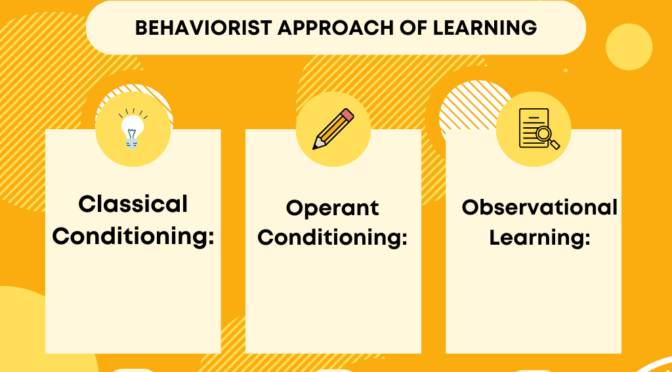
Behaviorism is a psychological theory that emphasizes observable behaviors and the role of environmental stimuli in shaping and controlling behavior. In the context of learning, behaviorist approaches focus on how behaviors are acquired, reinforced, and modified through experiences in the environment. Key approaches to learning from a behaviorist perspective include:
Classical Conditioning:
- Developed by Ivan Pavlov, classical conditioning is a process by which a neutral stimulus becomes associated with a meaningful stimulus and elicits a response.
- Learning occurs through the association of stimuli, where an initially neutral stimulus (conditioned stimulus, CS) becomes paired with a biologically significant stimulus (unconditioned stimulus, UCS), leading to a conditioned response (CR) similar to the unconditioned response (UCR) triggered by the UCS.
- Classical conditioning has been applied in various educational contexts, such as in behavior modification techniques and classroom management strategies.
Read more on the next page.
Also Read: Emotional Intelligence