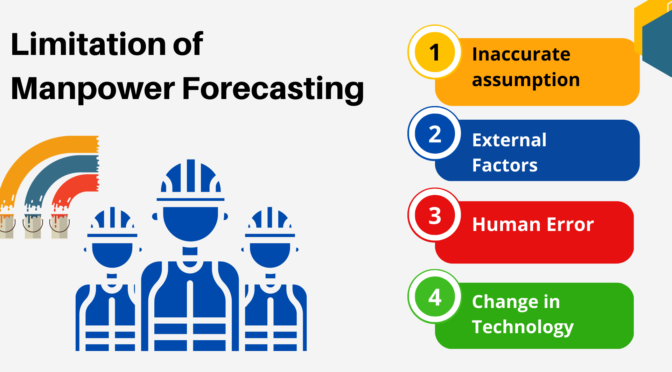
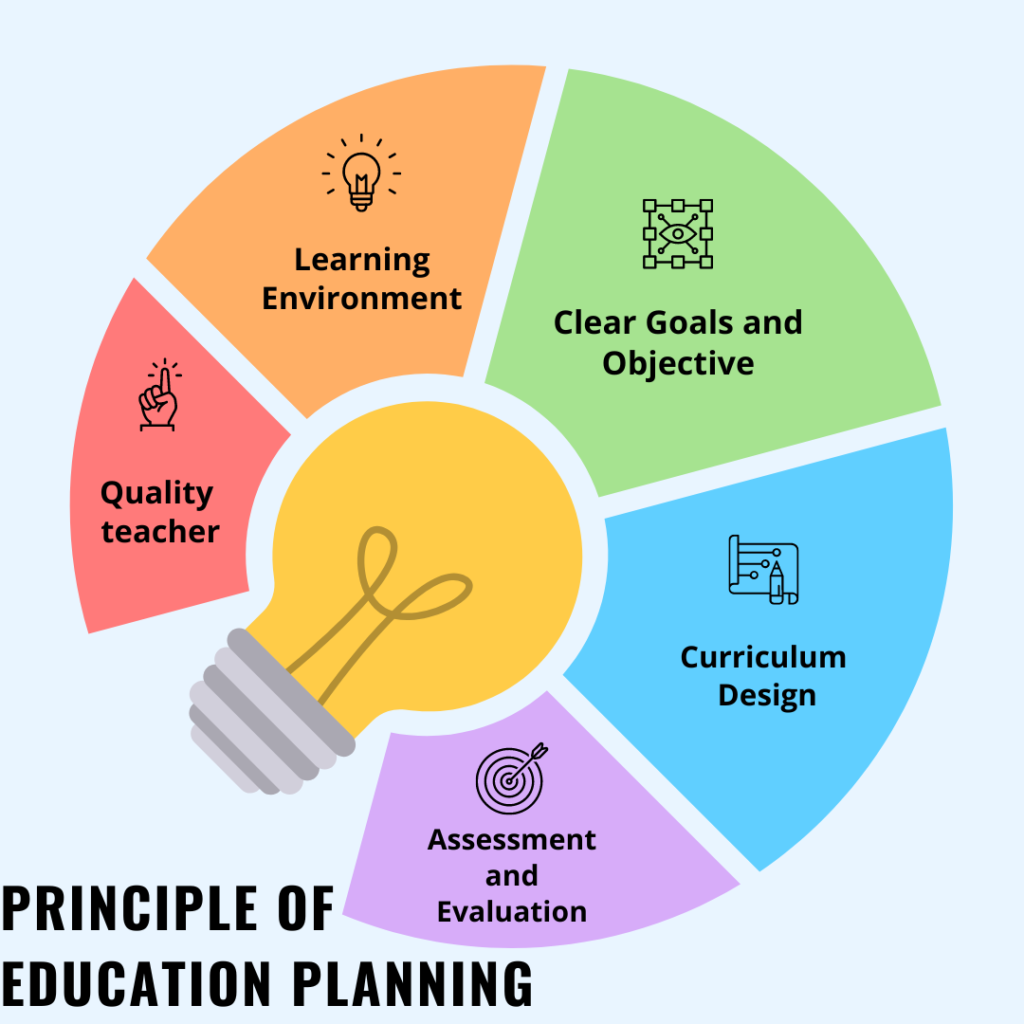
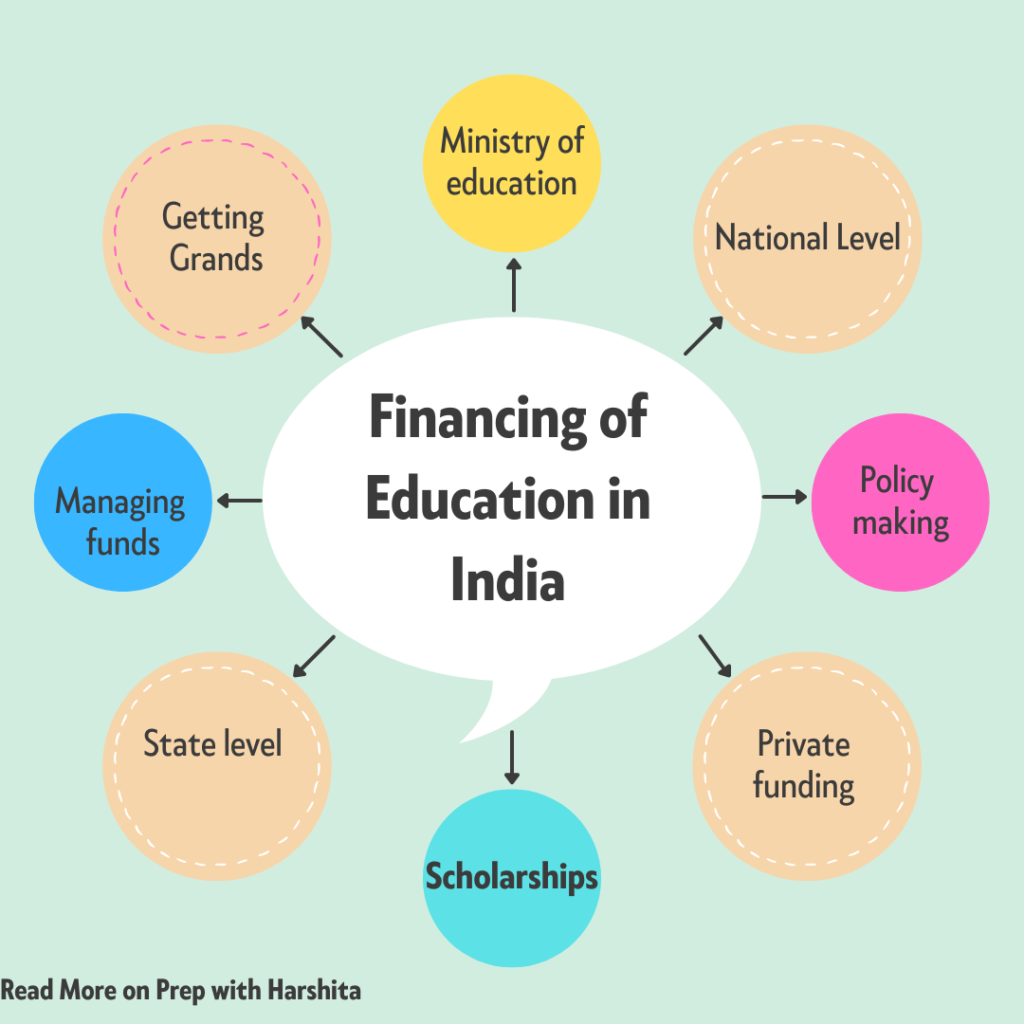
Educational planning is a crucial process for ensuring that secondary education is delivered effectively and efficiently. Planning at the secondary level involves setting goals and objectives, identifying resources and needs, and developing programs and policies to meet those needs.
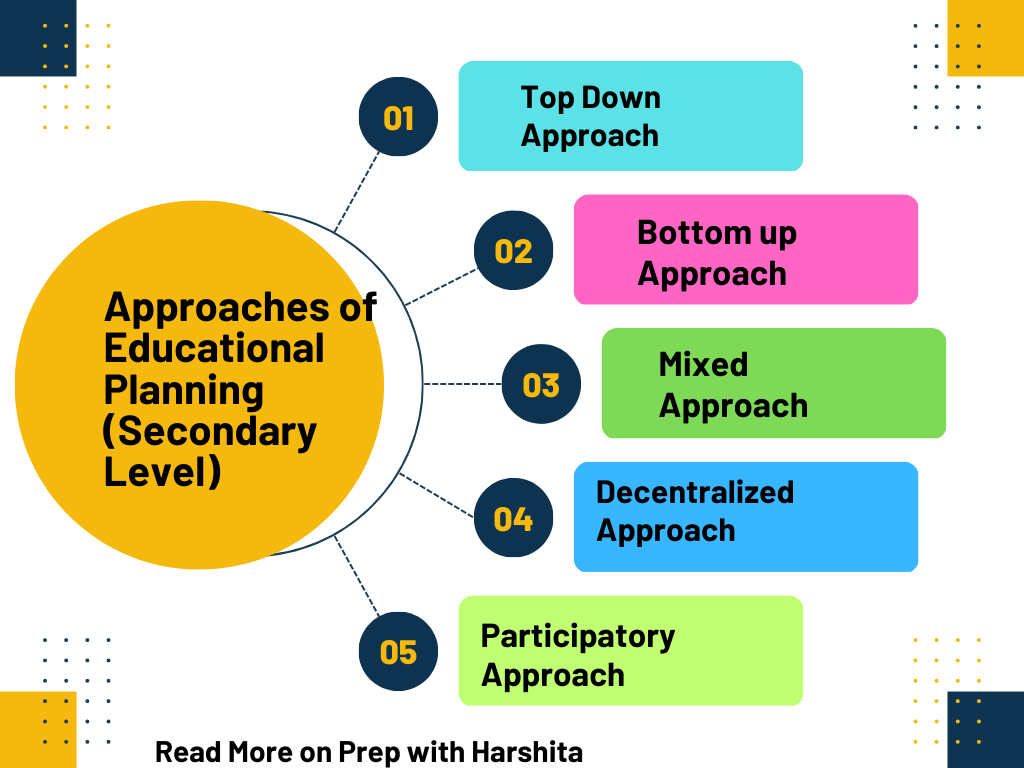
Approaches of Educational Planning :
There are several approaches to educational planning at the secondary level, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Here is a detailed explanation of these approaches:
- Top-down approach: The top-down approach to educational planning at the secondary level starts with the national government setting the goals and objectives for secondary education. The government provides the resources needed to achieve those goals and establishes policies and guidelines to ensure that they are met. The focus is on achieving consistency and coherence across the education system. This approach can be effective in ensuring that there is a clear national vision for secondary education and that resources are allocated in a way that supports that vision. However, it can also be inflexible and may not take into account local conditions and needs.
- Bottom-up approach: The bottom-up approach to educational planning at the secondary level starts at the local level and involves input from teachers, parents, and other stakeholders. The focus is on identifying the needs of students and the community and developing programs that meet those needs. This approach can be more flexible and responsive to local conditions, as it takes into account the unique characteristics of each community. However, it may not be as effective in ensuring consistency and coherence across the education system.
- Mixed approach: The mixed approach to educational planning combines elements of both the top-down and bottom-up approaches. It starts with a broad national framework but allows for flexibility and adaptation at the regional and local levels. This approach can help balance the need for consistency with the need for local responsiveness. It can also promote ownership and buy-in among stakeholders at all levels. However, it can be challenging to strike the right balance between national and local needs.
- Decentralized approach: This approach to educational planning involves devolving decision-making authority to the regional or local level. This can give local communities more control over their education systems and can lead to greater responsiveness to local needs. However, it can also lead to inconsistencies across regions and may require significant resources and capacity-building at the local level.
- Participatory approach: This approach to educational focus on the involvement of all stakeholders in the planning process. This includes students, parents, teachers, and community members. The goal is to build consensus and ownership of the education system among all stakeholders. This approach can be effective in ensuring that the needs of all stakeholders are taken into account. It can promote accountability and transparency. However, it can also be time-consuming and may require significant resources and capacity-building.
Each of these approaches has its own strengths and weaknesses, and the best approach will depend on the specific context and needs of the education system. A well-designed educational planning process will consider the strengths and limitations of each approach and tailor the process accordingly. Ultimately, the goal of educational planning at the secondary level should be to ensure that all students have access to high-quality education that prepares them for success in life.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita