Inclusive education refers to an educational approach that aims to provide equitable and quality education to all students, regardless of their abilities, disabilities, gender, ethnicity, social class, and cultural background.
In other words, inclusive education is about creating a learning environment where every student feels valued, respected, and supported to achieve their full potential.
Meaning and Need of Inclusive Education
The need for inclusive education arises from the fact that every student is unique and has their own strengths, challenges, and learning styles. By adopting an inclusive approach, schools and educators can ensure that every student receives the necessary support and resources to overcome barriers to learning and succeed academically, socially, and emotionally. Additionally, inclusive education can promote social cohesion, reduce discrimination, and foster a more tolerant and accepting society.
Also read: Concrete and Absolute Knowledge
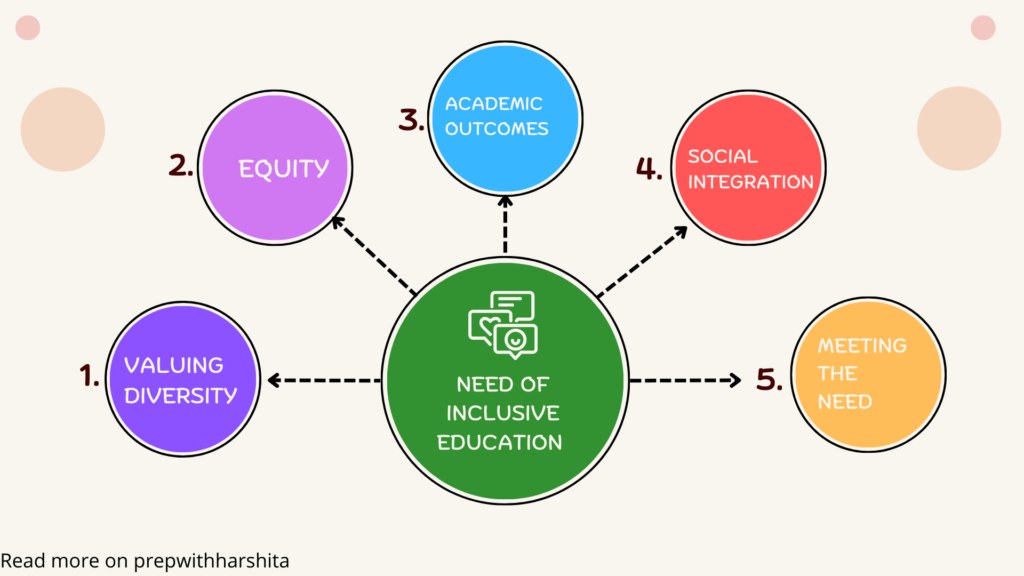
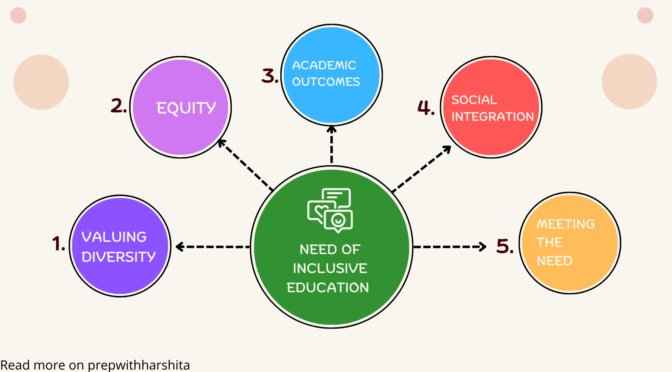
Here are some main points on why we need inclusive education:
- Equity and fairness: Inclusive education aims to provide equal educational opportunities to all students, regardless of their background, abilities, or disabilities. It is a fair and just approach that promotes equity and eliminates discrimination.
- Valuing diversity: Inclusive education recognizes and celebrates diversity in all its forms, including differences in culture, language, ethnicity, race, gender, sexual orientation, and abilities. It promotes respect for all individuals and their unique contributions to society.
- Meeting the needs of all learners: Inclusive education seeks to accommodate the needs of all learners, including those with disabilities or learning difficulties. It provides a supportive learning environment that encourages students to participate and succeed in their education.
- Promoting social integration: Inclusive education helps to break down barriers between different groups of students, promoting social integration and creating a sense of belonging. This helps to reduce stereotypes, prejudice, and discrimination.
- Improving academic outcomes: Inclusive education has been shown to improve academic outcomes for all students, not just those with disabilities or learning difficulties. It fosters a positive and supportive learning environment that can enhance motivation, engagement, and achievement.
- Meeting legal and ethical obligations: Inclusive education is a legal and ethical obligation for schools and educational institutions. It is required by law in many countries and is in line with the United Nations Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities.
Overall, inclusive education is essential for creating a fair, just, and equitable society that values diversity and promotes the well-being and success of all its members.