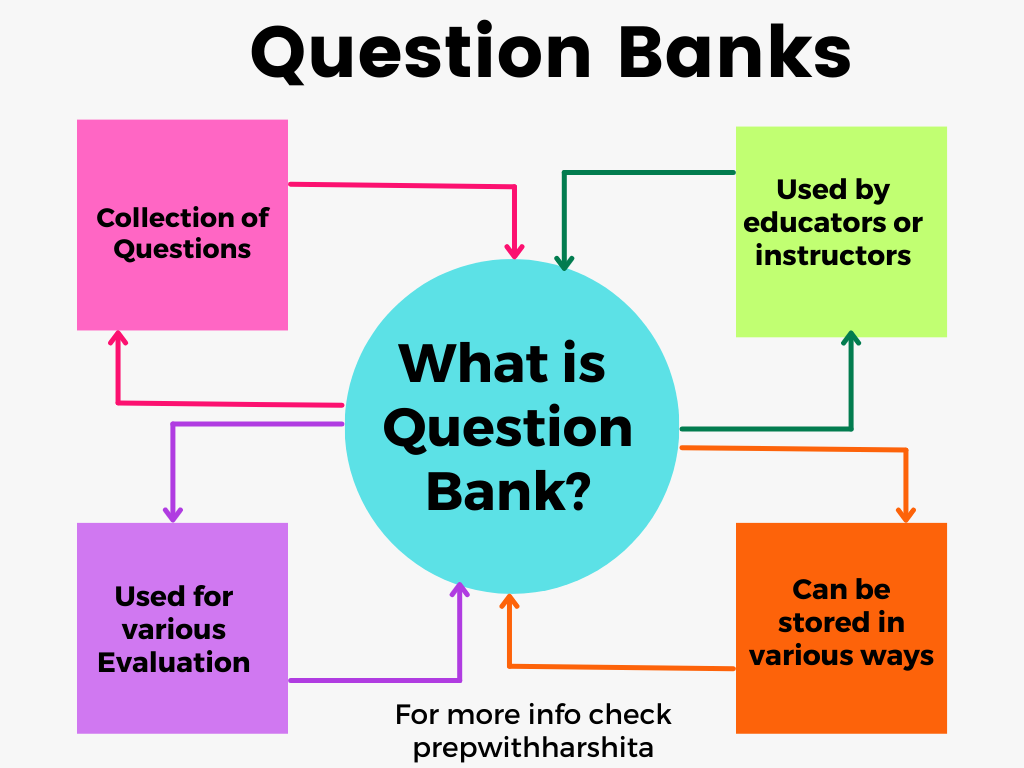
A question bank is a collection of questions, typically used in educational settings such as schools, colleges, and universities. These questions can be multiple-choice, true/false, short answer, essay, or any other type of question used in assessments.
Question banks are often used by instructors and educators to create exams, quizzes, and other assessments. They can be stored electronically in a database or in a physical format such as a binder.
By using a question bank, instructors can save time by not having to create new questions for every assessment and can ensure consistency in the level of difficulty and content coverage of the questions.
A question bank can be used for various types of evaluations, such as exams, quizzes, and assessments. Here are some features that a question bank may have specifically for evaluation purposes:
- Bloom’s Taxonomy Levels: Questions can be categorized based on the level of Bloom’s Taxonomy that they address. This can help instructors ensure that they are testing students at the appropriate level of thinking and learning.
- Learning Objectives: Questions can be aligned with specific learning objectives or outcomes. This helps instructors ensure that their assessments are measuring what they intended to measure.
- Assessment Types: It can contain questions for different types of assessments, such as formative assessments, summative assessments, and diagnostic assessments.
- Rubrics: It can include rubrics or scoring guidelines for each question or assessment. This helps ensure consistency in grading and provides students with clear expectations for what is required.
- Question Tags: Questions can be tagged with specific keywords or topics to help instructors quickly identify questions that address specific concepts or skills.
- Question History: It can track the history of each question, including who created it, when it was last modified, and how it has been used in previous assessments. This can help instructors ensure the quality and relevance of the questions.
- Reporting: It can generate reports on student performance, including individual and class-level statistics. This helps instructors identify areas where students are struggling and adjust their teaching accordingly.
There are several benefits of using a question bank in educational settings, including:
- Saves time: Creating new questions for each assessment can be time-consuming. By using a question bank, instructors can save time by not having to create new questions for every assessment.
- Increases efficiency: A question bank can make the assessment process more efficient by allowing instructors to quickly select questions that are appropriate for the assessment, rather than having to sift through irrelevant questions.
- Improves consistency: With question bank, instructors can ensure consistency in the level of difficulty and content coverage of the questions across multiple assessments.
- Enhances validity: Using a question bank that contains valid and reliable questions can help ensure that the assessment measures what it is intended to measure.
- Supports differentiation: They contain questions at different levels of difficulty, which can be helpful for instructors who need to differentiate assessments for students with different skill levels.
- Facilitates collaboration: They can be shared among multiple instructors or departments, which can facilitate collaboration.
- Provides data: Question bank can provide valuable data on student performance, which can be used to improve instruction.
Also Read : Attitude Scale