National Education Policy (NEP) 2020 was introduced in India to bring about significant reforms in the education system.
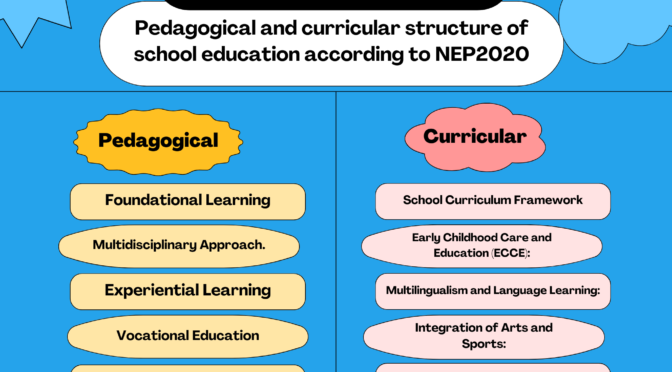
Pedagogical Structure :
Foundational Learning:
NEP 2020 emphasizes a strong focus on foundational literacy and numeracy in the early years of schooling. Foundational learning will be a priority, ensuring that students attain basic skills in reading, writing, and mathematics.
Multidisciplinary Approach:
The policy advocates for a multidisciplinary approach, allowing students to choose subjects across arts, sciences, and humanities. This is aimed at providing a more holistic education and reducing rigid subject boundaries.
Experiential Learning:
The policy encourages experiential learning and critical thinking. It promotes interactive and hands-on learning experiences to facilitate a deeper understanding of concepts and to develop problem-solving skills.
Vocational Education:
There is an increased emphasis on integrating vocational education into the school curriculum. Students will have the opportunity to develop practical skills and knowledge relevant to various professions.
Teacher Training and Professional Development:
NEP 2020 recognizes the importance of teacher training and continuous professional development. It aims to equip teachers with the necessary skills to implement innovative pedagogical practices.
Technology Integration:
The policy acknowledges the role of technology in education and emphasizes the integration of technology in teaching and learning processes. This includes the use of digital resources, online learning, and educational technology tools.
Curricular Structure:
School Curriculum Framework:
The NEP 2020 envisions a school curriculum framework that is flexible, integrated, and focused on the holistic development of learners. It aims to reduce the content overload in the existing curriculum.
Early Childhood Care and Education (ECCE):
The policy underscores the significance of Early Childhood Care and Education and proposes the integration of ECCE into the formal schooling system. This includes a play-based, activity-oriented approach for young learners.
Multilingualism and Language Learning:
NEP 2020 promotes multilingualism and proposes the implementation of a three-language formula. Students are encouraged to learn three languages, with an emphasis on proficiency in the mother tongue or local language.
Integration of Arts and Sports:
The curriculum is designed to integrate arts, sports, and other extracurricular activities to promote a well-rounded education. This is aimed at nurturing creativity, critical thinking, and physical well-being.
Board Exams:
Changes in the board examination structure are proposed, with an emphasis on testing core concepts and analytical abilities. Board exams are expected to be made easier to reduce stress on students.
Also read: Formation of School Subjects

Also Visit: Prep with Harshita