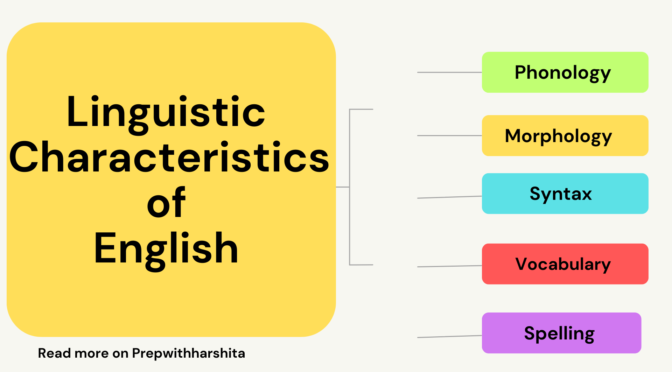
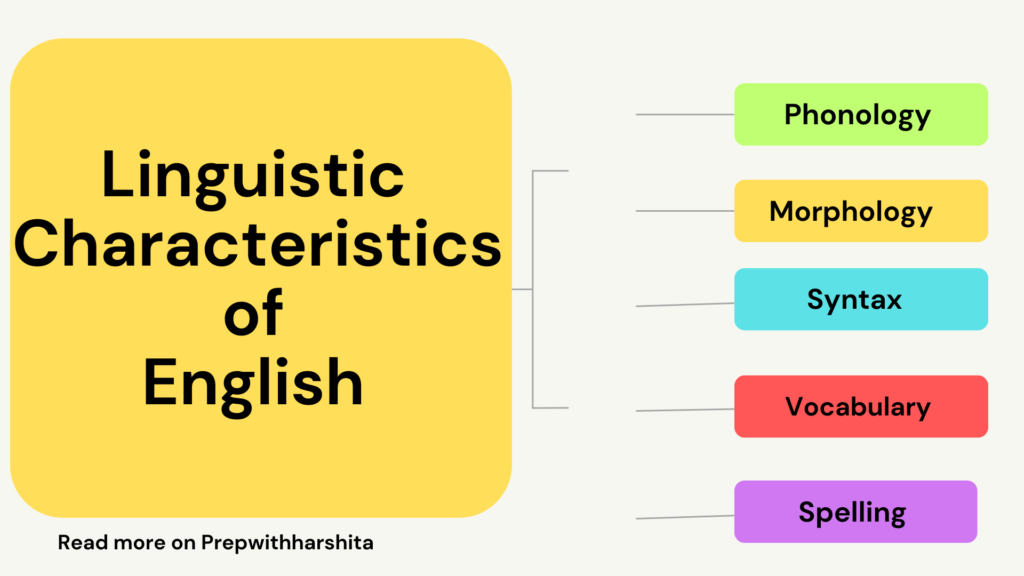
Micro and mega lessons are two different teaching techniques that are commonly used in the field of education.
Here is a detailed explanation of both concepts:
- Micro-lessons:
Micro-lessons are short and focused lessons that typically last anywhere from 1 to 10 minutes. They are designed to be highly specific and targeted, focusing on a single learning objective or concept. Micro-lessons are often used in online or blended learning environments, where students can access the lessons at their own pace and on their own schedule. They are also commonly used in flipped classroom models, where students watch a micro-lesson before coming to class and then work on related activities and assignments during class time.
Some of the key features of micro-lessons include:
- They are short and focused, typically lasting no more than 10 minutes
- They focus on a single learning objective or concept
- They are often delivered online or through video
- They can be accessed by students at any time and on any device
- They are designed to be highly engaging and interactive
- They can be used as part of a larger lesson plan or curriculum
- Mega-lessons:
Mega-lessons are longer and more comprehensive lessons that typically last anywhere from 45 minutes to several hours. They are designed to cover a broad range of learning objectives and concepts and are often used in traditional classroom environments. Mega-lessons can be used to introduce new topics or to provide a deeper understanding of complex concepts. They are typically delivered by a teacher or instructor in person, although they can also be delivered online or through video.
Some of the key features of mega-lessons include:
- They are longer and more comprehensive than micro-lessons
- They cover a broad range of learning objectives and concepts
- They are typically delivered in person by a teacher or instructor
- They can be used to introduce new topics or to provide a deeper understanding of complex concepts
- They often include a mix of lecture, discussion, and hands-on activities
- They can be used as standalone lessons or as part of a larger curriculum
In summary, micro-lessons are short and focused lessons that are often used in online or blended learning environments, while mega-lessons are longer and more comprehensive lessons that are typically used in traditional classroom environments. Both techniques have their own unique advantages and can be effective in helping students achieve their learning goals.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita

Also Read : Difference between Approach and Method