Open book system refers to an assessment method in which students are allowed to use their textbooks, notes, and other study materials during an exam. This type of assessment is different from traditional closed-book exams, where students are not allowed to refer to any materials during the exam.
In an open book system, students are expected to have a better understanding of the material and be able to apply critical thinking skills to solve problems. They are also expected to be able to use their textbooks and notes to support their answers and provide evidence for their reasoning.
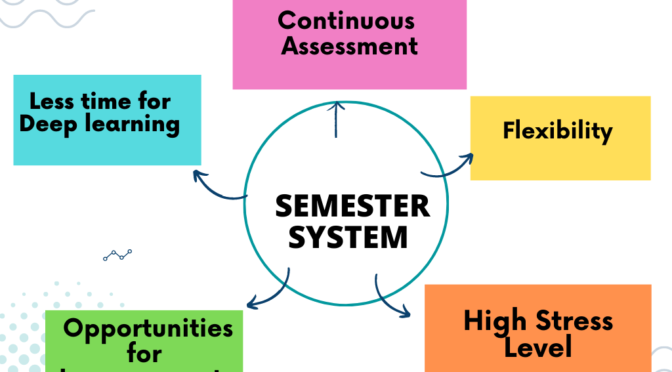
Some of the advantages of the open book system include:
- Encourages deeper learning: Since students are allowed to use their study materials, the open book system encourages them to read and understand the material in depth, as they will need to apply their knowledge to solve problems.
- Fosters critical thinking skills: It may requires students to analyze and interpret information, apply concepts, and draw conclusions, which fosters critical thinking skills.
- Reduces stress and anxiety: Students may feel less stressed and anxious during an open book exam as they have access to their study materials.
- Provides more accurate assessment: It may provide a more accurate assessment of a student’s knowledge and skills as they are required to apply their knowledge and skills to solve problems.
However, the open book system also has some disadvantages, such as:
- Requires time management skills: Students must manage their time effectively during an open book exam, as they may have more material to review than in a closed-book exam.
- May reduce the importance of memorization: Since students are allowed to use their study materials, they may not place as much importance on memorization, which may affect their long-term retention of the material.
- Can lead to cheating: It may lead to cheating, as students may be tempted to collaborate with others or use unauthorized resources during the exam.
- May not be suitable for all subjects: It may not be suitable for subjects that require memorization, such as language learning or mathematics, where the ability to recall information is essential.
Also Read : Difference between Measurement and Evaluation

Also Visit : Prep with Harshita