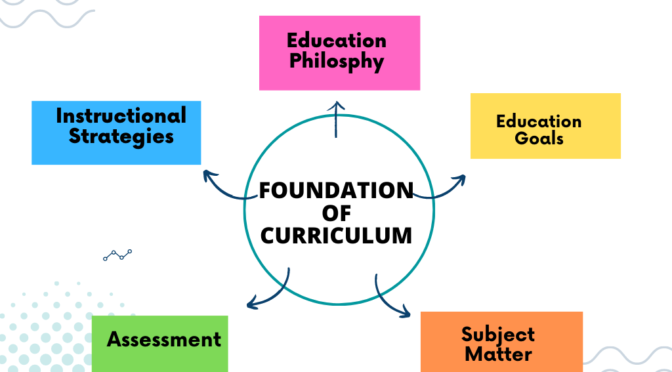
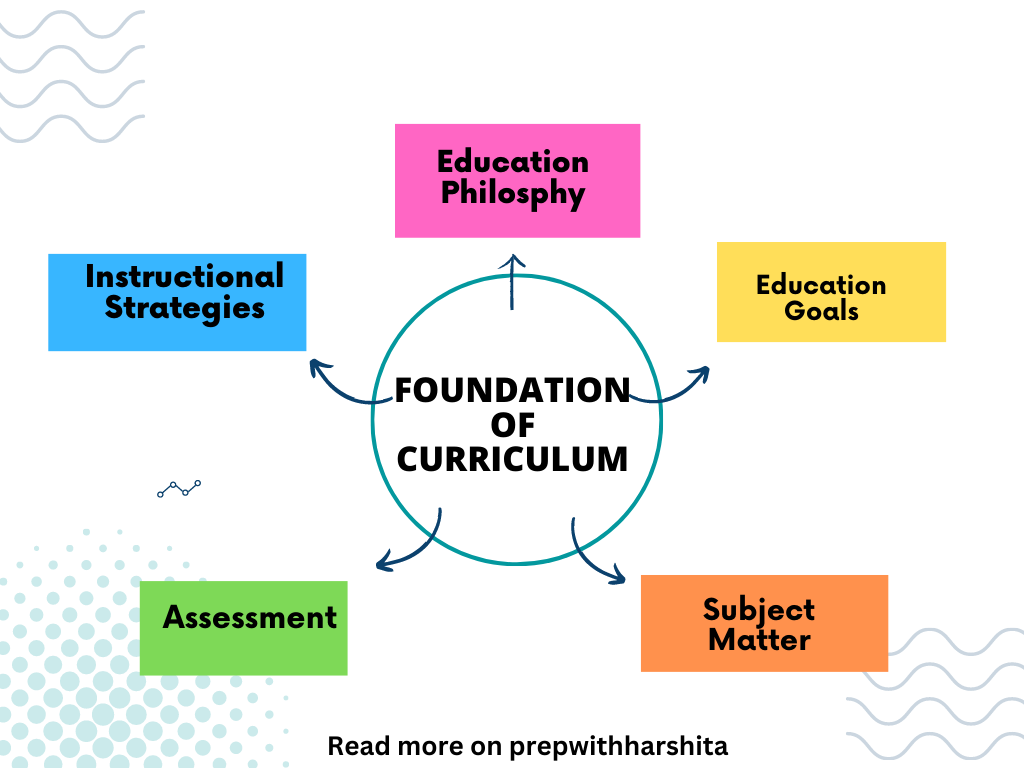
Curriculum research in India involves the study and analysis of the educational curriculum used in schools and universities throughout the country. It aims to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the curriculum and identify ways to improve its effectiveness.
Curriculum research in India is typically conducted through a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods. Here are some common steps involved in conducting curriculum research in India:
- Review of existing literature: Curriculum researchers in India often begin by reviewing existing literature on the curriculum, including textbooks, syllabi, and academic journals.
- Data collection: Researchers collect data through various methods, such as surveys, interviews, focus groups, and observation. This data is used to identify gaps, challenges, and opportunities for improvement in the curriculum.
- Analysis of data: Data collected from different sources is analyzed to identify patterns and trends, as well as to understand the strengths and weaknesses of the curriculum.
- Collaboration with stakeholders: Curriculum researchers collaborate with various stakeholders, including teachers, students, parents, and policymakers, to gather feedback and input on the curriculum. This helps to ensure that the curriculum is relevant and effective.
- Curriculum design and development: Based on the findings of the research, curriculum researchers work with education policymakers and curriculum developers to design and develop curriculum materials that address the identified gaps and challenges.
- Implementation and evaluation: Once the curriculum has been developed, researchers monitor its implementation and evaluate its effectiveness in meeting its intended goals and objectives.
Also read: Issues and Trends in Curriculum development
Here are some key aspects of curriculum research in India:
- Curriculum design: It involves the development and design of the curriculum, which includes determining the subjects to be taught, the grade levels at which they will be taught, and the learning outcomes that students are expected to achieve.
- Curriculum evaluation: It also involves the evaluation of the effectiveness of the curriculum in meeting its stated goals and objectives. This includes assessing the relevance and applicability of the curriculum to the needs of students and the changing demands of the workforce.
- Teacher training: It also includes the development of teacher training programs to ensure that teachers are adequately trained to deliver the curriculum effectively.
- Student assessment: Curriculum research involves the development of methods to assess student learning outcomes and to monitor student progress throughout their education.
- Stakeholder engagement: It also involves engaging with various stakeholders, including teachers, students, parents, and employers to gather feedback and input on the effectiveness of the curriculum.