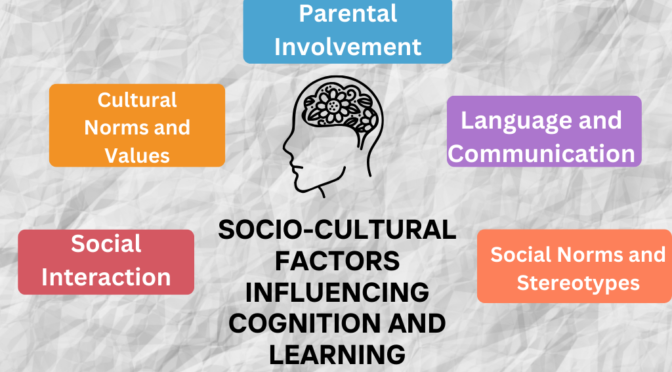
Socio-cultural factors play a significant role in shaping cognition and learning processes. These factors encompass the social, cultural, and environmental influences that affect how individuals think, learn, and acquire knowledge.
Let’s study some major socio-cultural factors and their impact on cognition and learning:
Social Interaction: Social interactions with family members, peers, teachers, and other community members contribute to cognitive development. Through conversations, collaboration, and shared experiences, individuals acquire language skills, cultural knowledge, and social understanding.
Cultural Norms and Values: Cultural values, beliefs, and norms shape cognitive processes and influence the way individuals approach learning. Different cultures may emphasize particular ways of thinking, problem-solving, and decision-making, impacting cognitive styles and preferences.
Read more on the next page.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita