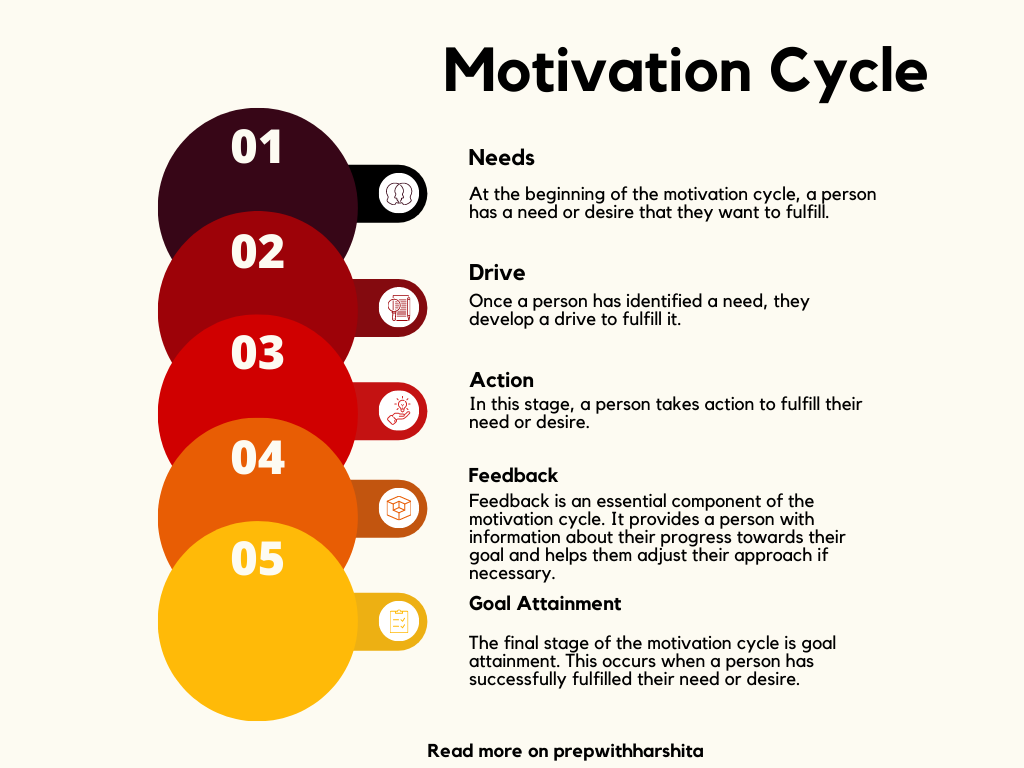
The motivation cycle is a psychological framework that explains how human beings are motivated to achieve their goals. It involves several stages, including:
- Needs: At the beginning of the motivation cycle, a person has a need or desire that they want to fulfill. This could be anything from basic physiological needs like food and water to more complex needs like love, achievement, and recognition.
- Drive: Once a person has identified a need, they develop a drive to fulfill it. This drive is the energy that propels a person towards their goal. It can be influenced by internal factors like emotions and external factors like incentives and rewards.
- Action: In this stage, a person takes action to fulfill their need or desire. They may use problem-solving skills, creativity, and perseverance to overcome obstacles and achieve their goal.
- Feedback: Feedback is an essential component of the the cycle. It provides a person with information about their progress towards their goal and helps them adjust their approach if necessary. Positive feedback can increase motivation, while negative feedback can decrease it.
- Goal attainment: The final stage of the cycle is goal attainment. This occurs when a person has successfully fulfilled their need or desire. Achieving a goal can provide a sense of satisfaction, accomplishment, and self-efficacy.
The motivation cycle is an ongoing process that can be repeated as a person identifies new needs and desires. Understanding this cycle can help individuals and organizations develop strategies to increase motivation and achieve their goals.
Also Read: Types of Motivation