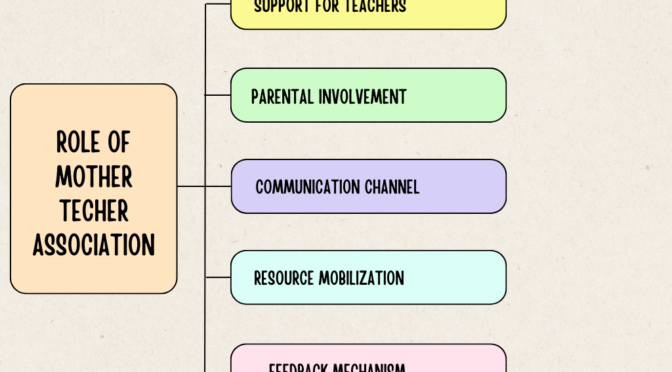
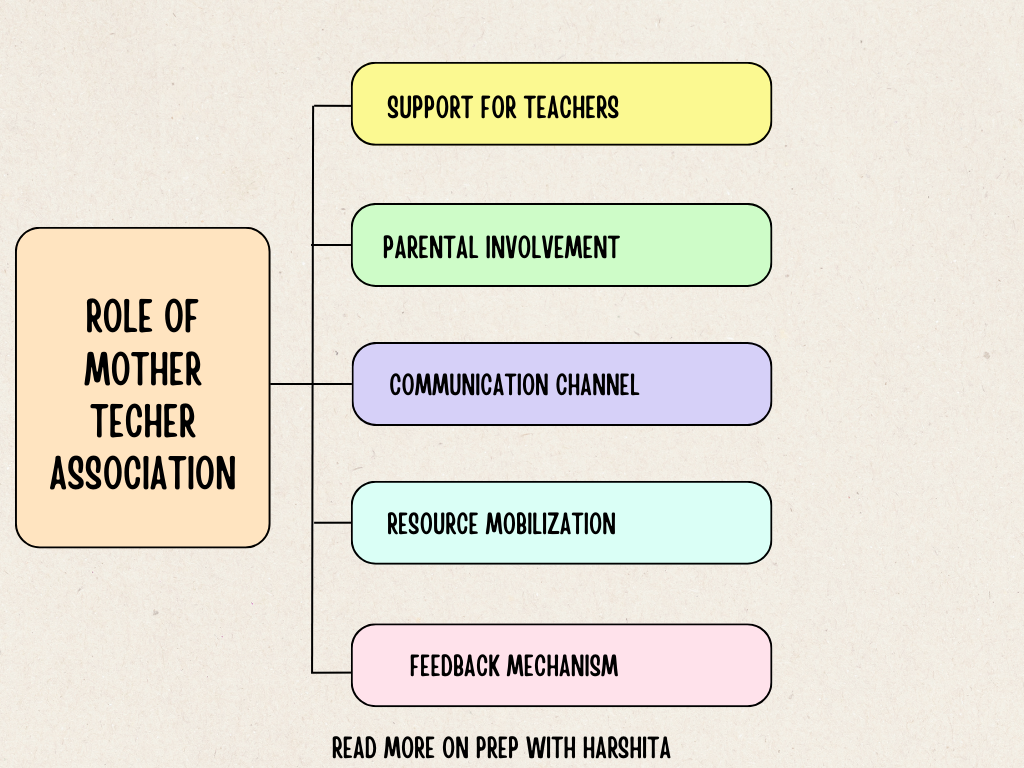
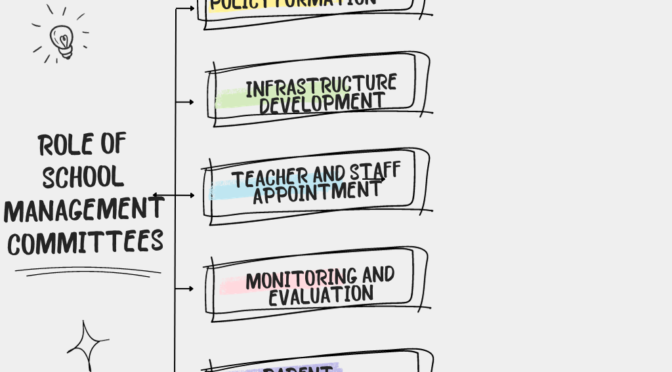
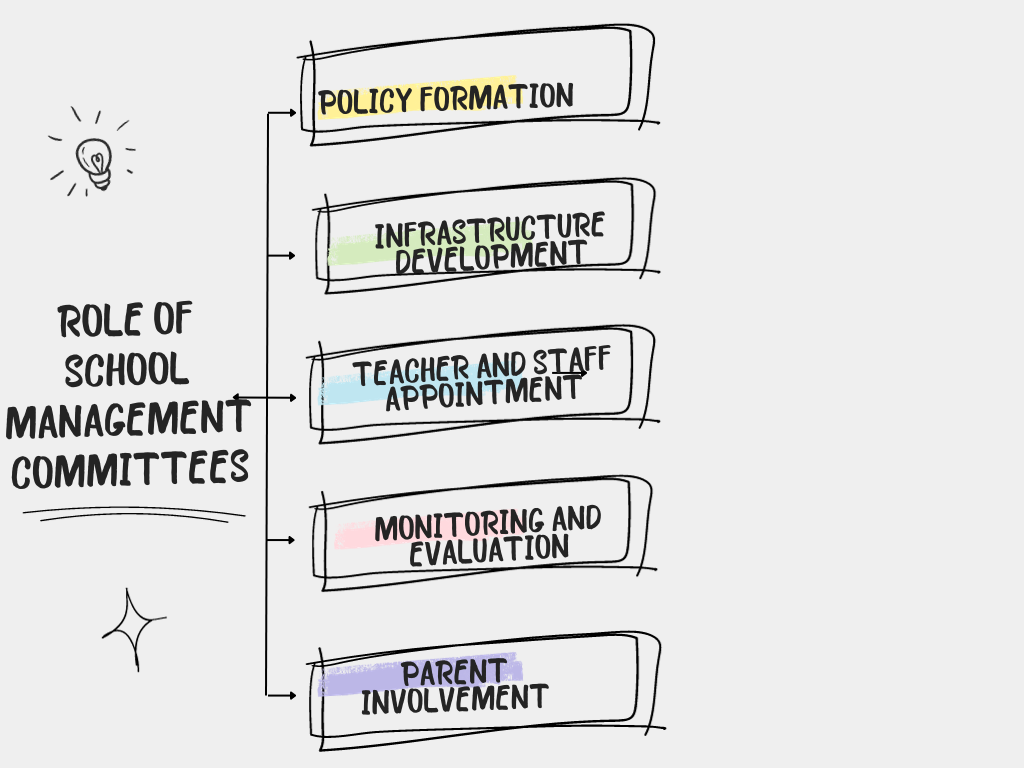
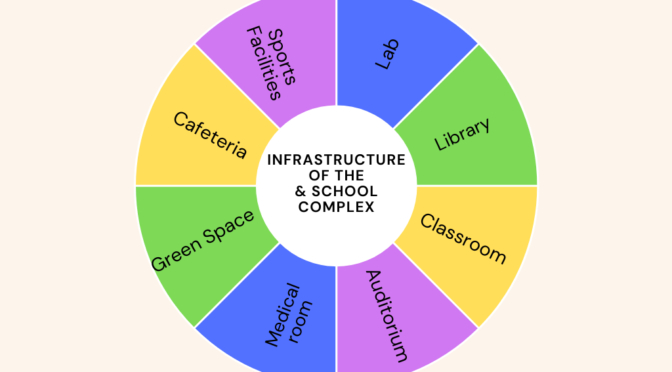
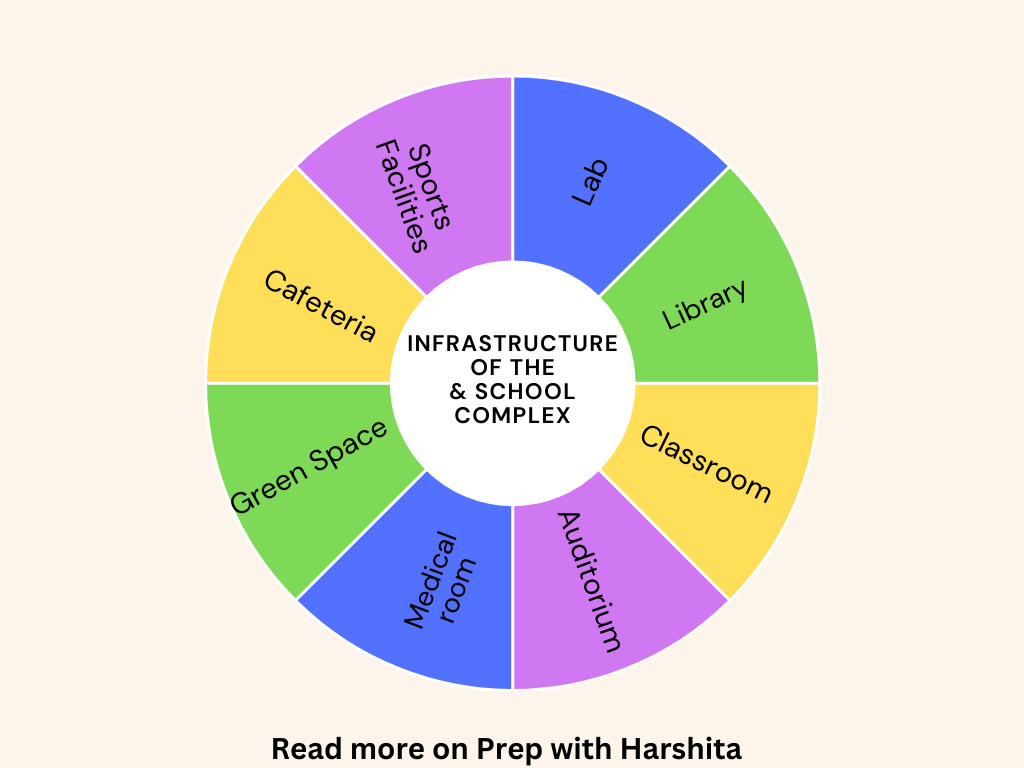
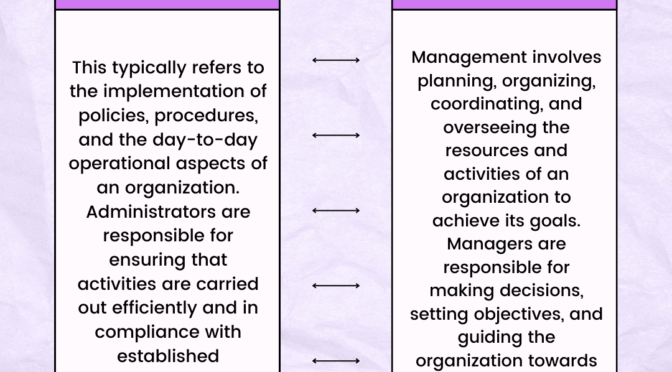
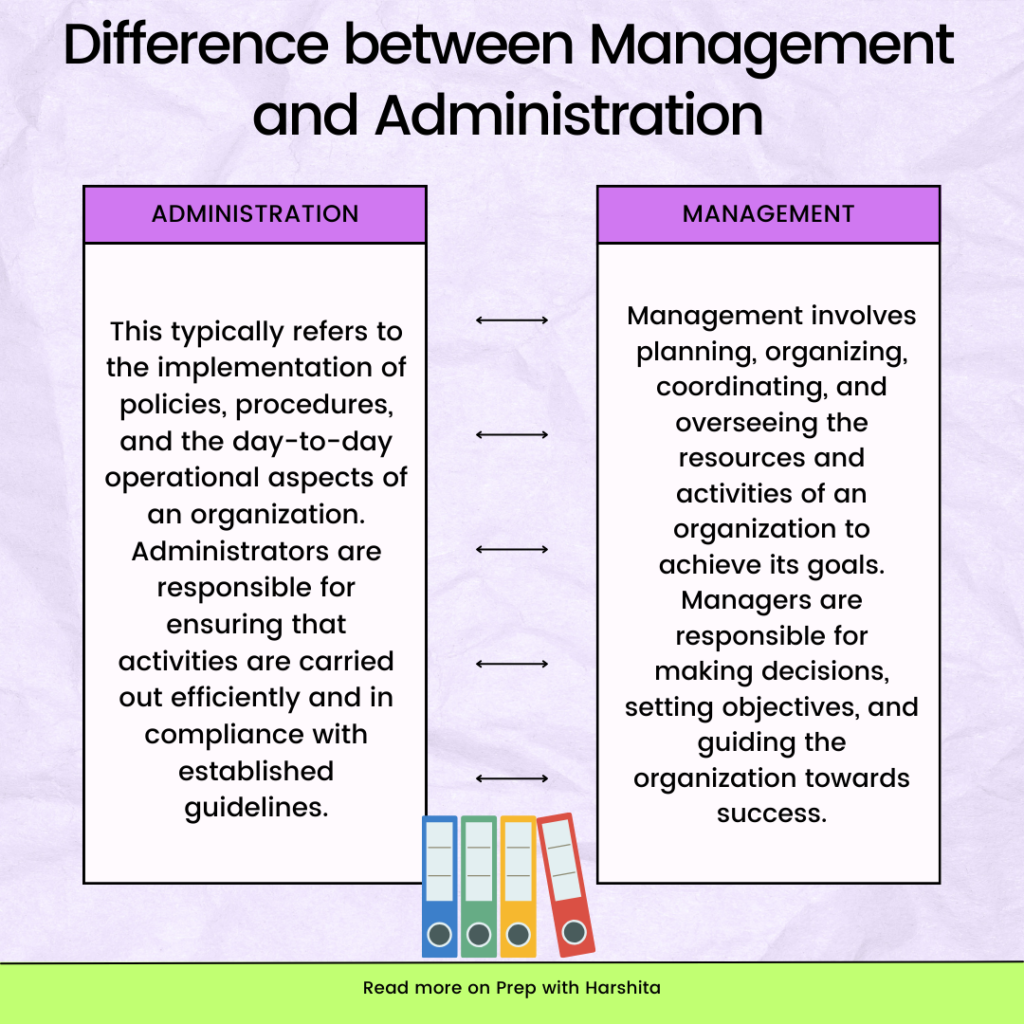
Language and communication are related concepts, but they refer to different aspects of human interaction. Here are the key differences between language and communication:
Definition:
- Language: Language refers to a system of symbols, sounds, and rules used by humans to convey meaning. It is a structured code that enables individuals to express thoughts, feelings, and ideas.
- Communication: Communication is the broader process of exchanging information, ideas, thoughts, or feelings between individuals. It can occur through various means, including language, gestures, facial expressions, and other non-verbal cues.
Scope:
- Language: Language specifically pertains to the use of words, grammar, and syntax to convey meaning. It involves the construction of sentences and the adherence to linguistic rules.
- Communication: Communication encompasses a wider range of activities, including both verbal and non-verbal forms of expression. It includes gestures, body language, facial expressions, and written or visual forms of conveying messages.
Also Read : Multilingualism in the classroom
Forms:
- Language: Language can take various forms, including spoken language (oral communication) and written language. Sign language is also a form of language used by individuals with hearing impairments.
- Communication: Communication can take place through verbal means (speech, writing) as well as non-verbal means (body language, facial expressions, gestures).
Learning Process:
- Language: Learning a language involves acquiring vocabulary, understanding grammar rules, and developing proficiency in speaking, listening, reading, and writing.
- Communication: Communication skills encompass the ability to convey messages effectively using language and non-verbal elements. It involves not only linguistic competence but also social awareness and adaptability.
Purpose:
- Language: The primary purpose of language is to convey meaning through a structured system of symbols and sounds.
- Communication: Communication serves the broader purpose of exchanging information, building relationships, and expressing emotions.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita