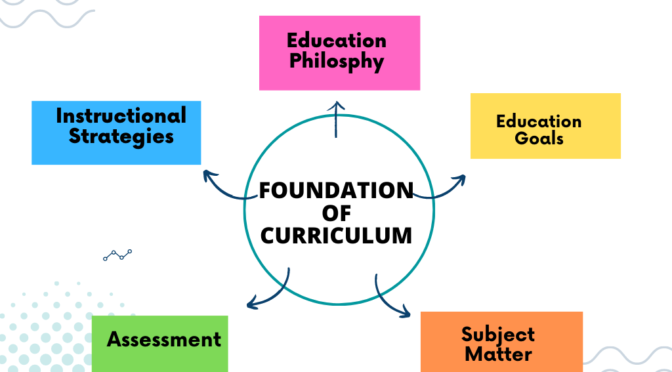
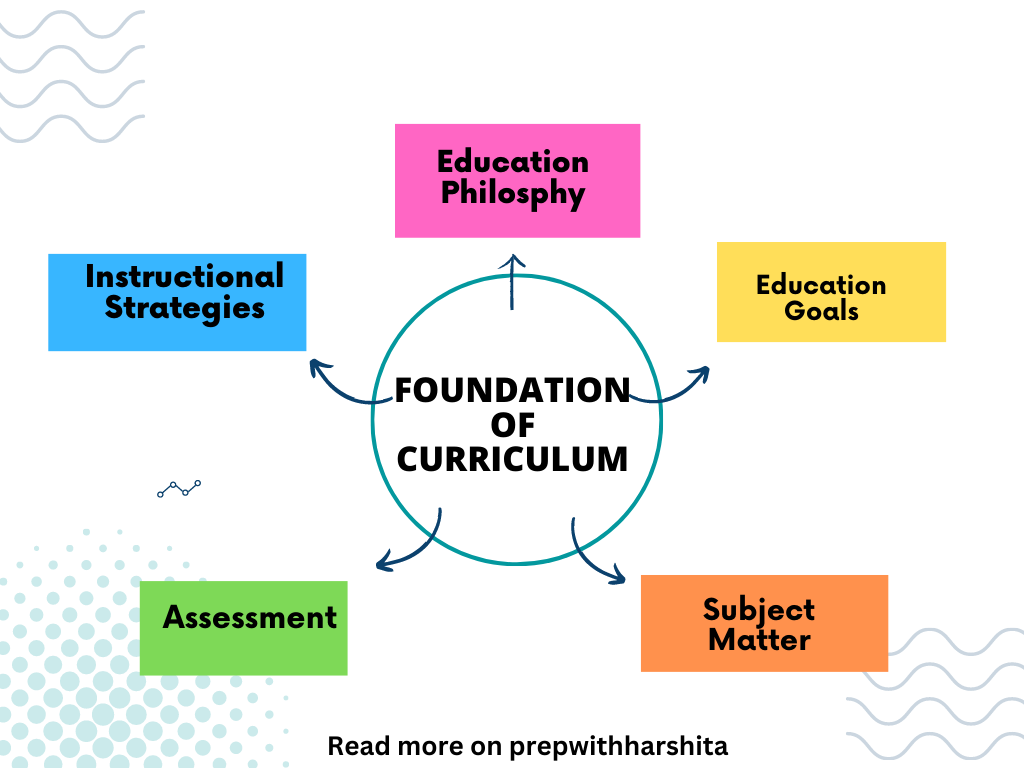
Conservatism Curriculum Theory is a traditional approach to education that emphasizes the transmission of knowledge and cultural heritage from one generation to the next.
Basis of this theory :
- The theory is based on the belief that there is a core body of knowledge that is essential for all students to learn, and that this knowledge should be taught in a systematic and rigorous manner.
- The main goal of Conservatism Curriculum Theory is to produce well-rounded individuals who are knowledgeable, responsible, and able to make informed decisions.
- It emphasizes the importance of a structured and disciplined approach to education, with an emphasis on memorization, rote learning, and the acquisition of basic skills.
- The theory also emphasizes the importance of moral and ethical values, and views education as a means of instilling these values in students. According to this theory, education should be designed to produce individuals who are capable of making good moral judgments and who have a strong sense of right and wrong.
- The curriculum in this typically includes traditional academic subjects such as mathematics, science, literature, and history. These subjects are viewed as essential for a well-rounded education and are taught in a systematic and rigorous manner.
- It also places a strong emphasis on discipline and order in the classroom. Students are expected to be respectful and obedient to their teachers and to follow rules and procedures.
Critics of Conservatism Curriculum Theory:
Critics of this theory argue that it is too focused on tradition and does not take into account the diverse needs and interests of students. They argue that it may not be effective in preparing students for the realities of a rapidly changing world and may not be inclusive of students from diverse cultural backgrounds.
Despite these criticisms, Conservatism Curriculum Theory continues to be influential in many educational settings, particularly in schools that place a strong emphasis on academic achievement and the acquisition of basic skills.
Also Read : Good Research Tool

Also Visit : Prep with Harshita