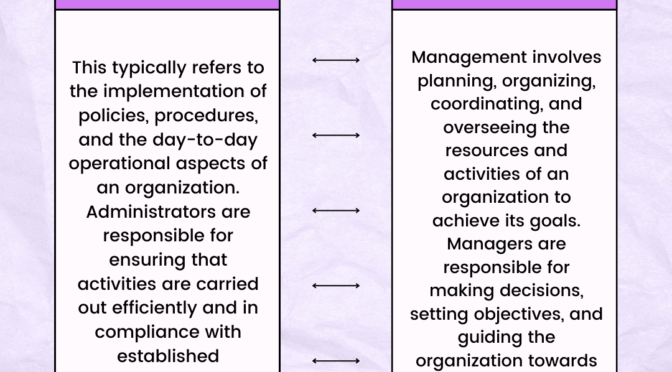
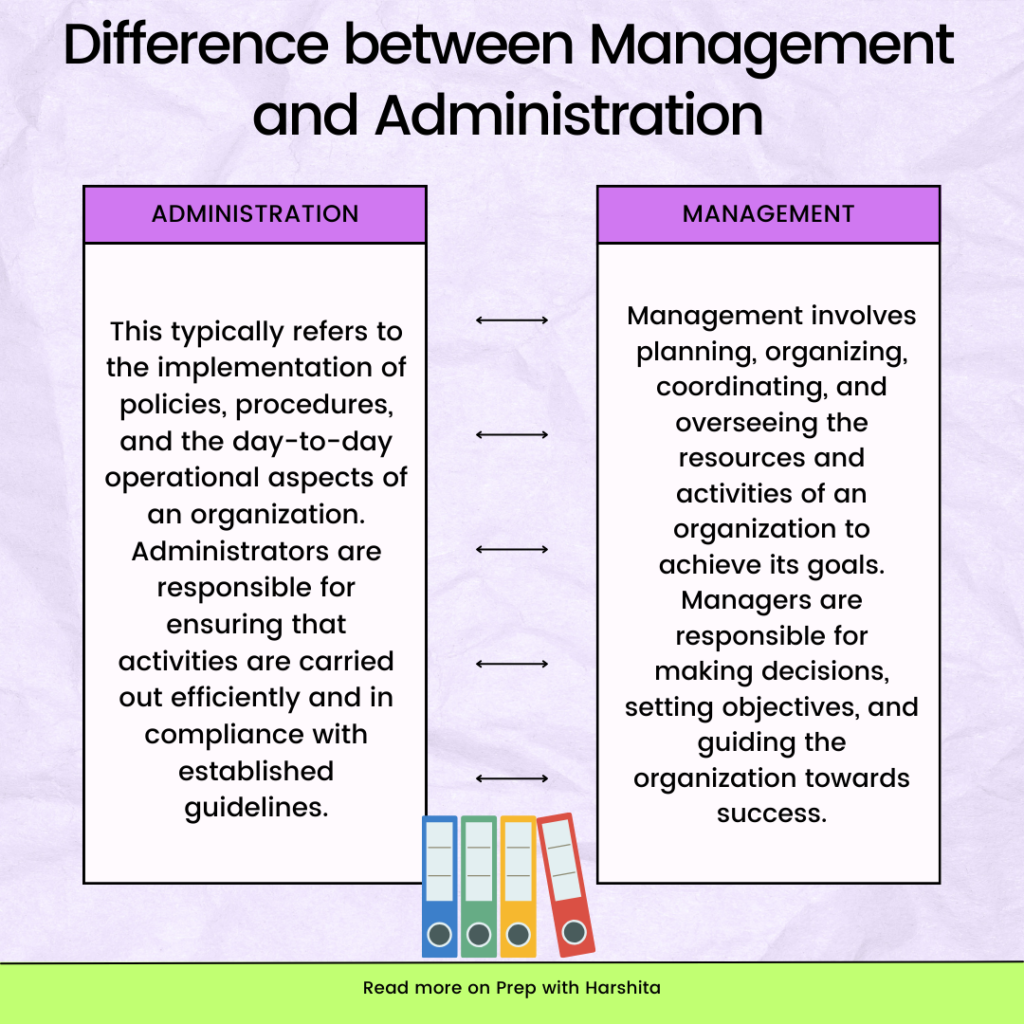
Mother Teacher Associations (MTAs) are organizations that aim to foster collaboration and communication between mothers (parents) and teachers for the betterment of a child’s education and overall development. These role of mother teacher association is creating a supportive environment for both teachers and parents.
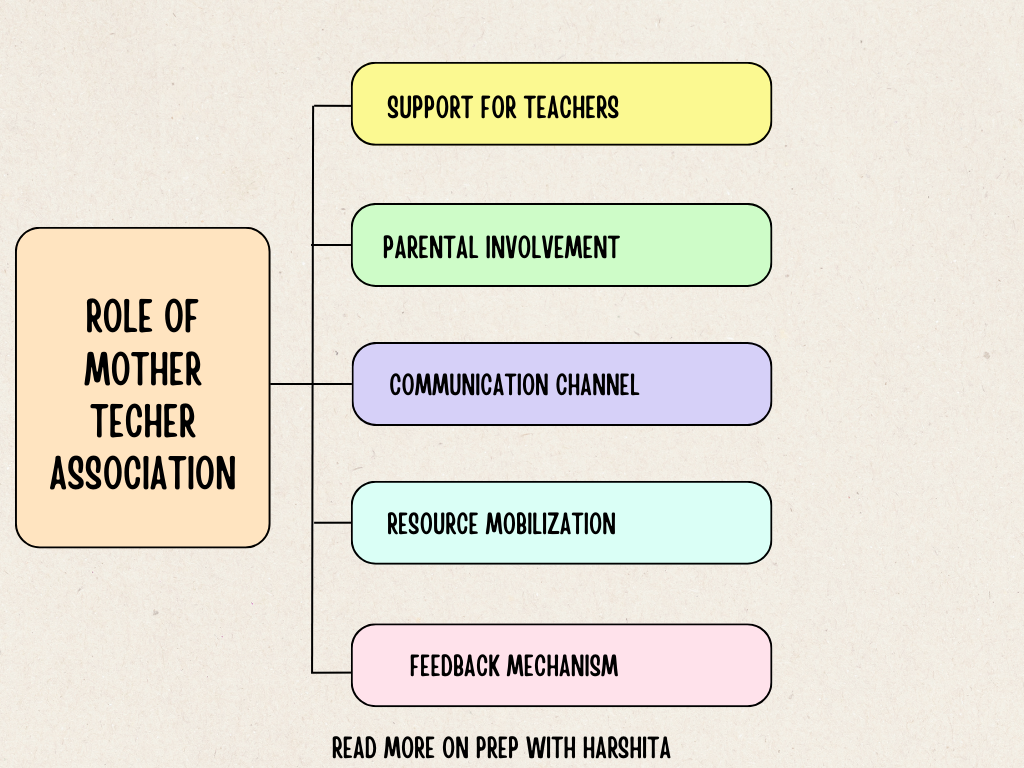
Role of Mother Teacher Association:
Support for Teachers: MTAs focus on providing support and encouragement to teachers. The association recognizes the important role teachers play in a child’s education and seeks to create a positive and collaborative relationship.
Parental Involvement: MTAs encourage active parental involvement in the education of their children. This involvement can take various forms, such as attending parent-teacher meetings, participating in school events, and volunteering in classrooms.
Communication Channel: MTAs serve as a communication channel between parents and teachers. They facilitate open and transparent communication, enabling parents to stay informed about their child’s progress, school activities, and any concerns.
Also Read : ICT
Parent Education: MTAs may organize workshops, seminars, or informational sessions for parents to enhance their understanding of educational practices, child development, and ways to support their children’s learning at home.
Building a Supportive Community: MTAs contribute to building a sense of community within the school. By fostering positive relationships among parents, teachers, and students, MTAs create a supportive network that enhances the overall educational experience.
Feedback Mechanism: MTAs serve as a feedback mechanism, allowing parents to share their thoughts, concerns, and suggestions with teachers and school administrators. This feedback can inform decision-making processes and improvements within the school.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita