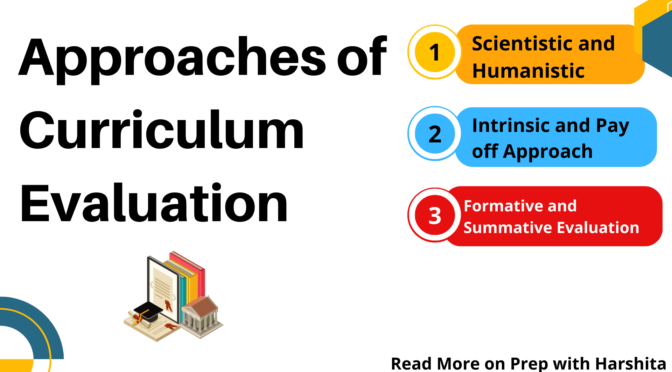
Approaches of Curriculum Evaluation can be categorized into various types:
Scientistic and Humanistic Approach
Cronbach (1 982) has identified two approaches to evaluation – the scientistic ideals approach and the humanistic ideals approach. The scientistic end advocates experimentation and the humanistic end does not have faith in experimentation.
The scientistic approach and the humanistic approach are two different ways of evaluating curriculum. Here are some of the key differences between them:
- Focus: The scientistic approach focuses on measurable outcomes, such as test scores and academic achievement. The humanistic approach focuses on the personal and social dimensions of learning, such as critical thinking, communication skills, and personal values.
- Methodology: The scientistic approach uses quantitative data and statistical analysis to evaluate the curriculum. The humanistic approach uses qualitative data and subjective feedback, such as interviews and observations.
- Values: The scientistic approach values objectivity, control, and predictability. The humanistic approach values subjectivity, empathy, and personal experience.
- Goals: The scientistic approach is primarily concerned with academic outcomes and the effectiveness of the curriculum in achieving those outcomes. The humanistic approach is concerned with the personal and social development of learners, as well as their academic achievement.
- Outcomes: The outcomes of the scientistic approach are typically focused on academic achievement and the effectiveness of the curriculum in meeting specific learning goals. The outcomes of the humanistic approach are more diverse and may include personal growth, social responsibility, and other non-academic dimensions of learning.
Intrinsic and Pay-off Evaluation:
The intrinsic and pay-off evaluations are two different approaches used in curriculum evaluation to assess the effectiveness of educational programs.
The intrinsic approach focuses on evaluating the curriculum based on its internal components, such as the learning objectives, content, and teaching methods. This approach involves analyzing the curriculum to determine whether it aligns with the goals of the educational institution, whether it is effective in achieving those goals, and whether it provides a meaningful and engaging learning experience for students. The intrinsic evaluation assesses the quality of the curriculum itself and is concerned with the curriculum’s internal validity.
In contrast, the pay-off evaluation assesses the effectiveness of the curriculum based on its external outcomes, such as the success of students in academic or career settings. This approach involves measuring the performance of students who have completed the curriculum and comparing it to the performance of those who have not. The pay-off evaluation focuses on the curriculum’s external validity and its impact on the students’ future lives, such as their academic achievement or job prospects.
The main difference between intrinsic and pay-off evaluation is their focus. Intrinsic evaluation is focused on the internal quality of the curriculum, while pay-off evaluation is focused on the external outcomes of the curriculum. Both approaches have their advantages and limitations, and a comprehensive evaluation of the curriculum should consider both approaches to provide a complete picture of the curriculum’s effectiveness.
Formative and Summative Evaluation:
These are two types of assessments that are commonly used in education, training, and other fields to measure learning outcomes and evaluate the effectiveness of programs or interventions.
Formative is an ongoing process that takes place during the learning or training process. It is designed to provide feedback to learners, teachers, or trainers on their progress and to help identify areas where they need further support or improvement. Formative evaluation is often informal and may involve self-reflection, peer feedback, or teacher feedback. The goal of formative evaluation is to improve learning and promote student success.
On the other hand, summative evaluation is a final assessment that takes place at the end of a learning or training program. Its purpose is to evaluate the overall effectiveness of the program and to determine whether the program’s learning objectives have been achieved. Summative evaluation is often formal and involves assessments such as exams, tests, or project evaluations. The goal of summative evaluation is to measure the success of a program or intervention.
In summary, formative evaluation is ongoing and designed to improve learning, while summative evaluation is a final assessment that measures the overall effectiveness of a program or intervention. Both types of evaluation are important for measuring learning outcomes and evaluating the effectiveness of educational and training programs.
Also Read: Curriculum Development Stages

Also Visit: Prep with Harshita