What is the Kirkpatrick Model?
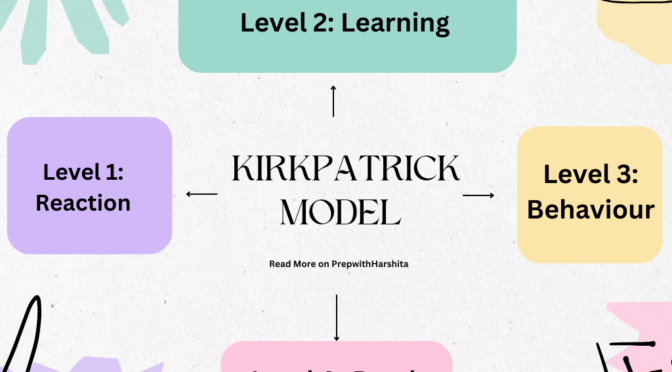
The Kirkpatrick Model is a four-level framework designed to measure the impact of training programs. It provides insights into how well participants respond to the training, how much they learn, how it influences their behavior, and how it impacts organizational results.
Evaluating the success of training programs is essential for educators and organizations alike. The Kirkpatrick Model, developed by Donald Kirkpatrick in 1959, remains one of the most popular frameworks for assessing training effectiveness. This article breaks down the Kirkpatrick Model into its four levels and explains how to use it effectively.
Level 1: Reaction
This first level evaluates how participants feel about the training. Were they engaged? Did they find the content relevant? Collecting feedback through surveys or questionnaires can provide valuable insights to improve future sessions.
Level 2: Learning
Here, the focus shifts to assessing the knowledge or skills participants gained during the training. This can be measured using pre-and post-training assessments, quizzes, or practical demonstrations.
Level 3: Behavior
The third level looks at how participants apply what they’ve learned to their jobs. This involves observing their performance over time or conducting follow-up surveys with managers to see if the training has led to behavioral changes.
Level 4: Results
The final level assesses the overall impact of the training on organizational goals. Metrics like increased productivity, improved customer satisfaction, or higher revenue can indicate successful outcomes.
Also Read : Individual Need and Interest Model