A peer support program is a structured intervention in which people who share common experiences or circumstances provide support, guidance, and encouragement to each other.
Peer support programs can be used in a variety of settings, including schools, workplaces, hospitals, and community organizations.
The goals of peer support programs are to enhance social support, improve mental health outcomes, and promote recovery and resilience.
Peer support programs can be particularly helpful for people who are dealing with mental health challenges, substance abuse issues, or other difficult life circumstances.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita
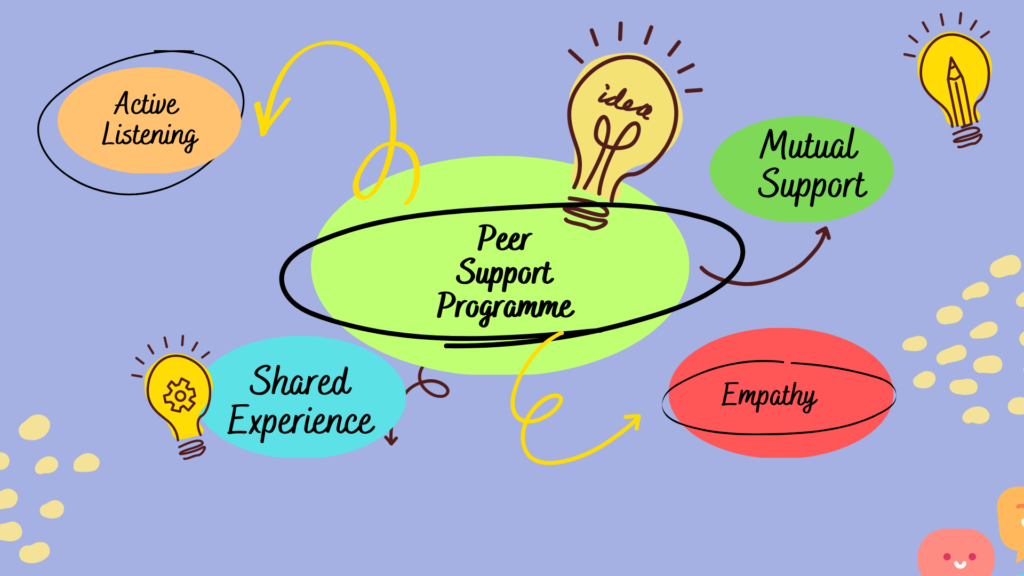
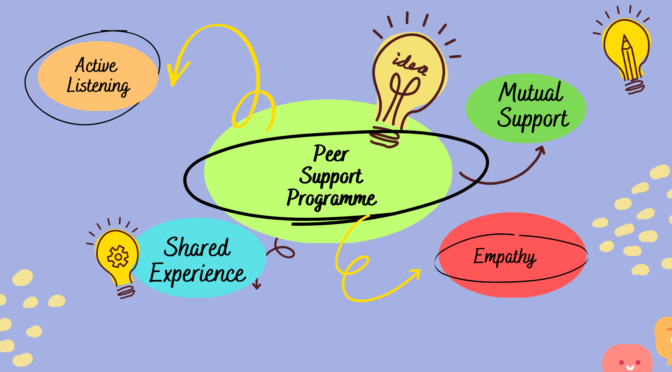
Some key features of peer support programs include:
- Shared experience: Peer support programs are based on the principle that people who have experienced similar challenges can offer unique insights and understanding to each other.
- Empathy and understanding: Peer support programs provide a safe and non-judgmental space where participants can share their experiences .
- Active listening: Peer support programs emphasize the importance of active listening and providing emotional support to others.
- Mutual support: Peer support programs emphasize the importance of reciprocity and mutual support, with participants providing support to each other in a balanced and equitable way.
- Peer-led: Peer support programs are often led by trained peers who have personal experience with the challenges being addressed.
In summary, such programs can be a valuable resource for individuals who are dealing with challenging life circumstances and help them.
Also, Read Multilingual Approach