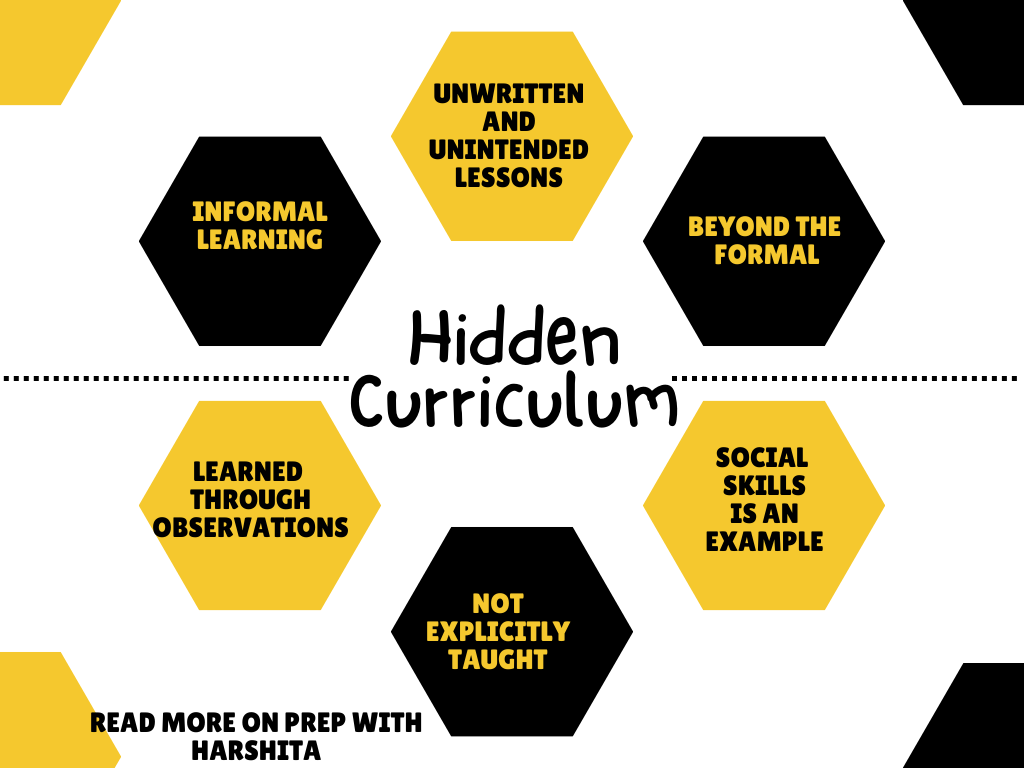
The hidden curriculum refers to the unwritten, implicit, and often unintended lessons, values, and norms that students learn in schools, beyond the formal and explicit curriculum. It is called “hidden” because it is not explicitly taught but is rather transmitted through the socialization and culture of schools. The hidden curriculum can have both positive and negative effects on student’s academic and social development.
Examples of the hidden curriculum include:
- Socialization: Schools not only teach academic skills but also teach social skills. For eg, such as how to interact with others, follow rules, and respect authority. These social skills are often learned through observation and imitation of teachers and peers.
- Conformity: Schools reinforce conformity to social norms and expectations, such as following dress codes, speaking in standard English, and adhering to classroom rules. This can lead to students suppressing their individuality and creativity in order to fit in.
- Gender roles: Schools reinforce traditional gender roles, such as boys being encouraged to participate in sports and girls being encouraged to pursue artistic or nurturing activities. This can limit students’ opportunities and perpetuate gender stereotypes.
- Cultural biases: Schools can transmit cultural biases, such as racism, sexism, and homophobia, through the curriculum, textbooks, and classroom interactions. This can lead to discrimination and marginalization of certain groups of students.
- Work ethic: Schools often emphasize the importance of hard work, punctuality, and discipline. While these values are important for academic success, they can also lead to stress, anxiety, and burnout in students who feel pressured to perform.
- Informal Learning: It is an informal way of learning. It is not directly taught but is transmitted through the socialization and culture of the institution. It is learned through the observation and imitation of behaviors and actions of teachers, peers, and the environment.
- Unconscious Learning: Students are often unaware that they are learning the hidden curriculum as it is not explicitly taught. The hidden curriculum is often implicit and unconscious, and students learn it through the socialization process of the school.
- Impact on Student Development: The hidden curriculum can have a significant impact on the social and emotional development of students. It can shape their attitudes toward education, work, and society.
It is important for educators to be aware of the hidden curriculum and examine the messages that students are receiving. By being intentional about the values and norms that they promote, educators can create a more equitable and inclusive learning environment.

i learn alot from u thanku soo much
Buy Private proxies: BEST PRIVATE PROXIES – Exclusive level of quality, Any number of data transfer useage, 1000 mb/s superspeed, 99,9 uptime, Neo step by step IP’s, Zero practices rules, A number of subnets, USA and even European union proxies – Get At this point – DreamProxies.com
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was searching for!
I like this post, enjoyed this one thanks for putting up.
Impacto mecanico
Sistemas de ajuste: fundamental para el funcionamiento uniforme y efectivo de las equipos.
En el mundo de la innovación avanzada, donde la eficiencia y la fiabilidad del dispositivo son de suma relevancia, los equipos de equilibrado cumplen un rol fundamental. Estos aparatos especializados están concebidos para balancear y estabilizar partes dinámicas, ya sea en maquinaria industrial, transportes de desplazamiento o incluso en electrodomésticos caseros.
Para los técnicos en soporte de equipos y los técnicos, utilizar con dispositivos de balanceo es crucial para garantizar el desempeño estable y seguro de cualquier aparato dinámico. Gracias a estas herramientas avanzadas innovadoras, es posible minimizar considerablemente las vibraciones, el zumbido y la carga sobre los rodamientos, prolongando la duración de piezas valiosos.
También trascendental es el papel que desempeñan los equipos de balanceo en la atención al comprador. El soporte profesional y el reparación regular utilizando estos equipos facilitan proporcionar soluciones de excelente estándar, mejorando la bienestar de los clientes.
Para los titulares de emprendimientos, la aporte en estaciones de ajuste y dispositivos puede ser esencial para mejorar la eficiencia y eficiencia de sus sistemas. Esto es especialmente trascendental para los dueños de negocios que dirigen reducidas y modestas organizaciones, donde cada punto cuenta.
Asimismo, los dispositivos de balanceo tienen una gran uso en el área de la protección y el control de excelencia. Facilitan detectar posibles errores, evitando arreglos onerosas y perjuicios a los sistemas. Más aún, los indicadores recopilados de estos equipos pueden emplearse para maximizar procedimientos y aumentar la visibilidad en sistemas de investigación.
Las sectores de uso de los equipos de equilibrado incluyen numerosas industrias, desde la elaboración de bicicletas hasta el control ecológico. No importa si se refiere de extensas producciones industriales o limitados locales caseros, los dispositivos de equilibrado son necesarios para promover un operación eficiente y sin riesgo de interrupciones.
You completed a number of fine points there. I did a search on the theme and found mainly folks will consent with your blog.
As I web-site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling excellent , appreciate it for your efforts. You should keep it up forever! Best of luck.
Very great post. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to mention that I have really loved surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing to your rss feed and I am hoping you write once more soon!
Wow! This could be one particular of the most helpful blogs We’ve ever arrive across on this subject. Basically Excellent. I’m also an expert in this topic so I can understand your hard work.
After all, what a great site and informative posts, I will upload inbound link – bookmark this web site? Regards, Reader.
I like this site so much, saved to fav.
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
Wow! This could be one particular of the most helpful blogs We have ever arrive across on this subject. Actually Great. I am also a specialist in this topic therefore I can understand your effort.
Those are yours alright! . We at least need to get these people stealing images to start blogging! They probably just did a image search and grabbed them. They look good though!
Hi there, You have done an excellent job. I’ll definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I’m sure they will be benefited from this web site.
Hey there just wanted to give you a quick heads up. The text in your article seem to be running off the screen in Firefox. I’m not sure if this is a formatting issue or something to do with internet browser compatibility but I figured I’d post to let you know. The design look great though! Hope you get the problem solved soon. Kudos
There is noticeably a bundle to find out about this. I assume you made certain good factors in options also.
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
I conceive this website has very good composed content content.
I conceive you have observed some very interesting details, thanks for the post.
A powerful share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing a bit of evaluation on this. And he in truth purchased me breakfast because I found it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I really feel strongly about it and love studying extra on this topic. If possible, as you turn out to be expertise, would you mind updating your blog with extra details? It is extremely helpful for me. Massive thumb up for this blog publish!
Hi would you mind letting me know which webhost you’re utilizing? I’ve loaded your blog in 3 different web browsers and I must say this blog loads a lot faster then most. Can you recommend a good hosting provider at a honest price? Kudos, I appreciate it!
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
Some genuinely good content on this web site, regards for contribution. “It is not often that someone comes along who is a true friend and a good writer.” by E. B. White.
An impressive share, I just given this onto a colleague who was doing a little analysis on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast because I found it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! But yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I feel strongly about it and love reading more on this topic. If possible, as you become expertise, would you mind updating your blog with more details? It is highly helpful for me. Big thumb up for this blog post!
I got what you mean , thankyou for posting.Woh I am happy to find this website through google. “Food is the most primitive form of comfort.” by Sheila Graham.
Along with the whole thing that seems to be building inside this specific subject material, many of your opinions are actually relatively refreshing. On the other hand, I am sorry, because I can not give credence to your entire theory, all be it exhilarating none the less. It seems to everybody that your opinions are generally not completely rationalized and in fact you are yourself not completely convinced of your assertion. In any case I did enjoy looking at it.
Helpful info. Fortunate me I discovered your website by chance, and I’m surprised why this coincidence did not happened in advance! I bookmarked it.
Utterly indited articles, Really enjoyed studying.
you are really a good webmaster. The site loading speed is incredible. It seems that you’re doing any unique trick. Moreover, The contents are masterpiece. you have done a wonderful job on this topic!
Perfect work you have done, this web site is really cool with excellent info .
Thank you for another informative website. Where else could I get that kind of info written in such a perfect way? I’ve a project that I’m just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such info.
A person essentially help to make seriously posts I would state. This is the first time I frequented your web page and thus far? I surprised with the research you made to make this particular publish extraordinary. Great job!
Very interesting info !Perfect just what I was searching for!
But wanna input that you have a very decent website , I like the pattern it actually stands out.
I simply couldn’t depart your web site prior to suggesting that I actually enjoyed the standard info an individual supply in your guests? Is gonna be again frequently to investigate cross-check new posts.
I was suggested this web site by way of my cousin. I am not sure whether this put up is written by way of him as nobody else know such certain approximately my trouble. You are incredible! Thank you!
Very interesting subject, appreciate it for posting.
Great post, you have pointed out some superb details , I also believe this s a very great website.
As a Newbie, I am always browsing online for articles that can benefit me. Thank you
I really like your writing style, good information, thankyou for posting : D.
This website is my inhalation, rattling excellent layout and perfect written content.
I do trust all the ideas you’ve introduced on your post. They are really convincing and will certainly work. Nonetheless, the posts are too quick for starters. May you please prolong them a bit from subsequent time? Thanks for the post.
Valuable information. Lucky me I found your site by accident, and I am shocked why this accident did not happened earlier! I bookmarked it.
hello!,I like your writing so so much! share we communicate more about your article on AOL? I require an expert on this house to solve my problem. May be that is you! Looking forward to look you.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
There is noticeably a lot to know about this. I believe you made some nice points in features also.
Greetings I am so grateful I found your webpage, I really found you by mistake, while I was browsing on Aol for something else, Anyhow I am here now and would just like to say thank you for a marvelous post and a all round enjoyable blog (I also love the theme/design), I don’t have time to read it all at the minute but I have saved it and also included your RSS feeds, so when I have time I will be back to read a lot more, Please do keep up the fantastic job.
Excellent blog! Do you have any hints for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own website soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you suggest starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally overwhelmed .. Any ideas? Many thanks!
What i don’t understood is in reality how you’re no longer actually a lot more well-favored than you may be now. You’re so intelligent. You understand thus considerably in the case of this topic, produced me in my view consider it from a lot of various angles. Its like women and men don’t seem to be involved unless it’s one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your individual stuffs nice. At all times deal with it up!
Attractive element of content. I simply stumbled upon your blog and in accession capital to claim that I acquire in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing in your augment and even I success you get right of entry to consistently fast.
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
Attractive section of content. I just stumbled upon your weblog and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
Great blog here! Additionally your website lots up fast! What host are you the usage of? Can I am getting your affiliate hyperlink in your host? I desire my website loaded up as quickly as yours lol
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored subject matter stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come further formerly again as exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this increase.
Today, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a forty foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is completely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Very interesting subject , thankyou for posting.
I cling on to listening to the news bulletin lecture about receiving free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the most excellent site to get one. Could you tell me please, where could i get some?
Thanx for the effort, keep up the good work Great work, I am going to start a small Blog Engine course work using your site I hope you enjoy blogging with the popular BlogEngine.net.Thethoughts you express are really awesome. Hope you will right some more posts.
Normally I don’t learn article on blogs, but I would like to say that this write-up very forced me to take a look at and do so! Your writing taste has been surprised me. Thank you, quite great post.
Utterly pent subject matter, Really enjoyed studying.
It is really a nice and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this web site. Thank you, I will try and check back more often. How frequently you update your site?
Hey there, You have done an incredible job. I will certainly digg it and for my part recommend to my friends. I’m sure they’ll be benefited from this web site.
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
Have you ever thought about adding a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is valuable and all. However imagine if you added some great pictures or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with pics and video clips, this site could certainly be one of the best in its niche. Awesome blog!
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
Very great post. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to mention that I’ve truly enjoyed browsing your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing in your feed and I am hoping you write again soon!
I’m still learning from you, but I’m trying to achieve my goals. I certainly enjoy reading everything that is written on your site.Keep the tips coming. I liked it!
I haven’t checked in here for a while since I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I’ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Hey! I’m at work browsing your blog from my new iphone 3gs! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the great work!
fantastic post.Ne’er knew this, regards for letting me know.
Awsome blog! I am loving it!! Will come back again. I am bookmarking your feeds also.
I view something truly special in this internet site.
Hey, you used to write excellent, but the last several posts have been kinda boring?K I miss your super writings. Past several posts are just a bit out of track! come on!
I’m really loving the theme/design of your weblog. Do you ever run into any web browser compatibility issues? A couple of my blog visitors have complained about my website not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Firefox. Do you have any recommendations to help fix this problem?
Your place is valueble for me. Thanks!…
I don’t even know how I ended up here, but I thought this post was great. I don’t know who you are but definitely you are going to a famous blogger if you are not already 😉 Cheers!
of course like your website but you have to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I to find it very bothersome to tell the reality however I will surely come back again.
I have been surfing on-line greater than three hours nowadays, yet I by no means found any interesting article like yours. It is beautiful worth enough for me. In my view, if all website owners and bloggers made just right content material as you probably did, the web will be a lot more useful than ever before. “Revolution is not a onetime event.” by Audre Lorde.
It’s hard to find knowledgeable people on this topic, but you sound like you know what you’re talking about! Thanks
Pretty component to content. I just stumbled upon your site and in accession capital to say that I acquire actually loved account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your feeds and even I success you get admission to consistently rapidly.
I am often to running a blog and i actually respect your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I am going to bookmark your site and hold checking for brand spanking new information.
I?¦ve recently started a site, the info you offer on this site has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
I enjoy examining and I believe this website got some truly useful stuff on it! .
Great write-up, I?¦m regular visitor of one?¦s blog, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
I have been exploring for a little for any high quality articles or weblog posts on this kind of area . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this site. Reading this info So i’m happy to exhibit that I’ve an incredibly excellent uncanny feeling I came upon exactly what I needed. I such a lot no doubt will make sure to do not overlook this site and give it a look regularly.
Compre visualizações e espectadores reais para suas lives no YouTube, Instagram, Twitch, TikTok e Facebook. Aumente seu engajamento e credibilidade online com serviços seguros e confiáveis. Impulsione suas transmissões ao vivo hoje!
You made some decent factors there. I appeared on the web for the issue and found most people will associate with with your website.
Loving the information on this internet site, you have done outstanding job on the articles.
At Nursing Professionals Certifications Online, we are dedicated to providing accessible, convenient, and high-quality medical certification courses to healthcare professionals worldwide. Our platform is designed to meet the evolving needs of medical professionals seeking to enhance their skills, expand their knowledge, and advance their careers. Do you have problems passing your exam? We provide medical students with certificates, licenses, questions, and answers and upgrade previous scores for Prometric exams. #ECFMG #MCAT #SCFHS #MSNCB #OET #DHA #NLCEX #HAAD #MOH #MRCGP #MCAT #OMSB #SMLE #USMLE #QCHP #NHRA #DHCC #AMC #MRCS #MRCOG. You can obtain the above certificate and license online without attending the exam. Provide leaked questions bank and answers before the exam date. You can also upgrade your previous results. Study materials and tips are available for your upcoming exam dates. Chat on WhatsApp with +971 56 954 4538
I?¦ve learn some excellent stuff here. Certainly value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot attempt you place to create any such magnificent informative web site.
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was searching for!
I’m impressed, I need to say. Really rarely do I encounter a weblog that’s each educative and entertaining, and let me let you know, you’ve got hit the nail on the head. Your idea is outstanding; the difficulty is one thing that not sufficient people are talking intelligently about. I am very comfortable that I stumbled throughout this in my seek for one thing relating to this.
Hey! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and say I genuinely enjoy reading through your posts. Can you recommend any other blogs/websites/forums that deal with the same subjects? Appreciate it!
A powerful share, I simply given this onto a colleague who was doing a bit of evaluation on this. And he the truth is bought me breakfast because I discovered it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the treat! But yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I feel strongly about it and love studying extra on this topic. If potential, as you grow to be expertise, would you mind updating your weblog with extra particulars? It is extremely useful for me. Large thumb up for this blog put up!
Hi my friend! I want to say that this post is amazing, great written and include almost all important infos. I¦d like to peer more posts like this .
I wish to show thanks to you for bailing me out of such a issue. Just after exploring throughout the the web and getting methods which are not productive, I thought my life was over. Being alive without the approaches to the issues you’ve solved all through this short post is a crucial case, as well as the kind that might have adversely damaged my entire career if I hadn’t come across your blog. Your personal natural talent and kindness in touching a lot of stuff was vital. I’m not sure what I would have done if I had not encountered such a solution like this. I’m able to at this moment look ahead to my future. Thanks very much for this expert and result oriented help. I will not hesitate to refer your blog post to any person who requires guidance on this issue.
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
This site is known as a stroll-through for the entire info you needed about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse right here, and also you’ll definitely uncover it.
Howdy very nice website!! Guy .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I will bookmark your blog and take the feeds also?KI’m glad to seek out numerous helpful information right here in the put up, we want develop more strategies on this regard, thank you for sharing. . . . . .
The Salt Trick is a natural technique that involves using specific salts, such as Blue Salt, to enhance male performance
I view something truly special in this website .
Hi there very cool web site!! Man .. Excellent .. Wonderful .. I’ll bookmark your site and take the feeds additionally…I’m happy to seek out so many useful info right here in the post, we want develop extra techniques in this regard, thanks for sharing.
ProDentim is a chewable oral probiotic supplement formulated with a unique mix of probiotics, prebiotics, herbs, and nutrients.
hi!,I love your writing so a lot! proportion we be in contact extra approximately your article on AOL? I need an expert on this area to solve my problem. Maybe that’s you! Having a look forward to see you.
The Ice Water Hack has been gaining popularity as a simple method to aid weight loss. After reading about its potential benefits, I decided to give it a shot and see how it worked for me. Here’s what I found!
Thank you for another informative web site. The place else may just I am getting that type of information written in such a perfect means? I’ve a project that I am just now working on, and I have been at the glance out for such info.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem with your web site in internet explorer, would test this… IE still is the market leader and a large portion of people will miss your wonderful writing because of this problem.
I will immediately clutch your rss as I can not in finding your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly allow me recognize so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
I believe this website contains some very superb information for everyone :D. “Morality, like art, means a drawing a line someplace.” by Oscar Wilde.
I’d must test with you here. Which is not something I normally do! I take pleasure in reading a publish that will make people think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to remark!
Thank you for the auspicious writeup. It in fact was a amusement account it. Look advanced to far added agreeable from you! However, how can we communicate?
I gotta favorite this website it seems very useful very helpful
Great blog here! Also your web site loads up very fast! What host are you using? Can I get your affiliate link to your host? I wish my site loaded up as quickly as yours lol
If you’ve been looking for a way to unlock your full mental potential and attract wealth effortlessly, Billionaire Brain Wave might just be the breakthrough you’ve been waiting for!
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
Terrific work! This is the type of information that should be shared around the net. Shame on the search engines for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my website . Thanks =)
Howdy! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the superb work!
Hi! Quick question that’s totally off topic. Do you know how to make your site mobile friendly? My weblog looks weird when browsing from my apple iphone. I’m trying to find a theme or plugin that might be able to correct this issue. If you have any suggestions, please share. Thanks!
I discovered your blog site on google and check a few of your early posts. Continue to keep up the very good operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading more from you later on!…
It is really a great and useful piece of information. I’m glad that you shared this useful information with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thanks for sharing.
You really make it seem so easy with your presentation but I find this matter to be really something which I think I would never understand. It seems too complex and very broad for me. I am looking forward for your next post, I’ll try to get the hang of it!
Very good blog! Do you have any helpful hints for aspiring writers? I’m planning to start my own blog soon but I’m a little lost on everything. Would you advise starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many options out there that I’m completely confused .. Any tips? Many thanks!
Good V I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related information ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Excellent task..
hello!,I love your writing very much! proportion we keep in touch more approximately your article on AOL? I need an expert on this space to solve my problem. Maybe that is you! Taking a look forward to peer you.
naturally like your web-site but you need to test the spelling on several of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the reality then again I?¦ll definitely come back again.
I genuinely enjoy studying on this site, it contains great blog posts.
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site :).
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for! “It’s not the having, its the getting.” by Elizabeth Taylor.
Helpful info. Lucky me I discovered your site unintentionally, and I’m stunned why this twist of fate didn’t came about earlier! I bookmarked it.
Everything is very open and very clear explanation of issues. was truly information. Your website is very useful. Thanks for sharing.
hey there and thanks to your info – I’ve definitely picked up something new from right here. I did alternatively experience several technical issues the usage of this web site, as I experienced to reload the web site lots of times previous to I could get it to load correctly. I had been considering in case your hosting is OK? Now not that I am complaining, but sluggish loading circumstances times will sometimes impact your placement in google and can damage your high quality score if advertising and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Well I’m adding this RSS to my email and could glance out for much more of your respective intriguing content. Ensure that you update this again soon..
Greetings! Very helpful advice on this article! It is the little changes that make the biggest changes. Thanks a lot for sharing!
I think this is one of the most important information for me. And i am satisfied reading your article. But want to observation on some normal things, The website taste is wonderful, the articles is in point of fact nice : D. Excellent process, cheers
Hello my family member! I want to say that this post is awesome, great written and include almost all vital infos. I’d like to see extra posts like this.
I was just looking for this info for some time. After six hours of continuous Googleing, at last I got it in your web site. I wonder what is the lack of Google strategy that do not rank this type of informative websites in top of the list. Usually the top sites are full of garbage.
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this site? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be great if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more from this post. I am very glad to see such magnificent information being shared freely out there.
Loving the information on this web site, you have done great job on the content.
Please let me know if you’re looking for a article writer for your blog. You have some really great articles and I believe I would be a good asset. If you ever want to take some of the load off, I’d really like to write some content for your blog in exchange for a link back to mine. Please shoot me an email if interested. Cheers!
This really answered my problem, thank you!
Precisely what I was looking for, thankyou for putting up.
Greetings! I’ve been following your web site for some time now and finally got the bravery to go ahead and give you a shout out from Lubbock Tx! Just wanted to tell you keep up the good job!
You really make it seem so easy together with your presentation however I in finding this matter to be really one thing which I believe I might never understand. It sort of feels too complex and very huge for me. I’m looking ahead to your next submit, I will attempt to get the cling of it!
Hola! I’ve been following your website for a long time now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from Houston Tx! Just wanted to tell you keep up the excellent job!
Just what I was searching for, thankyou for posting.
I think this is among the most vital information for me. And i am glad reading your article. But should remark on some general things, The website style is great, the articles is really excellent : D. Good job, cheers
It’s really a nice and useful piece of information. I’m glad that you just shared this helpful info with us. Please keep us up to date like this. Thank you for sharing.
I¦ve recently started a website, the information you provide on this site has helped me greatly. Thanks for all of your time & work.
I envy your piece of work, thanks for all the interesting content.
You can certainly see your skills in the work you write. The world hopes for even more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart.
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my website :).
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was looking for!
I envy your piece of work, regards for all the interesting content.
fantastic put up, very informative. I’m wondering why the other experts of this sector do not understand this. You should continue your writing. I’m confident, you’ve a great readers’ base already!
hello there and thanks for your information – I have certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise a few technical issues the usage of this site, since I experienced to reload the website a lot of times previous to I could get it to load properly. I have been brooding about if your hosting is OK? Now not that I am complaining, but sluggish loading circumstances instances will often have an effect on your placement in google and could harm your quality score if ads and ***********|advertising|advertising|advertising and *********** with Adwords. Well I’m adding this RSS to my e-mail and could look out for a lot more of your respective exciting content. Make sure you update this again soon..
Lovely just what I was searching for.Thanks to the author for taking his clock time on this one.
I?¦ve recently started a website, the information you provide on this web site has helped me tremendously. Thanks for all of your time & work.
What i don’t understood is in truth how you’re no longer really much more well-preferred than you might be now. You’re so intelligent. You already know thus significantly relating to this matter, made me individually imagine it from numerous numerous angles. Its like men and women don’t seem to be fascinated until it’s one thing to accomplish with Woman gaga! Your individual stuffs outstanding. At all times care for it up!
Hey this is kinda of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding knowledge so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
An impressive share, I simply given this onto a colleague who was doing a little analysis on this. And he the truth is bought me breakfast as a result of I found it for him.. smile. So let me reword that: Thnx for the deal with! However yeah Thnkx for spending the time to discuss this, I really feel strongly about it and love reading more on this topic. If attainable, as you develop into experience, would you thoughts updating your weblog with extra details? It is highly useful for me. Massive thumb up for this blog publish!
I consider something really special in this website.
What¦s Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It positively helpful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to give a contribution & help other customers like its aided me. Great job.
I haven’t checked in here for some time because I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are great quality so I guess I will add you back to my daily bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
Having read this I thought it was very informative. I appreciate you taking the time and effort to put this article together. I once again find myself spending way to much time both reading and commenting. But so what, it was still worth it!
Some genuinely interesting info , well written and loosely user friendly.
You have observed very interesting points! ps decent site. “Recompense injury with justice, and recompense kindness with kindness.” by Confucius.
Howdy! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 4! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Keep up the great work!
Good day! This is my first visit to your blog! We are a collection of volunteers and starting a new initiative in a community in the same niche. Your blog provided us valuable information to work on. You have done a outstanding job!
Loving the info on this website , you have done outstanding job on the blog posts.
Perfectly written subject matter, appreciate it for information. “Necessity is the mother of taking chances.” by Mark Twain.
I am no longer positive where you are getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend some time learning more or working out more. Thanks for great information I was searching for this information for my mission.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your weblog and wanted to say that I have truly enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I’ll be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again soon!
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
I view something truly interesting about your site so I saved to bookmarks.
Well I truly liked reading it. This subject procured by you is very practical for proper planning.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
I am pleased that I discovered this blog, precisely the right information that I was searching for! .
Aqua Sculpt is an advanced body contouring treatment that uses hydrating active ingredients, cooling technology, and sometimes ultrasound or RF-based devices (depending on the version) to target fat cells and tighten the skin.
Nice post. I was checking continuously this blog and I am impressed! Very helpful information particularly the last part 🙂 I care for such info much. I was seeking this particular information for a long time. Thank you and good luck.
I’ll right away grab your rss as I can’t find your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service. Do you’ve any? Kindly let me know so that I could subscribe. Thanks.
PrimeBiome is a dietary supplement designed to support gut health by promoting a balanced microbiome, enhancing digestion, and boosting overall well-being.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
Hi there would you mind stating which blog platform you’re working with? I’m going to start my own blog soon but I’m having a hard time selecting between BlogEngine/Wordpress/B2evolution and Drupal. The reason I ask is because your layout seems different then most blogs and I’m looking for something completely unique. P.S Apologies for getting off-topic but I had to ask!
Merely wanna comment that you have a very decent website , I love the style it actually stands out.
I’m really enjoying the theme/design of your website. Do you ever run into any browser compatibility problems? A small number of my blog audience have complained about my site not operating correctly in Explorer but looks great in Chrome. Do you have any ideas to help fix this issue?
You got a very excellent website, Gladiola I found it through yahoo.
There are some fascinating time limits in this article but I don’t know if I see all of them heart to heart. There’s some validity however I will take hold opinion until I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we wish more! Added to FeedBurner as well
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I get in fact enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I will be subscribing to your feeds and even I achievement you access consistently rapidly.
Some genuinely fantastic information, Gladiolus I found this. “If you find it in your heart to care for somebody else, you will have succeeded.” by Maya Angelou.
You could certainly see your expertise in the work you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they believe. Always go after your heart.
Utterly indited written content, Really enjoyed examining.
I’ve recently started a website, the information you offer on this website has helped me tremendously. Thank you for all of your time & work.
But a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw outstanding design.
As soon as I observed this site I went on reddit to share some of the love with them.
of course like your web-site but you need to check the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Several of them are rife with spelling issues and I find it very bothersome to inform the truth then again I’ll surely come back again.
Some really interesting information, well written and broadly speaking user genial.
I am glad to be a visitor of this utter weblog! , thankyou for this rare info ! .
I believe this internet site holds some very wonderful info for everyone. “Variety is the soul of pleasure.” by Aphra Behn.
F*ckin’ remarkable things here. I’m very satisfied to look your article. Thank you so much and i’m having a look forward to contact you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
I’ve been surfing online greater than 3 hours nowadays, but I by no means found any interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth sufficient for me. Personally, if all webmasters and bloggers made excellent content material as you probably did, the web will likely be much more useful than ever before. “Perfection of moral virtue does not wholly take away the passions, but regulates them.” by Saint Thomas Aquinas.
Hey! I know this is kinda off topic however I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog post or vice-versa? My website covers a lot of the same topics as yours and I think we could greatly benefit from each other. If you are interested feel free to send me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Superb blog by the way!
Pretty! This was a really wonderful post. Thank you for your provided information.
You are a very smart individual!
I have been exploring for a little for any high quality articles or blog posts on this kind of space . Exploring in Yahoo I ultimately stumbled upon this website. Reading this information So i am satisfied to express that I have an incredibly good uncanny feeling I found out exactly what I needed. I so much surely will make sure to do not fail to remember this site and give it a look regularly.
I like what you guys are up too. Such clever work and reporting! Carry on the excellent works guys I’ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my site :).
I think other website owners should take this internet site as an model, very clean and superb user genial design.
very nice submit, i certainly love this web site, carry on it
Very fantastic information can be found on blog. “You have to learn that if you start making sure you feel good, everything will be okay.” by Ruben Studdard.
You made some clear points there. I did a search on the subject matter and found most persons will go along with with your website.
There is noticeably a bundle to know about this. I assume you made certain nice points in features also.
Does your blog have a contact page? I’m having trouble locating it but, I’d like to shoot you an email. I’ve got some creative ideas for your blog you might be interested in hearing. Either way, great website and I look forward to seeing it improve over time.
Heya i’m for the first time here. I found this board and I find It really useful & it helped me out much. I hope to give something back and aid others like you helped me.
I like this blog very much so much good information.
I conceive other website proprietors should take this web site as an model, very clean and wonderful user genial style and design.
Great write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s web site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a long time.
It is truly a great and helpful piece of information. I’m satisfied that you shared this helpful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thanks for sharing.
Wonderful site you have here but I was curious about if you knew of any user discussion forums that cover the same topics talked about in this article? I’d really like to be a part of community where I can get comments from other knowledgeable individuals that share the same interest. If you have any recommendations, please let me know. Cheers!
You are my inspiration , I own few blogs and infrequently run out from to post : (.
I saw a lot of website but I believe this one has got something extra in it in it
Way cool, some valid points! I appreciate you making this article available, the rest of the site is also high quality. Have a fun.
I gotta bookmark this site it seems invaluable extremely helpful
You made some nice points there. I looked on the internet for the topic and found most individuals will consent with your website.
As I website owner I conceive the content material here is really wonderful, thankyou for your efforts.
Regards for this fantastic post, I am glad I found this internet site on yahoo.
Some genuinely fantastic info , Sword lily I noticed this.
After examine a couple of of the blog posts in your website now, and I actually like your method of blogging. I bookmarked it to my bookmark web site record and might be checking back soon. Pls check out my website as effectively and let me know what you think.
I have to express my thanks to this writer just for rescuing me from this challenge. After browsing throughout the world wide web and coming across basics which were not helpful, I assumed my entire life was over. Living without the answers to the issues you have solved as a result of your good site is a crucial case, as well as ones that might have negatively damaged my entire career if I hadn’t come across your site. Your main skills and kindness in taking care of all things was useful. I’m not sure what I would have done if I had not come across such a subject like this. It’s possible to at this point look ahead to my future. Thanks very much for the impressive and effective guide. I won’t be reluctant to suggest the sites to any individual who desires recommendations on this situation.
naturally like your web-site but you have to test the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling problems and I find it very bothersome to tell the truth then again I will certainly come again again.
Hi there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it is really informative. I’m going to watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
I have recently started a blog, the information you offer on this web site has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
This is very interesting, You are a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your rss feed and look forward to seeking more of your excellent post. Also, I have shared your web site in my social networks!
What’s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It absolutely useful and it has aided me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist other users like its helped me. Good job.
Great beat ! I would like to apprentice while you amend your web site, how can i subscribe for a blog site? The account helped me a acceptable deal. I had been a little bit acquainted of this your broadcast provided bright clear idea
Thanks for sharing excellent informations. Your website is very cool. I’m impressed by the details that you?¦ve on this blog. It reveals how nicely you perceive this subject. Bookmarked this website page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found simply the information I already searched all over the place and simply could not come across. What a perfect site.
Very informative and excellent anatomical structure of articles, now that’s user friendly (:.
Woh I like your blog posts, bookmarked! .
Very interesting subject , thanks for putting up.
Hello, Neat post. There’s an issue together with your website in web explorer, could test this… IE still is the marketplace chief and a good section of other people will omit your excellent writing due to this problem.
Thank you, I have just been looking for information about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I’ve discovered so far. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
I don’t normally comment but I gotta say appreciate it for the post on this great one : D.
Those are yours alright! . We at least need to get these people stealing images to start blogging! They probably just did a image search and grabbed them. They look good though!
Yay google is my king assisted me to find this great site! .
Great – I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your web site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs and related information ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or anything, site theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task..
he blog was how do i say it… relevant, finally something that helped me. Thanks
Simply wanna remark on few general things, The website style and design is perfect, the content is real excellent : D.
Perfect piece of work you have done, this internet site is really cool with wonderful info .
Thank you for sharing excellent informations. Your web-site is very cool. I am impressed by the details that you have on this web site. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my pal, ROCK! I found just the info I already searched everywhere and simply could not come across. What a perfect web site.
Great paintings! This is the type of info that should be shared across the internet. Disgrace on Google for no longer positioning this submit upper! Come on over and consult with my site . Thanks =)
I truly appreciate this post. I?¦ve been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You have made my day! Thank you again
I likewise conceive hence, perfectly written post! .
I really enjoy studying on this website , it has got great blog posts.
The other day, while I was at work, my cousin stole my iphone and tested to see if it can survive a twenty five foot drop, just so she can be a youtube sensation. My apple ipad is now broken and she has 83 views. I know this is entirely off topic but I had to share it with someone!
Well I definitely liked studying it. This information provided by you is very effective for accurate planning.
Hello.This post was extremely remarkable, especially since I was browsing for thoughts on this issue last Thursday.
Hi, Neat post. There’s an issue with your website in web explorer, could test this… IE still is the market leader and a huge component to folks will omit your excellent writing because of this problem.
I really enjoy examining on this site, it holds great articles. “The living is a species of the dead and not a very attractive one.” by Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche.
Great – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your website. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs and related information ended up being truly simple to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Quite unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, website theme . a tones way for your client to communicate. Nice task..
I was more than happy to seek out this internet-site.I wanted to thanks in your time for this excellent read!! I definitely having fun with each little bit of it and I’ve you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
Thank you for any other informative blog. Where else may I am getting that kind of info written in such a perfect way? I’ve a mission that I’m just now running on, and I have been on the look out for such info.
Only a smiling visitor here to share the love (:, btw outstanding layout. “Everything should be made as simple as possible, but not one bit simpler.” by Albert Einstein.
Well I really liked studying it. This article procured by you is very useful for proper planning.
I will right away grasp your rss as I can not find your e-mail subscription link or newsletter service. Do you have any? Please allow me recognize so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
Some truly excellent articles on this internet site, thanks for contribution. “Such evil deeds could religion prompt.” by Lucretius.
I do agree with all the ideas you’ve presented in your post. They’re really convincing and will certainly work. Still, the posts are very short for novices. Could you please extend them a bit from next time? Thanks for the post.
When I originally commented I clicked the -Notify me when new comments are added- checkbox and now each time a comment is added I get four emails with the same comment. Is there any way you can remove me from that service? Thanks!
Terrific work! This is the type of info that should be shared around the web. Shame on Google for not positioning this post higher! Come on over and visit my website . Thanks =)
What i do not realize is in fact how you are now not really much more well-preferred than you might be right now. You are so intelligent. You understand thus considerably relating to this matter, produced me individually believe it from numerous various angles. Its like women and men are not involved until it is something to accomplish with Girl gaga! Your personal stuffs nice. All the time take care of it up!
I keep listening to the newscast speak about receiving free online grant applications so I have been looking around for the finest site to get one. Could you advise me please, where could i find some?
Hey there, I think your site might be having browser compatibility issues. When I look at your website in Ie, it looks fine but when opening in Internet Explorer, it has some overlapping. I just wanted to give you a quick heads up! Other then that, very good blog!
Woh I enjoy your articles, saved to fav! .
We are a group of volunteers and opening a new scheme in our community. Your site offered us with valuable information to work on. You’ve done a formidable job and our entire community will be grateful to you.
Keep up the wonderful piece of work, I read few articles on this website and I think that your web blog is very interesting and has bands of superb info .
I will right away grab your rss as I can’t to find your e-mail subscription hyperlink or newsletter service. Do you have any? Kindly let me recognise so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
You could certainly see your expertise within the paintings you write. The arena hopes for even more passionate writers like you who are not afraid to say how they believe. At all times follow your heart.
Keep functioning ,great job!
Someone necessarily lend a hand to make severely articles I would state. That is the first time I frequented your website page and up to now? I amazed with the analysis you made to create this particular publish incredible. Excellent task!
Have you ever considered publishing an e-book or guest authoring on other blogs? I have a blog based upon on the same information you discuss and would love to have you share some stories/information. I know my readers would appreciate your work. If you are even remotely interested, feel free to shoot me an e mail.
I discovered your blog site on google and check a few of your early posts. Continue to keep up the very good operate. I just additional up your RSS feed to my MSN News Reader. Seeking forward to reading more from you later on!…
Hi there! I’m at work surfing around your blog from my new iphone 3gs! Just wanted to say I love reading through your blog and look forward to all your posts! Carry on the superb work!
Regards for this marvellous post, I am glad I observed this website on yahoo.
Hi this is kinda of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
As I site possessor I believe the content matter here is rattling wonderful , appreciate it for your hard work. You should keep it up forever! Good Luck.
Really Appreciate this article, how can I make is so that I receive an update sent in an email when you publish a fresh post?
Just what I was searching for, regards for putting up.
I’m typically to blogging and i really admire your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your website and keep checking for brand new information.
I wish to show my appreciation to you just for bailing me out of such a setting. Because of researching throughout the internet and finding things which are not productive, I figured my entire life was gone. Living without the presence of strategies to the issues you have fixed all through your entire post is a crucial case, as well as ones that could have in a wrong way affected my career if I hadn’t discovered your web blog. Your primary talents and kindness in touching all the things was very helpful. I am not sure what I would have done if I had not come across such a solution like this. I am able to at this time look ahead to my future. Thanks very much for your expert and result oriented guide. I won’t hesitate to suggest your web blog to anyone who needs and wants support on this situation.
I believe you have mentioned some very interesting points, thankyou for the post.
Hi there this is kind of of off topic but I was wanting to know if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding know-how so I wanted to get guidance from someone with experience. Any help would be greatly appreciated!
I have been browsing online greater than three hours as of late, but I never discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It is pretty price enough for me. In my view, if all site owners and bloggers made excellent content material as you probably did, the web will be a lot more helpful than ever before.
Can I just say what a relief to find someone who actually knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You definitely know how to bring an issue to light and make it important. More people need to read this and understand this side of the story. I cant believe youre not more popular because you definitely have the gift.
Hey are using WordPress for your blog platform? I’m new to the blog world but I’m trying to get started and set up my own. Do you need any html coding expertise to make your own blog? Any help would be greatly appreciated!
What¦s Taking place i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I have found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & assist different customers like its helped me. Great job.
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Carry on the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my web site 🙂
I’ve been browsing on-line more than 3 hours today, but I never discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It?¦s pretty value enough for me. Personally, if all site owners and bloggers made good content material as you probably did, the net might be a lot more helpful than ever before.
I will right away clutch your rss feed as I can’t to find your email subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me recognise so that I may subscribe. Thanks.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
I was very pleased to find this web-site.I wanted to thanks for your time for this wonderful read!! I definitely enjoying every little bit of it and I have you bookmarked to check out new stuff you blog post.
Some genuinely prize blog posts on this internet site, saved to bookmarks.
Very well written story. It will be supportive to everyone who employess it, as well as me. Keep up the good work – can’r wait to read more posts.
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
Very well written story. It will be supportive to everyone who utilizes it, including yours truly :). Keep up the good work – for sure i will check out more posts.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem together with your site in internet explorer, would check this… IE still is the marketplace chief and a good part of people will leave out your excellent writing due to this problem.
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
You made some decent points there. I did a search on the subject and found most guys will consent with your site.
you’re actually a just right webmaster. The website loading speed is incredible. It sort of feels that you are doing any unique trick. Furthermore, The contents are masterpiece. you’ve done a excellent activity on this matter!
I’ve been absent for some time, but now I remember why I used to love this blog. Thank you, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your web site?
Hi there, I discovered your website by means of Google whilst looking for a comparable topic, your web site got here up, it seems to be good. I’ve bookmarked it in my google bookmarks.
This really answered my problem, thank you!
This is the right blog for anyone who wants to find out about this topic. You realize so much its almost hard to argue with you (not that I actually would want…HaHa). You definitely put a new spin on a topic thats been written about for years. Great stuff, just great!
Fantastic goods from you, man. I’ve keep in mind your stuff previous to and you’re just too excellent. I actually like what you’ve bought right here, really like what you are stating and the way wherein you assert it. You’re making it enjoyable and you continue to care for to stay it wise. I can’t wait to learn far more from you. That is actually a wonderful web site.
I have recently started a website, the information you offer on this website has helped me greatly. Thank you for all of your time & work.
Hey this is kinda of off topic but I was wondering if blogs use WYSIWYG editors or if you have to manually code with HTML. I’m starting a blog soon but have no coding skills so I wanted to get advice from someone with experience. Any help would be enormously appreciated!
You completed a few good points there. I did a search on the matter and found the majority of folks will agree with your blog.
It?¦s truly a great and useful piece of info. I am satisfied that you shared this useful information with us. Please stay us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Nice read, I just passed this onto a friend who was doing a little research on that. And he actually bought me lunch because I found it for him smile Thus let me rephrase that: Thank you for lunch!
Prostadine is a liquid supplement made from a blend of natural plant-based ingredients, minerals, and antioxidants. Its primary goal is to help
Pretty nice post. I just stumbled upon your blog and wished to say that I’ve really enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing to your feed and I hope you write again very soon!
I view something really interesting about your site so I saved to fav.
Hi there! Do you know if they make any plugins to safeguard against hackers? I’m kinda paranoid about losing everything I’ve worked hard on. Any suggestions?
I’d have to examine with you here. Which isn’t one thing I normally do! I get pleasure from studying a publish that will make individuals think. Additionally, thanks for allowing me to comment!
I have been browsing online more than 3 hours as of late, but I never discovered any attention-grabbing article like yours. It’s lovely price sufficient for me. In my opinion, if all site owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the internet will likely be a lot more useful than ever before.
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me & my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our area library but I think I learned more from this post. I am very glad to see such excellent info being shared freely out there.
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is tasteful, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get got an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly very often inside case you shield this hike.
I’m often to running a blog and i really respect your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for new information.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
As a Newbie, I am always browsing online for articles that can aid me. Thank you
Perfectly pent articles, Really enjoyed reading.
Hi! I know this is kinda off topic but I’d figured I’d ask. Would you be interested in exchanging links or maybe guest authoring a blog article or vice-versa? My blog goes over a lot of the same subjects as yours and I feel we could greatly benefit from each other. If you might be interested feel free to shoot me an email. I look forward to hearing from you! Fantastic blog by the way!
I have not checked in here for some time since I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are good quality so I guess I¦ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
WONDERFUL Post.thanks for share..extra wait .. …
My coder is trying to convince me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on various websites for about a year and am anxious about switching to another platform. I have heard very good things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress content into it? Any kind of help would be really appreciated!
Well I sincerely liked studying it. This information provided by you is very constructive for good planning.
Really Appreciate this article, can I set it up so I get an email sent to me every time you make a new post?
It’s hard to seek out educated individuals on this topic, but you sound like you understand what you’re speaking about! Thanks
Vibración de motor
¡Vendemos máquinas para balanceo!
Somos fabricantes, elaborando en tres naciones simultáneamente: España, Argentina y Portugal.
✨Nuestros equipos son de muy alta calidad y al ser fabricantes y no intermediarios, nuestro precio es inferior al de nuestros competidores.
Disponemos de distribución global sin importar la ubicación, lea la descripción de nuestros equipos de equilibrio en nuestro sitio web.
El equipo de equilibrio es transportable, ligero, lo que le permite balancear cualquier eje rotativo en cualquier condición.
I’m truly enjoying the design and layout of your site. It’s a very easy on the eyes which makes it much more pleasant for me to come here and visit more often. Did you hire out a designer to create your theme? Fantastic work!
You could definitely see your expertise in the work you write. The sector hopes for more passionate writers such as you who are not afraid to say how they believe. All the time go after your heart.
Great wordpress blog here.. It’s hard to find quality writing like yours these days. I really appreciate people like you! take care
Perfect work you have done, this website is really cool with fantastic information.
This design is incredible! You obviously know how to keep a reader entertained. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Great job. I really enjoyed what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
It?¦s really a nice and helpful piece of information. I am glad that you just shared this helpful information with us. Please keep us informed like this. Thank you for sharing.
Wohh just what I was searching for, thanks for posting.
so much wonderful info on here, : D.
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
I don’t unremarkably comment but I gotta state regards for the post on this one : D.
Great awesome things here. I?¦m very glad to peer your post. Thank you so much and i am having a look forward to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a e-mail?
I am typically to running a blog and i really appreciate your content. The article has really peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your site and keep checking for new information.
Good post. I learn one thing tougher on different blogs everyday. It will at all times be stimulating to learn content from other writers and follow slightly one thing from their store. I’d desire to make use of some with the content on my weblog whether you don’t mind. Natually I’ll give you a hyperlink on your web blog. Thanks for sharing.
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
certainly like your website however you need to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the truth then again I will surely come again again.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
I like what you guys are up also. Such clever work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it will improve the value of my site 🙂
Pretty section of content. I just stumbled upon your website and in accession capital to assert that I acquire actually enjoyed account your blog posts. Any way I’ll be subscribing to your augment and even I achievement you access consistently quickly.
Well I truly liked reading it. This article procured by you is very constructive for correct planning.
Wow, amazing blog structure! How long have you ever been blogging for? you make running a blog glance easy. The whole look of your website is wonderful, let alone the content!
I conceive other website proprietors should take this internet site as an example , very clean and great user pleasant design and style.
I was examining some of your blog posts on this website and I conceive this website is real instructive! Continue posting.
Very interesting topic, thanks for putting up.
Thank you for sharing superb informations. Your web site is so cool. I am impressed by the details that you?¦ve on this website. It reveals how nicely you understand this subject. Bookmarked this web page, will come back for extra articles. You, my friend, ROCK! I found just the information I already searched everywhere and just could not come across. What a perfect site.
I think other web-site proprietors should take this site as an model, very clean and wonderful user genial style and design, as well as the content. You are an expert in this topic!
very nice submit, i certainly love this web site, keep on it
Hi, i believe that i saw you visited my weblog so i came to “return the desire”.I am trying to to find issues to enhance my site!I guess its adequate to use a few of your ideas!!
Some genuinely fantastic info , Gladiola I found this. “What we want is to see the child in pursuit of knowledge, and not knowledge in pursuit of the child.” by George Bernard Shaw.
hey there and thank you for your info – I’ve certainly picked up anything new from right here. I did however expertise several technical issues using this website, since I experienced to reload the site many times previous to I could get it to load correctly. I had been wondering if your web host is OK? Not that I’m complaining, but slow loading instances times will very frequently affect your placement in google and could damage your high quality score if advertising and marketing with Adwords. Well I am adding this RSS to my e-mail and can look out for a lot more of your respective exciting content. Ensure that you update this again very soon..
Thank you for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do a little research about this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I am very glad to see such excellent info being shared freely out there.
I really like your blog.. very nice colors & theme. Did you create this website yourself or did you hire someone to do it for you? Plz answer back as I’m looking to design my own blog and would like to know where u got this from. cheers
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
This actually answered my downside, thank you!
Very interesting info!Perfect just what I was looking for!
I conceive this website has some rattling excellent info for everyone :D. “As ill-luck would have it.” by Miguel de Cervantes.
Today, I went to the beach front with my kids. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She placed the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is totally off topic but I had to tell someone!
I got what you intend,saved to my bookmarks, very nice internet site.
I like what you guys are up also. Such smart work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I have incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my website 🙂
I loved as much as you will receive carried out right here. The sketch is attractive, your authored material stylish. nonetheless, you command get bought an nervousness over that you wish be delivering the following. unwell unquestionably come more formerly again since exactly the same nearly a lot often inside case you shield this hike.
Useful information. Lucky me I found your website accidentally, and I am surprised why this twist of fate did not took place in advance! I bookmarked it.
Great write-up, I¦m regular visitor of one¦s web site, maintain up the excellent operate, and It is going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
I like this site its a master peace ! Glad I found this on google .
I like what you guys are up also. Such intelligent work and reporting! Keep up the superb works guys I?¦ve incorporated you guys to my blogroll. I think it’ll improve the value of my site 🙂
You should take part in a contest for top-of-the-line blogs on the web. I’ll advocate this site!
This design is spectacular! You definitely know how to keep a reader amused. Between your wit and your videos, I was almost moved to start my own blog (well, almost…HaHa!) Wonderful job. I really loved what you had to say, and more than that, how you presented it. Too cool!
I like this site very much, Its a real nice spot to read and get info .
There is evidently a bunch to identify about this. I consider you made some nice points in features also.
whoah this blog is fantastic i love reading your articles. Keep up the great work! You know, lots of people are searching around for this info, you can help them greatly.
I know this if off topic but I’m looking into starting my own weblog and was curious what all is needed to get set up? I’m assuming having a blog like yours would cost a pretty penny? I’m not very web smart so I’m not 100 positive. Any tips or advice would be greatly appreciated. Cheers
Mitolyn is a cutting-edge natural dietary supplement designed to support effective weight loss and improve overall wellness.
very nice put up, i certainly love this website, keep on it
great post.Ne’er knew this, thanks for letting me know.
Hepatoburn is a premium liver support and metabolic enhancement supplement. The liver plays a critical role in detoxification, metabolism, and fat processing. When the liver is overloaded with toxins or functioning poorly, it can slow down metabolism, cause fatigue, and contribute to weight gain
I don’t unremarkably comment but I gotta tell regards for the post on this perfect one : D.
Just want to say your article is as astounding. The clearness for your post is just excellent and i could suppose you are knowledgeable on this subject. Well with your permission let me to seize your RSS feed to stay updated with coming near near post. Thank you one million and please carry on the enjoyable work.
Prime Biome is a cutting-edge probiotic and gut health supplement designed to support digestive wellness, boost immunity, and enhance overall vitality.
You could definitely see your skills within the paintings you write. The world hopes for more passionate writers like you who aren’t afraid to say how they believe. At all times go after your heart. “We may pass violets looking for roses. We may pass contentment looking for victory.” by Bern Williams.
Tonic Greens is an all-natural immune-boosting supplement designed to support your overall wellness with the power of antioxidants, vitamins, and superfoods. It comes in a convenient powdered form that you can easily mix with water, juice, or your favorite smoothie.
Fantastic post however I was wondering if you could write a litte more on this subject? I’d be very grateful if you could elaborate a little bit further. Many thanks!
Heya i’m for the primary time here. I came across this board and I to find It really helpful & it helped me out a lot. I’m hoping to provide something again and aid others such as you aided me.
Currently it seems like WordPress is the top blogging platform available right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
Nerve Calm is an advanced nerve support formula that combines a synergistic blend of essential vitamins, minerals, and herbal extracts.
Good – I should certainly pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all the tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it in the least. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..
I think this is among the most significant info for me. And i’m glad reading your article. But want to remark on some general things, The web site style is perfect, the articles is really great : D. Good job, cheers
There is apparently a lot to realize about this. I think you made some nice points in features also.
Undeniably believe that that you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be at the web the simplest factor to take into account of. I say to you, I certainly get irked whilst people think about concerns that they just don’t recognise about. You controlled to hit the nail upon the top and defined out the whole thing with no need side-effects , people can take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
I got what you mean ,saved to fav, very nice web site.
I like this web blog very much, Its a rattling nice position to read and incur info . “Perpetual optimism is a force multiplier.” by Colin Powell.
Wohh exactly what I was searching for, thanks for putting up.
I like the helpful info you provide in your articles. I’ll bookmark your blog and test again right here regularly. I’m fairly sure I’ll be told lots of new stuff right right here! Best of luck for the following!
I enjoy you because of all of the work on this web page. My mother loves setting aside time for investigation and it’s obvious why. My spouse and i know all relating to the compelling method you provide priceless guidelines through the website and even strongly encourage response from some others on this concept and our favorite daughter has always been studying so much. Have fun with the rest of the new year. You have been conducting a dazzling job.
Some really nice stuff on this web site, I enjoy it.
I believe you have observed some very interesting points, thanks for the post.
I have been absent for a while, but now I remember why I used to love this website. Thank you, I will try and check back more frequently. How frequently you update your site?
I see something genuinely special in this website .
Thanks for the sensible critique. Me and my neighbor were just preparing to do some research on this. We got a grab a book from our local library but I think I learned more clear from this post. I am very glad to see such fantastic info being shared freely out there.
I like this site so much, saved to favorites.
I have read some just right stuff here. Definitely value bookmarking for revisiting. I wonder how a lot attempt you place to create this kind of magnificent informative website.
I will right away clutch your rss as I can’t in finding your email subscription hyperlink or e-newsletter service. Do you have any? Please let me recognise so that I may just subscribe. Thanks.
Thank you, I’ve recently been searching for info about this topic for ages and yours is the greatest I have discovered so far. But, what about the bottom line? Are you sure about the source?
Along with almost everything which appears to be building throughout this particular area, a significant percentage of perspectives are quite stimulating. Even so, I beg your pardon, because I can not give credence to your whole plan, all be it exhilarating none the less. It would seem to everyone that your opinions are actually not entirely justified and in actuality you are generally yourself not even fully convinced of the point. In any case I did appreciate reading through it.
Good write-up, I’m normal visitor of one’s website, maintain up the nice operate, and It’s going to be a regular visitor for a lengthy time.
I like forgathering useful info, this post has got me even more info! .
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
I have learn several just right stuff here. Certainly worth bookmarking for revisiting. I surprise how a lot attempt you put to make such a great informative web site.
I don’t even understand how I stopped up here, but I believed this submit was good. I do not recognise who you’re however certainly you’re going to a famous blogger when you aren’t already 😉 Cheers!
My programmer is trying to persuade me to move to .net from PHP. I have always disliked the idea because of the expenses. But he’s tryiong none the less. I’ve been using Movable-type on various websites for about a year and am concerned about switching to another platform. I have heard great things about blogengine.net. Is there a way I can import all my wordpress posts into it? Any kind of help would be greatly appreciated!
F*ckin’ tremendous things here. I am very satisfied to peer your post. Thanks so much and i’m looking ahead to touch you. Will you kindly drop me a mail?
naturally like your web site however you have to check the spelling on several of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very bothersome to inform the reality nevertheless I will surely come again again.
What¦s Happening i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely useful and it has aided me out loads. I’m hoping to give a contribution & help other users like its helped me. Good job.
very nice publish, i actually love this web site, carry on it
Very nice post. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and wished to say that I’ve really enjoyed browsing your weblog posts. After all I will be subscribing for your rss feed and I am hoping you write once more very soon!
Agen Taruhan Basket Pertama di Indonesia Poster agenhkbtoto.club agenhkbtoto.info agenhkbtoto.top agenhkbtoto.xyz agenhkbtoto.rocks moviequestions user Agenbolabet188world askpub user Agenbolabet188world turnkeylinux.org user 664943 spreaker user 11309128 sketchfab Agenbolabet188world Agen Bola Sbobet Ibcbet | Taruhan Bola | Agen Casino Online | Agen Taruhan Bola IBCBET Terpercaya | Nikmati Permainan Judi Online Bersama Agen Ibcbet Thanks for ur article.. good job !Agen Bola SbobetAgen Sbobet TermurahAgen Sbobet TerpercayaDaftar Agen Sbobet TermurahDaftar Agen Sbobet Terpercaya Situs Judi Casino Online Indonesia Tapestry moviequestions user Agenbolabet188world askpub user Agenbolabet188world turnkeylinux.org user 664943 spreaker user 11309128 sketchfab Agenbolabet188world
http://datos.techo.org/user/grosadostrel1978
This is very bad game please leave this game I am lost about 30k PKR and can’t win a single rupee it’s a frod and this game can lout a lot of peoples Dragon vs Tiger All game are harmful Card game enthusiasts, as well as slot machine lovers, will find Dragon Tiger Slots – Up Down the perfect blend of their favorite games. With a plethora of levels and strategic moves, this app offers an unlimited array of tactics and exhilarating surprises. Worst app totally fraud i just made two transactions but they are saying they didn’t receive the money i also provided them the screenshots but they are denying it APK, Google Play Teen Patti Diamond: 3 Patti is a free card title for mobile devices developed by Intermei Team. It is based on the popular teen patti game that takes inspiration from poker. It lets players compete with one another online. It works with all kinds of internet connections and does not require any registration to play.
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was looking for! “Being rich is having money being wealthy is having time.” by Margaret Bonnano.
Thank you, I have just been looking for info approximately this subject for a long time and yours is the greatest I have discovered so far. However, what concerning the bottom line? Are you certain about the source?
There are some attention-grabbing time limits in this article however I don’t know if I see all of them center to heart. There may be some validity but I will take maintain opinion till I look into it further. Good article , thanks and we would like extra! Added to FeedBurner as effectively
I am impressed with this web site, really I am a fan.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Hello. remarkable job. I did not anticipate this. This is a excellent story. Thanks!
Only wanna remark on few general things, The website style and design is perfect, the subject material is very excellent : D.
Magnificent site. Plenty of useful info here. I¦m sending it to a few buddies ans also sharing in delicious. And of course, thank you on your effort!
The Pink Salt Trick is a minimalist but effective morning routine: Just drink a glass of lukewarm water mixed with a pinch of Himalayan pink salt as soon as you wake up.
The Natural Mounjaro Recipe is more than just a diet—it’s a sustainable and natural approach to weight management and overall health.
Deference to author, some good information .
Howdy! This is my first comment here so I just wanted to give a quick shout out and tell you I truly enjoy reading through your articles. Can you suggest any other blogs/websites/forums that cover the same topics? Many thanks!
I was reading some of your content on this site and I believe this web site is rattling instructive! Retain putting up.
We’re a group of volunteers and starting a new scheme in our community. Your website provided us with valuable info to work on. You have performed an impressive task and our entire neighborhood can be thankful to you.
Thanks for the marvelous posting! I truly enjoyed reading it, you may be a great author.I will always bookmark your blog and will often come back later in life. I want to encourage you continue your great job, have a nice holiday weekend!
Can I just say what a reduction to search out someone who truly knows what theyre talking about on the internet. You positively know how one can convey an issue to gentle and make it important. More people have to learn this and perceive this facet of the story. I cant consider youre no more widespread because you undoubtedly have the gift.
Hi, Neat post. There is a problem together with your site in web explorer, might test thisK IE nonetheless is the market chief and a large portion of folks will miss your excellent writing because of this problem.
Hello! Do you use Twitter? I’d like to follow you if that would be ok. I’m undoubtedly enjoying your blog and look forward to new posts.
You have noted very interesting points! ps nice website .
[b]Eliminate Vibration Issues and Improve Equipment Performance[/b]
Vibration is a silent killer of industrial machines. Imbalance leads to worn-out bearings, misalignment, and costly breakdowns. [b]Balanset-1A[/b] is the ultimate tool for detecting and correcting vibration problems in electric motors, pumps, and turbines.
[b]What Makes Balanset-1A Stand Out?[/b]
– Precise vibration measurement & balancing
– Compact, lightweight, and easy to use
– Two kit options:
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT]Full Kit on Amazon[/url] – Advanced sensors & accessories, Software for real-time data analysis, Hard carrying case
Price: [b]2250 EUR[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT5CCKT][img]https://i.postimg.cc/SXSZy3PV/4.jpg[/img][/url]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR]OEM Kit on Amazon[/url] – Includes core balancing components, Same high-quality device
Price: [b]1978 EUR[/b]
[url=https://www.amazon.es/dp/B0DCT4P7JR][img]https://i.postimg.cc/cvM9G0Fr/2.jpg[/img][/url]
Prevent unexpected breakdowns – Invest in [b]Balanset-1A[/b] today!
Hi , I do believe this is an excellent blog. I stumbled upon it on Yahoo , i will come back once again. Money and freedom is the best way to change, may you be rich and help other people.
Hello There. I found your weblog the use of msn. This is a very smartly written article. I’ll be sure to bookmark it and come back to read extra of your useful info. Thanks for the post. I will certainly comeback.
Hi there! I know this is kinda off topic but I was wondering which blog platform are you using for this website? I’m getting fed up of WordPress because I’ve had problems with hackers and I’m looking at alternatives for another platform. I would be fantastic if you could point me in the direction of a good platform.
naturally like your website however you have to test the spelling on several of your posts. Many of them are rife with spelling issues and I to find it very troublesome to inform the truth however I¦ll certainly come back again.
I am always thought about this, regards for posting.
I truly enjoy studying on this website, it holds great articles. “Don’t put too fine a point to your wit for fear it should get blunted.” by Miguel de Cervantes.
Definitely believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the internet the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I certainly get annoyed while people think about worries that they plainly do not know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top as well as defined out the whole thing without having side-effects , people could take a signal. Will likely be back to get more. Thanks
A lot of thanks for your entire efforts on this website. My mom delights in conducting investigation and it’s really easy to see why. A number of us know all relating to the powerful ways you make both interesting and useful information by means of your website and even increase contribution from some other people on the subject so our favorite child has always been being taught a lot of things. Take advantage of the remaining portion of the year. Your carrying out a superb job.
certainly like your web-site however you need to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling issues and I in finding it very troublesome to tell the reality on the other hand I?¦ll surely come again again.
You should take part in a contest for one of the best blogs on the web. I will recommend this site!
Would love to forever get updated outstanding web blog! .
Some truly wondrous work on behalf of the owner of this web site, absolutely great subject matter.
Spot on with this write-up, I really suppose this web site needs way more consideration. I’ll most likely be again to learn rather more, thanks for that info.
Good day! I could have sworn I’ve been to this site before but after browsing through some of the post I realized it’s new to me. Nonetheless, I’m definitely happy I found it and I’ll be bookmarking and checking back frequently!
I have been examinating out many of your posts and i can state pretty good stuff. I will definitely bookmark your website.
Great post. I used to be checking continuously this blog and I’m inspired! Extremely helpful information specially the ultimate phase 🙂 I deal with such information much. I used to be looking for this particular info for a very long time. Thank you and good luck.
Well I truly liked studying it. This article provided by you is very helpful for accurate planning.
Outstanding post, I conceive blog owners should larn a lot from this blog its real user friendly.
I’d have to examine with you here. Which is not one thing I usually do! I take pleasure in reading a post that may make folks think. Additionally, thanks for permitting me to comment!
excellent issues altogether, you simply received a new reader. What could you suggest in regards to your submit that you just made some days in the past? Any positive?
Wonderful goods from you, man. I have understand your stuff previous to and you are just extremely wonderful. I actually like what you have acquired here, certainly like what you are stating and the way in which you say it. You make it entertaining and you still take care of to keep it smart. I can not wait to read much more from you. This is actually a wonderful site.
I went over this internet site and I believe you have a lot of great information, saved to fav (:.
I do love the manner in which you have framed this specific matter and it does supply us a lot of fodder for consideration. Nevertheless, because of everything that I have witnessed, I really hope as the comments stack on that folks remain on point and don’t embark on a tirade involving the news of the day. Anyway, thank you for this exceptional point and even though I do not really go along with this in totality, I respect your point of view.
Simply a smiling visitant here to share the love (:, btw great style and design. “He profits most who serves best.” by Arthur F. Sheldon.
Hello there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it’s really informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful if you continue this in future. Many people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
I must show my thanks to you just for rescuing me from such a trouble. Just after looking through the online world and finding notions which are not beneficial, I thought my life was well over. Being alive without the solutions to the difficulties you have resolved by way of your good guideline is a crucial case, and those that might have badly damaged my entire career if I hadn’t encountered your website. Your main talents and kindness in playing with all the details was valuable. I don’t know what I would’ve done if I hadn’t encountered such a subject like this. I can also now look ahead to my future. Thanks a lot very much for your expert and amazing guide. I will not hesitate to suggest your blog post to anybody who needs to have care on this topic.
Hello there, just became aware of your blog thru Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I’m going to watch out for brussels. I’ll be grateful in the event you proceed this in future. Lots of people might be benefited out of your writing. Cheers!
England Premier League According to IFAB’s Law 14, a penalty taker cannot touch the ball twice before another player makes contact. If this happens, the referee must award an indirect free-kick to the opposing team. ¡Penalty Shoot out es un juego de tragamonedas muy poco convencional, que expone una temática completa de fútbol, simulando que eres un jugador de fútbol, y toca tirar el penal hacia el arco del equipo contrario. 6,09 € € Asumimos un fuerte compromiso con nuestros clientes. Por esta razón, les ofrecemos servicios que se caracterizan por su alta calidad y estrictas normas de transparencia, ya que contamos con importantes licencias, tales como, Lotería de la Provincia Buenos Aires, Lotería de Santa Fe, Lotería de la Ciudad de Buenos Aires y Comisión Nacional de Juegos de Azar (CONAJZAR).
http://www.okaywan.com/home.php?mod=space&uid=672560
Mikilvæg tilkynning Ha llegado el momento de analizar este juego que ya hace presencia en varios casinos de gran importancia a nivel mundial. Por ejemplo, en el casino Brazino777 lo encontrarás como uno de los títulos más destacados del momento. Quédate conmigo para aprender a jugar a la tragamonedas Penalty Shoot Out y, por qué no, registrar buenas ganancias mientras te diviertes. Penalty Shoot Out es una opción emocionante para quienes buscan combinar la pasión por el fútbol con la emoción de las apuestas. Su formato rápido, gráficos envolventes y variedad de opciones de apuestas lo convierten en un juego atractivo tanto para principiantes como para jugadores experimentados. Aunque la suerte juega un papel importante, una gestión responsable del bankroll y el uso de promociones pueden mejorar tu experiencia. Si te apasiona el fútbol y disfrutas de los juegos de casino dinámicos, Penalty Shoot Out es una excelente elección para disfrutar de momentos llenos de adrenalina.
I have not checked in here for a while as I thought it was getting boring, but the last few posts are great quality so I guess I?¦ll add you back to my everyday bloglist. You deserve it my friend 🙂
What¦s Going down i’m new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely helpful and it has helped me out loads. I hope to contribute & help other users like its helped me. Good job.
Great post. I was checking continuously this blog and I am impressed! Very useful information specifically the last part 🙂 I care for such information much. I was seeking this particular info for a long time. Thank you and good luck.
Whats Going down i am new to this, I stumbled upon this I’ve found It absolutely useful and it has helped me out loads. I’m hoping to contribute & aid other users like its helped me. Good job.
I¦ve been exploring for a little for any high-quality articles or weblog posts in this kind of space . Exploring in Yahoo I eventually stumbled upon this web site. Reading this information So i¦m satisfied to convey that I have a very just right uncanny feeling I came upon just what I needed. I so much no doubt will make certain to don¦t fail to remember this site and give it a look regularly.
Very good written post. It will be useful to anyone who employess it, including me. Keep up the good work – i will definitely read more posts.
I am not certain where you are getting your information, but great topic. I needs to spend a while learning more or working out more. Thanks for magnificent info I used to be on the lookout for this information for my mission.
I truly appreciate this post. I have been looking everywhere for this! Thank goodness I found it on Bing. You’ve made my day! Thank you again
I think other website proprietors should take this website as an model, very clean and wonderful user genial style and design, as well as the content. You are an expert in this topic!
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours today, yet I never found any interesting article like yours. It is pretty worth enough for me. Personally, if all website owners and bloggers made good content as you did, the net will be much more useful than ever before.
What i don’t realize is actually how you’re not actually much more well-liked than you may be right now. You’re very intelligent. You realize thus significantly relating to this subject, produced me personally consider it from so many varied angles. Its like men and women aren’t fascinated unless it’s one thing to do with Lady gaga! Your own stuffs excellent. Always maintain it up!
Balanset-1A: Advanced Mobile Balancer & Vibration Analyzer
Next-generation Dynamic Balancing Solution
Balanset-1A serves as an revolutionary solution for dynamic balancing of rotors in their own bearings, engineered by Estonian company Vibromera OU. The device ensures professional equipment balancing at €1,751, which is 3-10 times more affordable than traditional vibration analyzers while preserving high measurement accuracy. The system allows in-place balancing directly at the equipment’s operational location without requiring dismantling, which is vital for preventing production downtime.
About the Manufacturer
Vibromera OU is an Estonian company focusing in the creation and production of equipment for technical diagnostics of industrial equipment. The company is registered in Estonia (registration number 14317077) and has representatives in Portugal.
Contact Information:
Official website: https://vibromera.eu/shop/2/
Technical Specifications
Measurement Parameters
Balanset-1A delivers precise measurements using a dual-channel vibration analysis system. The device measures RMS vibration velocity in the range of 0-80 mm/s with an accuracy of ±(0.1 + 0.1?Vi) mm/s. The operating frequency range is 5-550 Hz with possible extension to 1000 Hz. The system supports RPM measurement from 250 to 90,000 RPM with phase angle determination accuracy of ±1 degree.
Operating Principle
The device utilizes phase-sensitive vibration measurement technology with MEMS accelerometers ADXL335 and laser tachometry. Two uniaxial accelerometers measure mechanical vibrations proportional to acceleration, while a laser tachometer generates pulse signals for calculating rotation frequency and phase angle. Digital signal processing includes FFT analysis for frequency analysis and proprietary algorithms for automatic calculation of correction masses.
Full Kit Package
The standard Balanset-1A delivery includes:
Measurement unit with USB interface – main module with integrated preamplifiers, integrators, and ADC
2 vibration sensors (accelerometers) with 4m cables (optionally 10m)
Optical sensor (laser tachometer) with 50-500mm measuring distance
Magnetic stand for sensor mounting
Electronic scales for precise measurement of corrective masses
Software for Windows 7-11 (32/64-bit)
Plastic transport case
Complete set of cables and documentation
Performance Capabilities
Vibrometer Mode
Balanset-1A functions as a complete vibration analyzer with capabilities for measuring overall vibration level, FFT spectrum analysis up to 1000 Hz, measuring amplitude and phase of the fundamental frequency (1x), and continuous data recording. The system provides visualization of time signals and spectral analysis for equipment condition diagnostics.
Balancing Mode
The device supports one-plane (static) and two-plane (dynamic) balancing with automatic calculation of correction masses and their installation angles. The unique influence coefficient saving function allows significant acceleration of follow-up balancing of same-type equipment. A specialized grinding wheel balancing mode uses the three-correction-weight method.
Software
The easy-to-use program interface delivers step-by-step guidance through the balancing process, making the device accessible to personnel without special training. Key functions include:
Automatic tolerance calculation per ISO 1940
Polar diagrams for imbalance visualization
Result archiving with report generation capability
Metric and imperial system support
Multilingual interface (English, German, French, Polish, Russian)
Application Areas and Equipment Types
Industrial Equipment
Balanset-1A is successfully applied for balancing fans (centrifugal, axial), pumps (hydraulic, centrifugal), turbines (steam, gas), centrifuges, compressors, and electric motors. In manufacturing facilities, the device is used for balancing grinding wheels, machine spindles, and drive shafts.
Agricultural Machinery
The device provides exceptional value for agriculture, where continuous operation during season is essential. Balanset-1A is used for balancing combine threshing drums, shredders, mulchers, mowers, and augers. The possibility to balance on-site without equipment disassembly allows avoiding costly downtime during critical harvest periods.
Specialized Equipment
The device is effectively used for balancing crushers of various types, turbochargers, drone propellers, and other high-speed equipment. The rotation frequency range from 250 to 90,000 RPM covers virtually all types of industrial equipment.
Superiority Over Similar Products
Economic Effectiveness
At a price of €1,751, Balanset-1A provides the functionality of devices costing €10,000-25,000. The investment pays for itself after preventing just 2-3 bearing failures. Savings on external balancing specialist services amounts to thousands of euros annually.
Ease of Use
Unlike complicated vibration analyzers requiring months of training, mastering Balanset-1A takes 3-4 hours. The step-by-step guide in the software allows professional balancing by personnel without special vibration diagnostics training.
Portability and Autonomy
The complete kit weighs only 4 kg, with power supplied through the laptop’s USB port. This permits balancing in field conditions, at remote sites, and in inaccessible locations without separate power supply.
Versatile Application
One device is adequate for balancing the most extensive spectrum of equipment – from small electric motors to large industrial fans and turbines. Support for one and dual-plane balancing covers all standard tasks.
Real Application Results
Drone Propeller Balancing
A user achieved vibration reduction from 0.74 mm/s to 0.014 mm/s – a 50-fold improvement. This demonstrates the exceptional accuracy of the device even on small rotors.
Shopping Center Ventilation Systems
Engineers effectively balanced radial fans, achieving reduced energy consumption, eliminated excessive noise, and extended equipment lifespan. Energy savings recovered the device cost within several months.
Agricultural Equipment
Farmers note that Balanset-1A has become an indispensable tool preventing costly breakdowns during peak season. Reduced vibration of threshing drums led to lower fuel consumption and bearing wear.
Pricing and Delivery Terms
Current Prices
Complete Balanset-1A Kit: €1,751
OEM Kit (without case, stand, and scales): €1,561
Special Offer: €50 discount for newsletter subscribers
Volume Discounts: up to 15% for orders of 4+ units
Acquisition Options
Official Website: vibromera.eu (recommended)
eBay: verified sellers with 100% rating
Industrial Distributors: through B2B channels
Payment and Shipping Terms
Payment Methods: PayPal, bank cards, bank transfer
Shipping: 10-20 business days by international mail
Shipping Cost: from $10 (economy) to $95 (express)
Warranty: manufacturer’s warranty
Technical Support: included in price
Summary
Balanset-1A represents an ideal solution for organizations aiming to establish an successful equipment balancing system without substantial capital expenditure. The device makes accessible access to professional balancing, permitting small businesses and service centers to provide services at the level of large industrial companies.
The mix of affordable price, ease of use, and professional functionality makes Balanset-1A an indispensable tool for modern technical maintenance. Investment in this device is an investment in equipment reliability, decreased operating costs, and increased competitiveness of your company.
This actually answered my downside, thank you!
Hey there! I’ve been following your weblog for some time now and finally got the courage to go ahead and give you a shout out from Houston Tx! Just wanted to mention keep up the great job!
hi!,I like your writing very much! share we communicate more about your article on AOL? I require an expert on this area to solve my problem. Maybe that’s you! Looking forward to see you.
Well I really enjoyed reading it. This subject provided by you is very constructive for correct planning.
Pretty great post. I simply stumbled upon your weblog and wished to mention that I have truly enjoyed surfing around your blog posts. In any case I will be subscribing on your rss feed and I am hoping you write once more very soon!
Hi there, just became alert to your blog through Google, and found that it’s truly informative. I am gonna watch out for brussels. I will appreciate if you continue this in future. A lot of people will be benefited from your writing. Cheers!
Valuable information. Lucky me I discovered your web site unintentionally, and I am surprised why this coincidence did not came about earlier! I bookmarked it.
Well I really enjoyed reading it. This tip offered by you is very effective for good planning.
I like this post, enjoyed this one regards for putting up.
Thanks for another informative blog. Where else could I get that kind of information written in such an ideal way? I’ve a project that I am just now working on, and I have been on the look out for such information.
Today, I went to the beachfront with my children. I found a sea shell and gave it to my 4 year old daughter and said “You can hear the ocean if you put this to your ear.” She put the shell to her ear and screamed. There was a hermit crab inside and it pinched her ear. She never wants to go back! LoL I know this is completely off topic but I had to tell someone!
I couldn’t resist commenting
Unquestionably believe that which you stated. Your favorite reason appeared to be on the net the simplest thing to be aware of. I say to you, I definitely get annoyed while people think about worries that they plainly don’t know about. You managed to hit the nail upon the top and also defined out the whole thing without having side effect , people can take a signal. Will probably be back to get more. Thanks
You are a very clever individual!
Very interesting information!Perfect just what I was searching for!
Great V I should definitely pronounce, impressed with your site. I had no trouble navigating through all tabs as well as related info ended up being truly easy to do to access. I recently found what I hoped for before you know it at all. Reasonably unusual. Is likely to appreciate it for those who add forums or something, web site theme . a tones way for your customer to communicate. Nice task..
An interesting discussion is worth comment. I think that you should write more on this topic, it might not be a taboo subject but generally people are not enough to speak on such topics. To the next. Cheers
Great post. I am facing a couple of these problems.
Hello.This post was really motivating, especially because I was looking for thoughts on this issue last Saturday.
I am impressed with this internet site, very I am a fan.
Saved as a favorite, I really like your blog!