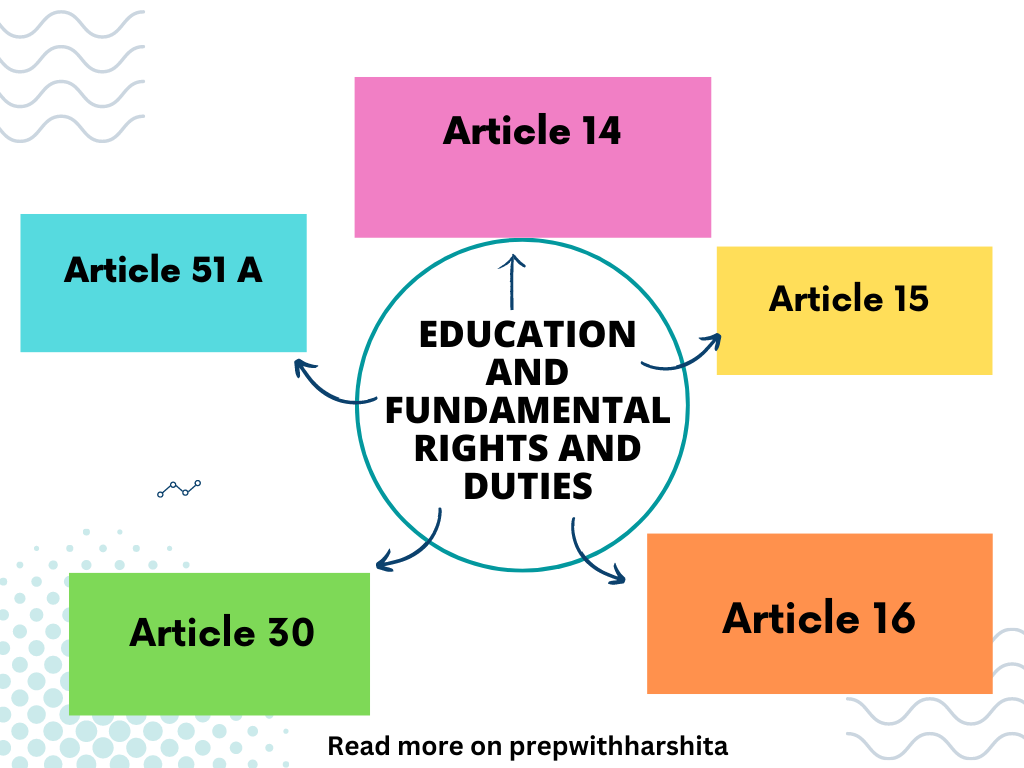
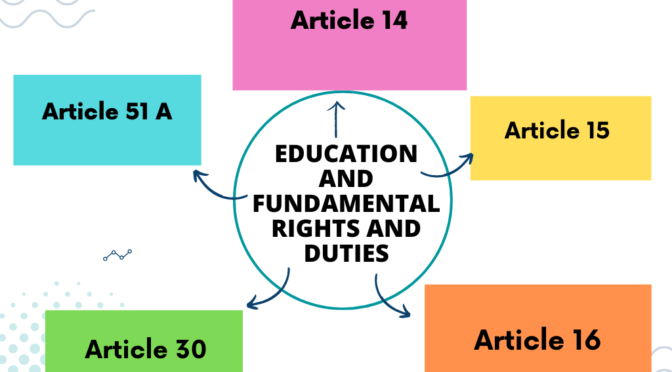
Education and fundamental rights are closely interconnected in the Indian Constitution. The following is a detailed explanation of how Articles 15, 16, 14, 30, and 51A relate to education and fundamental rights:
- Article 15:
- Article 15 prohibits discrimination on various grounds, including religion, race, caste, sex, and place of birth.
- In the context of education, Article 15 ensures that no citizen is denied access to educational institutions based on these discriminatory factors.
- It guarantees equal opportunity and prohibits educational institutions from discriminating against students in admissions, facilities, or resources.
- Article 15 also allows the State to make special provisions for the advancement of socially and educationally backward classes, Scheduled Castes, and Scheduled Tribes.
- This provision enables the implementation of reservation policies in educational institutions to provide equal opportunities to marginalized communities.
- Article 16:
- Article 16 guarantees equality of opportunity in matters of public employment.
- While it primarily addresses employment, the principles of equal opportunity and non-discrimination extend to education as well.
- Article 16 ensures that all citizens have equal access to educational institutions, particularly those established or aided by the State.
- It prohibits discrimination in educational institutions based on religion, race, caste, sex, descent, place of birth, or residence.
- The article also permits the State to make provisions for the reservation of seats or quotas in educational institutions for socially and educationally backward classes.
- Article 14:
- Article 14 enshrines the principle of equality before the law and equal protection of the laws.
- This fundamental right ensures that all individuals, including students, are treated equally under the law and have equal access to justice.
- In the realm of education, Article 14 guarantees that students are not subject to discriminatory practices in educational institutions or educational policies.
- It ensures that students are treated fairly, without any bias or prejudice, in matters such as admissions, examinations, discipline, and evaluation.
- Article 30:
- Article 30 grants the right to minorities to establish and administer educational institutions of their choice.
- It recognizes the significance of preserving and promoting the cultural and educational rights of religious and linguistic minorities.
- Article 30 allows minorities to establish educational institutions where they can impart education in a manner that aligns with their cultural, religious, or linguistic ethos.
- This provision ensures that minorities have the freedom to establish and manage educational institutions that cater to the specific needs and aspirations of their communities.
- Article 51A:
- Article 51A contains the fundamental duties of citizens of India.
- One of the fundamental duties mentioned in Article 51A(j) is to strive towards excellence in all spheres of individual and collective activity, including education.
- It emphasizes the responsibility of citizens to value education, pursue knowledge, and contribute to the overall progress and development of society.
- This duty highlights the significance of education as a fundamental right and encourages individuals to actively engage in their educational pursuits.
Collectively, these articles uphold the right to education, ensure equal opportunities, prohibit discrimination, and emphasize the importance of education in building a just and inclusive society. They aim to provide every citizen with the opportunity to access quality education, promote social equity, and empower individuals to realize their full potential.
Also Read: Democracy and Education