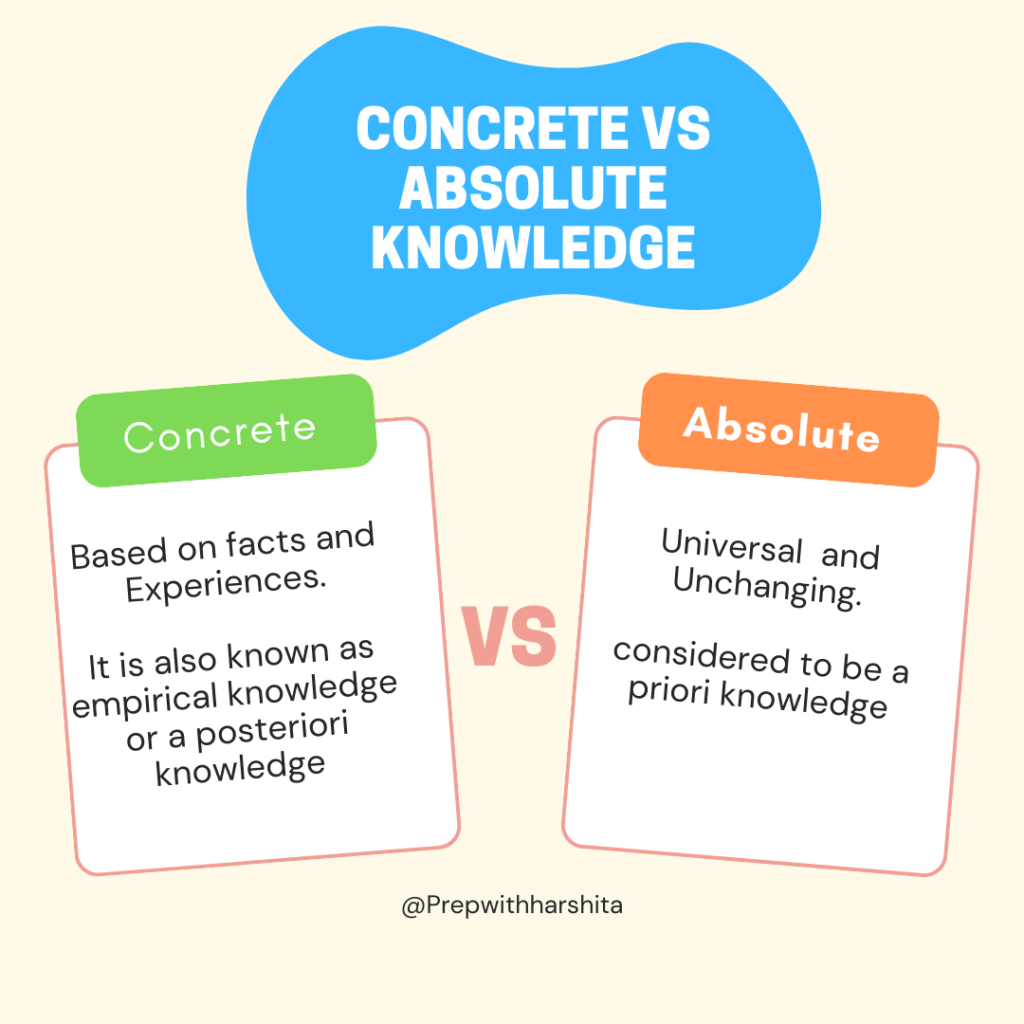
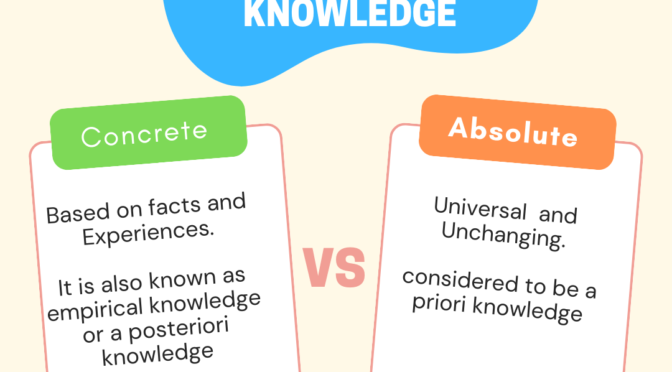
Concrete knowledge is the knowledge that is based on specific, observable facts and experiences, while absolute knowledge is the knowledge that is considered to be universal and unchanging, independent of individual perspectives or experiences.
Concrete is often more empirical and can be proven through observation and experimentation whereas absolute knowledge is often more philosophical and may not be able to be proven in the same way.
Concrete knowledge refers to knowledge of specific facts, events, and things. It is the knowledge that can be verified and proven to be true or false through empirical evidence and observation. It is also known as empirical knowledge or a posteriori knowledge.
Absolute knowledge refers to knowledge that is considered to be true and certain without the need for any further justification or proof. It is often associated with philosophical and religious beliefs and is considered to be a priori knowledge, which is the knowledge that is known independently of experience.
In summary, concrete knowledge is based on evidence and experience, while absolute knowledge is based on belief and cannot be verified through observation or experimentation.
Also Read: Contextual and Textual Knowledge