Synchronous and asynchronous learning refer to two different modes of education delivery, and they play a significant role in both traditional and online learning environments. These terms describe when students and instructors are engaged in learning activities.
Synchronous Learning:
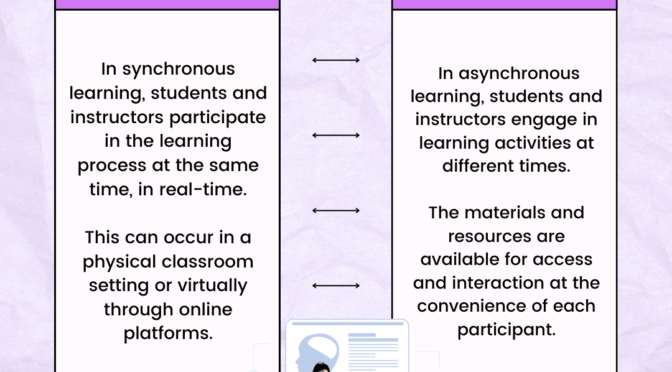
Definition: In synchronous learning, students and instructors participate in the learning process at the same time, in real-time. This can occur in a physical classroom setting or virtually through online platforms.
Examples:
- Traditional face-to-face lectures.
- Live online classes or webinars where students and instructors interact in real-time.
- Group discussions or activities conducted simultaneously.
Advantages:
- Immediate feedback and interaction.
- Simulates a traditional classroom experience.
- Facilitates real-time collaboration among students.
Challenges:
- Schedule constraints as all participants need to be available at the same time.
- Limited flexibility for students with different time zones or conflicting schedules.
Also Read : Scope of Educational Research
Read more on next page..