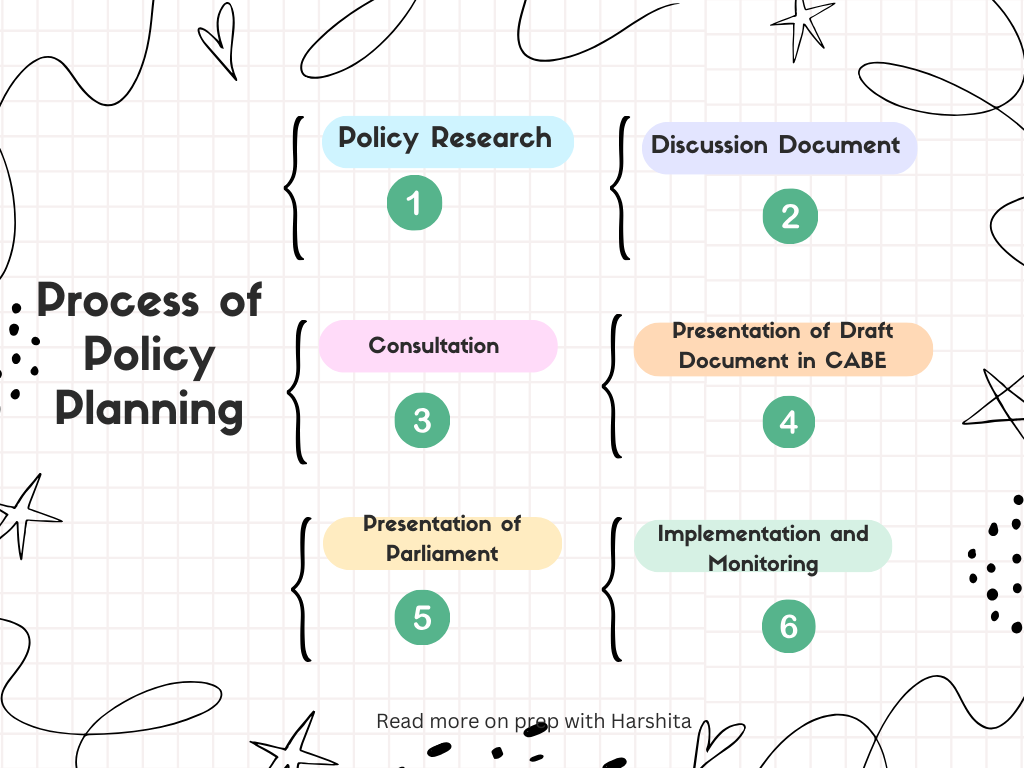
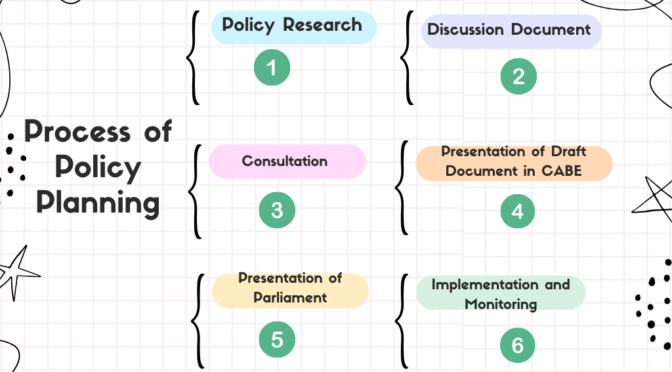
The process of policy formulation involves several stages, including policy research, the creation of discussion documents, consultations, the constitution of working groups, and the presentation of draft documents in relevant bodies like the Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE) and Parliament.
Let’s Discuss the Process of Policy Formation in Detail :
Policy Research
- Identification of Issues: The process begins with identifying the issues that need to be addressed through policy. This may involve research, analysis of existing data, and the identification of gaps or challenges in the current system.
- Data Collection and Analysis: The data is collected and analyzed to understand the scope and impact of the issues. This may involve quantitative and qualitative research methods.
- Review of Best Practices: Policymakers often review best practices from other regions or countries to gain insights into effective approaches to similar issues.
Discussion Document :
- Drafting a Discussion Document: Based on the research findings, a discussion document is drafted. This document outlines the issues, presents the research findings, and proposes potential policy options. It serves as a starting point for further discussions.
- Internal Review: The discussion document is typically reviewed internally within the policymaking body or government department to ensure clarity and alignment with broader government goals.
Consultations:
- Stakeholder Consultations: Policymakers engage in consultations with relevant stakeholders, including experts, community members, non-governmental organizations, and affected parties. This helps in gathering diverse perspectives and input.
- Public Consultations: Depending on the nature of the policy, there may be public consultations to ensure that the policy reflects the needs and concerns of the broader population.
Constitution of Working Groups:
- Formation of Working Groups: Based on the feedback received during consultations, working groups may be formed to go deeper into specific aspects of the policy. These groups typically consist of experts and representatives from relevant sectors.
- In-Depth Analysis: Working groups analyze the policy in detail, considering different scenarios, potential challenges, and alternative solutions. They may also conduct additional research to inform their recommendations.
Presentation of Draft Document in CABE:
- Central Advisory Board of Education (CABE): In the context of education policy, CABE is a crucial body for discussions and approvals. The draft policy document is presented to CABE for review and feedback.
- Feedback and Revision: CABE members provide feedback, and the draft may undergo revisions based on the discussions. This iterative process ensures that the policy aligns with the broader education goals and receives input from key stakeholders.
Presentation of Parliament
- Cabinet Approval: After CABE review and revisions, the draft policy is presented to the Cabinet for approval. The Cabinet, comprising senior government ministers, considers the policy’s implications, feasibility, and alignment with overall government priorities.
- Parliamentary Debate and Approval: Once approved by the Cabinet, the policy is presented to the Parliament for debate and approval. Members of Parliament discuss the policy, ask questions, and vote on its adoption.
Implementation and Monitoring:
- Implementation Plan: After parliamentary approval, an implementation plan is developed. This plan outlines the steps, timelines, and responsibilities for putting the policy into practice.
- Monitoring and Evaluation: Ongoing monitoring and evaluation are established to assess the policy’s effectiveness. This may involve regular reviews, data collection, and adjustments based on feedback and changing circumstances.
Also Read: Need of Educational Planning
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita

Here helpful content about how to become a digital intruder.
Data is shared in a clear and concise manner.
You may acquire a range of skills for bypassing protection.
Besides, there are working models that illustrate how to carry out these expertise.
how to become a hacker
All information is continuously improved to stay current with the up-to-date progress in hacking techniques.
Distinct concentration is paid to workable execution of the absorbed know-how.
Be aware that every procedure should be applied lawfully and according to proper guidelines only.
Within this platform, find an extensive selection virtual gambling platforms.
Searching for traditional options new slot machines, there’s a choice for every player.
The listed platforms checked thoroughly for safety, so you can play peace of mind.
play slots
What’s more, this resource offers exclusive bonuses along with offers targeted at first-timers as well as regulars.
Thanks to user-friendly browsing, discovering a suitable site happens in no time, making it convenient.
Stay updated about the latest additions with frequent visits, because updated platforms come on board often.
On this site, you can discover a variety internet-based casino sites.
Whether you’re looking for well-known titles latest releases, you’ll find an option for every player.
The listed platforms fully reviewed to ensure security, allowing users to gamble peace of mind.
free spins
Moreover, the site provides special rewards and deals to welcome beginners and loyal customers.
With easy navigation, locating a preferred platform is quick and effortless, enhancing your experience.
Be in the know regarding new entries with frequent visits, since new casinos come on board often.
Looking for exclusive 1xBet promo codes? This site offers verified promotional offers like 1XRUN200 for new users in 2024. Get up to 32,500 RUB as a first deposit reward.
Use trusted promo codes during registration to boost your rewards. Enjoy risk-free bets and exclusive deals tailored for casino games.
Find daily updated codes for 1xBet Kazakhstan with fast withdrawals.
All voucher is checked for validity.
Grab limited-time offers like 1x_12121 to double your funds.
Active for new accounts only.
https://images.google.ms/url?q=https://redfordtheatre.com/wp-content/pages/1xbet_promo_code___welcome_bonus_code.htmlKeep updated with top bonuses – apply codes like 1x_12121 at checkout.
Experience smooth benefits with easy redemption.
В этом ресурсе вы можете получить доступ к боту “Глаз Бога” , который может собрать всю информацию о любом человеке из публичных данных.
Данный сервис осуществляет поиск по номеру телефона и раскрывает данные из онлайн-платформ.
С его помощью можно пробить данные через официальный сервис , используя имя и фамилию в качестве ключевого параметра.
проверка автомобиля по вин
Алгоритм “Глаз Бога” автоматически собирает информацию из множества источников , формируя подробный отчет .
Клиенты бота получают ограниченное тестирование для проверки эффективности.
Сервис постоянно обновляется , сохраняя высокую точность в соответствии с требованиями времени .