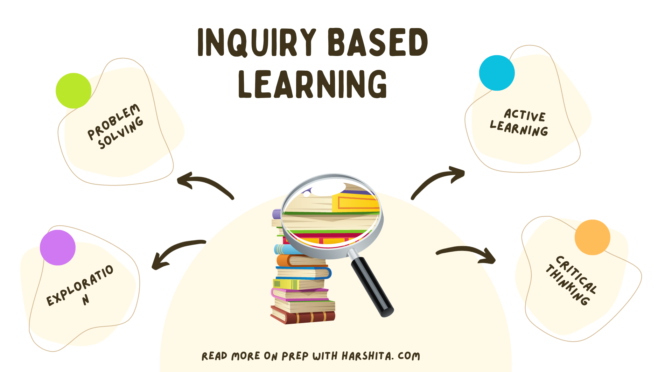
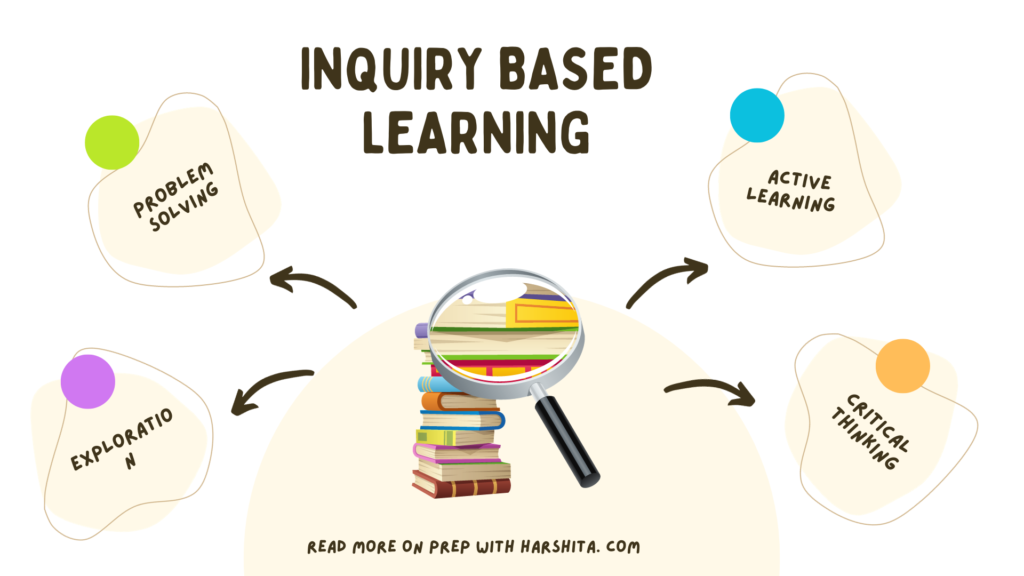
Inquiry Learning Model is a student-centered, active learning approach that places students at the center of the learning process.
Instead of traditional lecture-style teaching, where information is delivered to students passively, inquiry learning encourages students to ask questions, explore topics, and actively engage in problem-solving and critical thinking.
Here are the key elements and principles of an inquiry learning model:
- Questioning: Students are encouraged to ask questions and express their curiosity about a particular topic. These questions can be open-ended and drive the direction of their learning.
- Exploration: Students engage in hands-on activities, research, and investigations to gather information and data related to their questions. This may involve experiments, surveys, reading, or other forms of data collection.
- Critical Thinking: Through inquiry, students develop critical thinking skills by analyzing information, evaluating evidence, and making informed decisions or drawing conclusions based on their findings.
- Problem-Solving: Inquiry learning often presents students with real-world problems or challenges that require creative problem-solving. Students work independently or collaboratively to develop solutions.
- Active Participation: Students actively participate in their learning process. They are responsible for setting goals, planning their activities, and monitoring their progress.
- Teacher Facilitation: While students take a more active role in inquiry learning, teachers play a crucial role as facilitators. They guide students, provide resources, offer support, and help frame questions and problems.
- Reflection: Students are encouraged to reflect on their learning experiences. This reflection helps them consolidate their knowledge and develop metacognitive skills, allowing them to become more effective learners.
- Interdisciplinary Approach: Inquiry learning often blurs the boundaries between subjects. It allows students to explore topics from various angles, incorporating elements from multiple disciplines.
- Student Autonomy: Students have a degree of autonomy in choosing the topics they want to explore and the methods they want to use for investigation. This autonomy fosters a sense of ownership over their learning.
- Assessment: Assessment in inquiry learning focuses on the process as well as the product. It may involve self-assessment, peer assessment, and teacher evaluation of the skills and knowledge gained through the inquiry process.
- Continuous Learning: Inquiry learning promotes a culture of continuous learning. Students learn how to learn, develop a growth mindset, and become more self-directed in their pursuit of knowledge.
Inquiry Learning Model can be applied at various educational levels, from primary school through higher education. It encourages students to become active, engaged, and curious learners while developing critical thinking and problem-solving skills that are valuable in both academic and real-world contexts.
Also Read : Use of ICT in Education
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita