Accreditation and quality assurance play crucial roles in ensuring the effectiveness and standards of education. Different agencies are involved in these processes, each with specific roles and functions. Here’s an overview of the roles and functions of various agencies in school education:
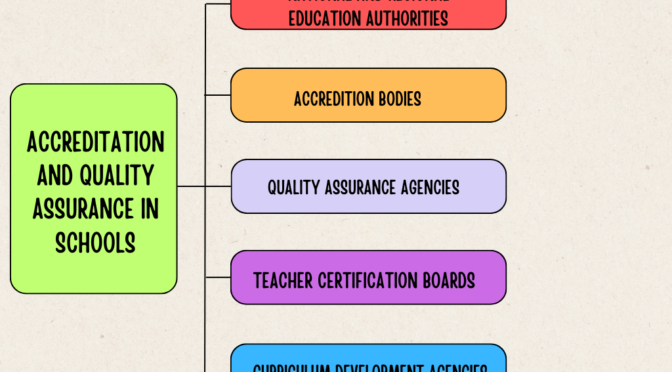
Accreditation and Quality Assurance in Schools
National and Regional Education Authorities:
- Role: National and regional education authorities are responsible for setting policies, standards, and guidelines for education at the national or regional level.
- Function: They establish the overall framework for accreditation and quality assurance in schools. These authorities often define the curriculum, teacher qualifications, and assessment standards.
Accreditation Bodies:
- Role: Accreditation bodies are organizations that evaluate schools against predetermined standards to ensure they meet specific quality criteria.
- Function: Accreditation bodies assess schools based on factors such as curriculum quality, faculty qualifications, infrastructure, and overall educational outcomes. They grant accreditation status to schools that meet or exceed established standards.
Also Read: Role of Parent Teacher Association
Quality Assurance Agencies:
- Role: Quality assurance agencies focus on monitoring and evaluating the quality and effectiveness of educational programs and services.
- Function: These agencies conduct regular reviews, audits, and evaluations of schools to ensure they maintain and improve educational standards. They may provide recommendations for improvement and monitor the implementation of corrective actions.
Teacher Certification Boards:
- Role: Teacher certification boards are responsible for establishing and maintaining standards for teacher qualifications and certification.
- Function: They ensure that teachers meet specific educational and professional requirements. Certification boards may conduct examinations, review credentials, and establish continuing education requirements for teachers.
Read More on the second page…