can be a barrier to inclusive education, as these assessments may not accurately reflect the abilities of students with disabilities. This can lead to these students being placed in lower-level classes or excluded from certain programs.
Facilitators of Inclusive Education:
- Positive attitudes and beliefs: A positive attitude and belief system is essential for promoting inclusive education. Teachers and other education professionals should believe that all students are capable of learning and should be provided with the necessary support and accommodations to succeed.
- Collaborative planning: Collaborative planning between teachers, parents, and other education professionals can help to identify the specific needs of students with disabilities and develop individualized education plans (IEPs) that address these needs.
- Professional development: Professional development opportunities for teachers and other education professionals can help to build knowledge and skills in working with students with disabilities. This can include training on inclusive teaching strategies, assistive technology, and classroom accommodations.
- Universal Design for Learning: Universal Design for Learning (UDL) is an approach to teaching that aims to create a learning environment that is accessible to all students, regardless of their abilities. UDL involves designing curriculum, instruction, and assessment in a way that is flexible and can be adapted to meet the needs of all learners.
- Parent and community involvement: Parent and community involvement can be a facilitator of inclusive education. When parents and community members are engaged in the education process, they can provide support to students with disabilities which create a culture of inclusion.
In conclusion, inclusive education is an essential component of ensuring that all students have access to a quality education. However, there are many barriers that must be overcome in order to achieve this goal. By addressing these barriers and implementing facilitators such as positive attitudes, collaborative planning, professional development, Universal Design for Learning, and parent and community involvement, schools and education systems can create a more inclusive and equitable learning environment for all students.
Also Read : Meaning and need of Inclusive Education