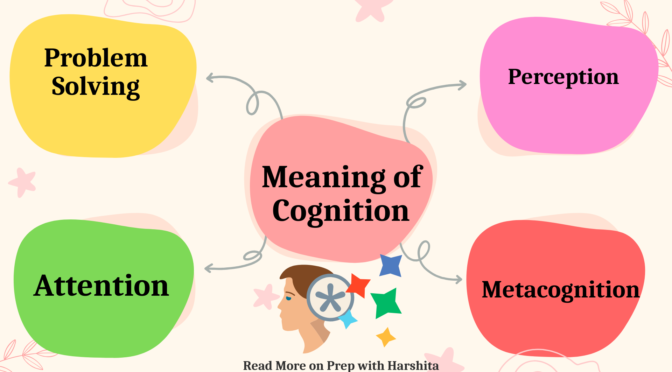
“Cognition” refers to the mental processes and activities related to acquiring, storing, processing, and using information. It includes various mental functions such as perception, attention, memory, language, problem-solving, and decision-making. In simpler terms, cognition involves the ways in which individuals think, understand, and learn about the world around them. The role of cognition in learning is very important, as learning itself is a cognitive process.
Let’s learn about the meaning of cognition and its role in learning in detail:
Perception: Cognition begins with perception, where individuals interpret and make sense of information from their environment. This includes processing sensory input such as seeing, hearing, and feeling.
Attention: Cognition involves focusing attention on specific stimuli or information. Attention is essential for learning, as it helps individuals filter and prioritize information, allowing them to concentrate on relevant parts of a task or subject.
Read more on the next page.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita