Application: Experiential learning emphasizes the application of knowledge and skills to real-world contexts. Learners are encouraged to apply what they have learned to solve problems, make decisions, or complete tasks in authentic settings.
Iterative process: Experiential learning often involves cycles of action, reflection, and refinement. Learners engage in activities, reflect on their experiences, adjust their strategies, and try again, leading to continuous improvement and deeper learning.
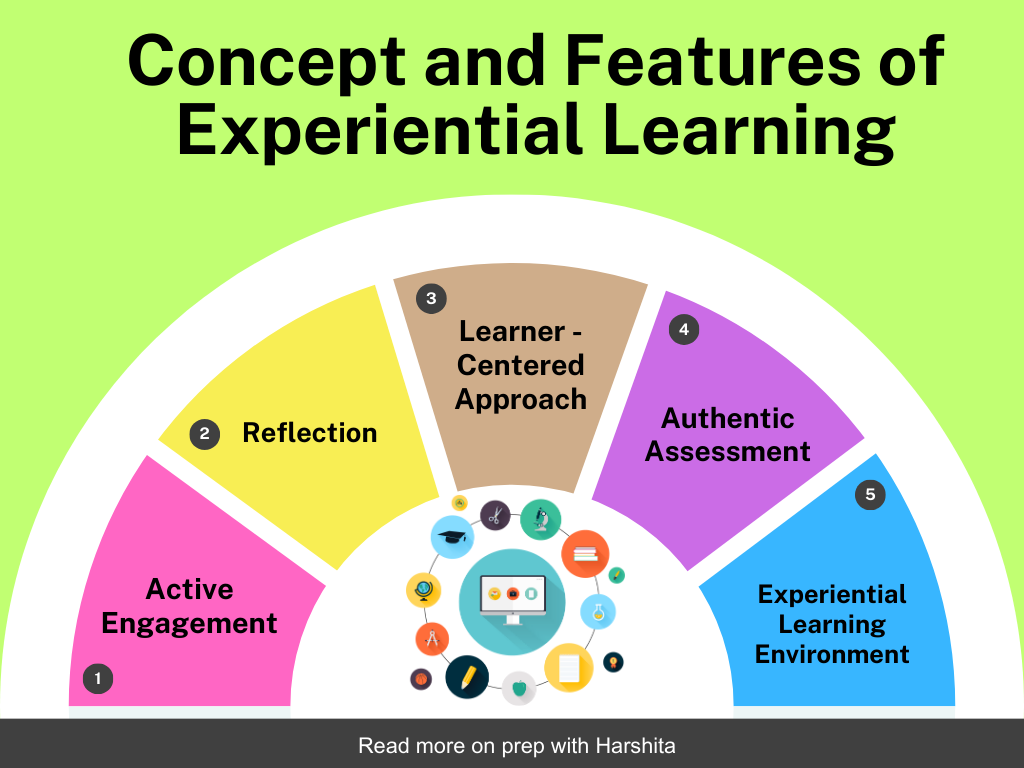
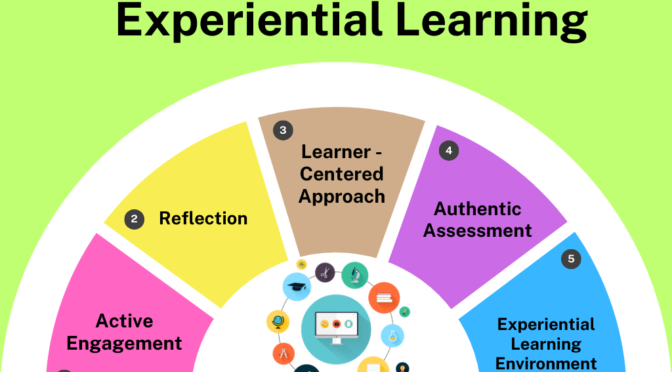
Learner-centered approach: Experiential learning is tailored to the needs, interests, and abilities of individual learners. It recognizes that learners have diverse learning styles and preferences and allows them to take ownership of their learning process.
Authentic assessment: Experiential learning emphasizes authentic assessment methods that evaluate learners’ ability to apply knowledge and skills in real-world contexts. Assessment may involve performance-based tasks, portfolios, presentations, or demonstrations of learning outcomes.
Experiential learning environments: Experiential learning can take place in various settings, including classrooms, laboratories, workplaces, outdoor environments, or community settings. These diverse environments provide opportunities for different types of experiences and learning activities.
Also Read: Meaning of Cognition

Best quality USA proxies – https://DreamProxies.com order with 50 discount!
GLOBAL BUSINESS ELITE YOUR WHOLESALE SUPPLIER OF AGRICULTURAL AND INDUSTRIAL COMMODITIES
We are a global company providing food, ingredients, agricultural solutions and industrial products that are vital for living. We connect farmers with markets so they can prosper. We connect customers with ingredients so they can make meals people love. And we connect families with daily essentials from eggs to edible oils, salt to skincare, feed to alternative fuel. https://globalbusinessltd.co.uk/
Global business elite
copper cathode
aluminium wire scrap
scrap processor
scrap cpus
waste paper scrap
fridge compressor scrap
cable scrap
scrap copper wire
waste paper for sale
ceramic cpu scrap
icumsa 100
cpu scrap
wholesale sugar suppliers uk
scrap processor
scrap central processing units
occ paper scrap
occ waste paper scrap
nut prosper globe
ocopper cathode specifications
sachet water filling and sealing machine
insulated copper wire scrap
waste paper supplier
recycled copper wire
copper scrap wire
occ waste paper suppliers in uk
processor gold recovery
waste paper supplier
ccopper wire scrap millberry
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..more wait .. …
You have noted very interesting details! ps decent web site.
F*ckin¦ awesome things here. I¦m very satisfied to see your post. Thanks a lot and i am taking a look ahead to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
Very interesting subject, regards for putting up.
I cling on to listening to the rumor lecture about getting boundless online grant applications so I have been looking around for the most excellent site to get one. Could you advise me please, where could i find some?
Hey there this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!