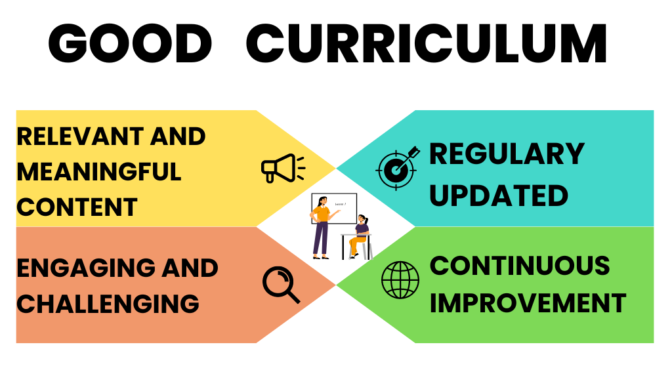
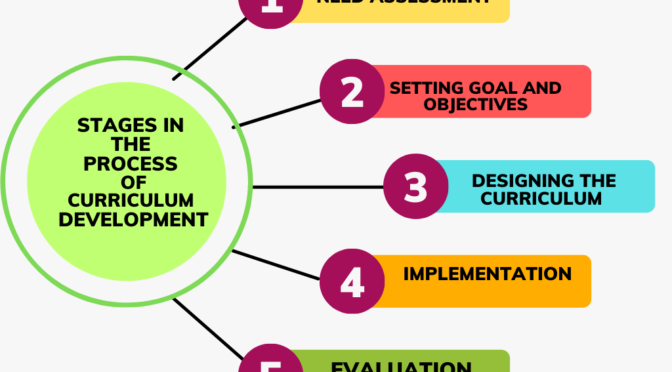
Impact of Science and Technology in Curriculum Development is major and multidimensional. Science and technology have had a profound impact on the development of curriculum in recent years.
Here are some of the ways in which science and technology have influenced curriculum development in detail:
- Emergence of new content areas:
Advances in science and technology have led to the emergence of new content areas in the curriculum, such as computer science, robotics, and biotechnology. These areas are now considered essential to prepare students for the 21st-century workforce, and they have been integrated into the curriculum in many schools.
For example, computer science has become a core subject in many countries as it is recognized as an important skill for the future. Robotics and biotechnology are also emerging fields that require specialized knowledge and skills that can be integrated into the science curriculum.
- Increased emphasis on STEM education:
Science and technology have also led to an increased emphasis on STEM (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics) education in the curriculum. STEM education is designed to prepare students for the jobs of the future, which are expected to require advanced skills in these areas.
STEM education focuses on developing skills such as critical thinking, problem-solving, and innovation. These skills are essential for students to succeed in the 21st-century workforce, where technology is rapidly advancing and changing the nature of work.
- Updated teaching methods:
Science and technology have also influenced the teaching methods used in the curriculum. New technologies, such as interactive whiteboards, tablets, and educational software, have transformed the way teachers deliver instruction and engage with students.
For example, teachers can now use interactive whiteboards to create engaging and interactive lessons that allow students to participate in the learning process. Educational software can also be used to create personalized learning experiences that are tailored to the needs and abilities of individual students.
- Improved access to information:
Advances in science and technology have also made it easier for students to access information and resources that support their learning. The internet, online databases, and digital libraries provide students with access to a wealth of information that was previously unavailable.
Students can now access information from anywhere in the world, allowing them to research topics and collaborate with peers and experts from around the globe. This has opened up new opportunities for learning and has made education more accessible to students from all backgrounds.
- Enhanced assessment tools:
It also led to the development of new assessment tools that provide more accurate and detailed feedback on student performance. Computer-based assessments, for example, can provide immediate feedback to students and teachers, allowing for more timely and effective interventions.
Assessment tools such as simulations and virtual labs have also been developed, allowing students to conduct experiments and simulations in a safe and controlled environment. This not only provides more accurate and detailed feedback but also allows students to develop critical thinking and problem-solving skills.
- Preparation for the future:
Finally, science and technology have influenced the curriculum by preparing students for the future. Students who are exposed to science and technology in the curriculum are better equipped to navigate the challenges of the modern world, whether it be in the workplace or in their personal lives.
By integrating science and technology into the curriculum, schools are preparing students for the future by developing the skills and knowledge they need to succeed in a rapidly changing world. This includes not only technical skills but also soft skills such as communication, collaboration, and creativity.
Also Read : Inert and Live Curriculum
In conclusion, science and technology have had a significant impact on curriculum development, leading to the emergence of new content areas, an increased emphasis on STEM education, updated teaching methods, improved access to information, enhanced assessment tools, and better preparation for the future. As science and technology continue to evolve, it is likely that they will continue to shape the curriculum in new and innovative ways.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita