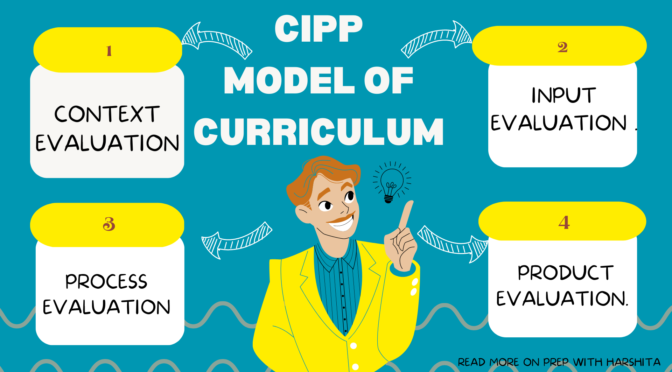
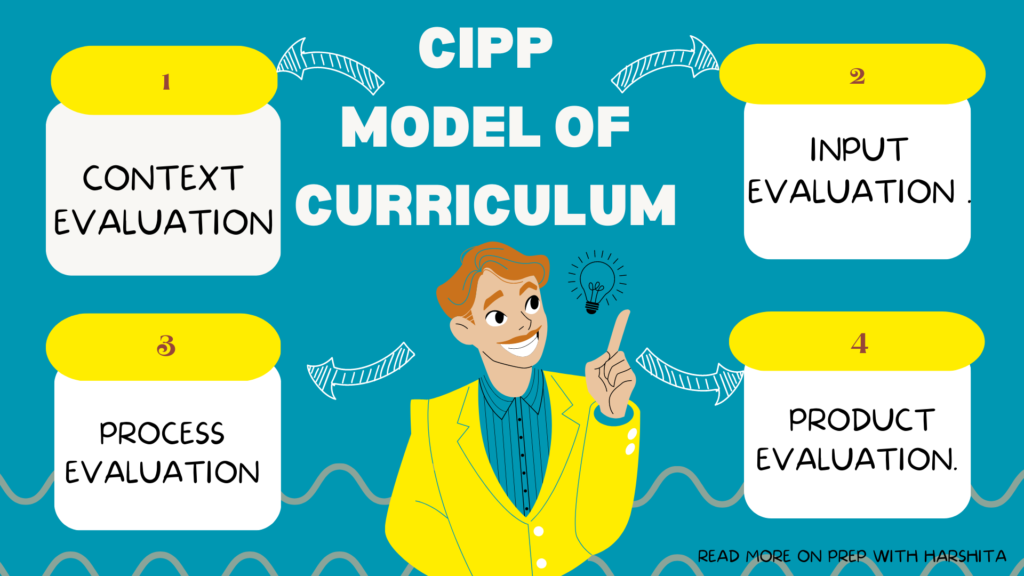
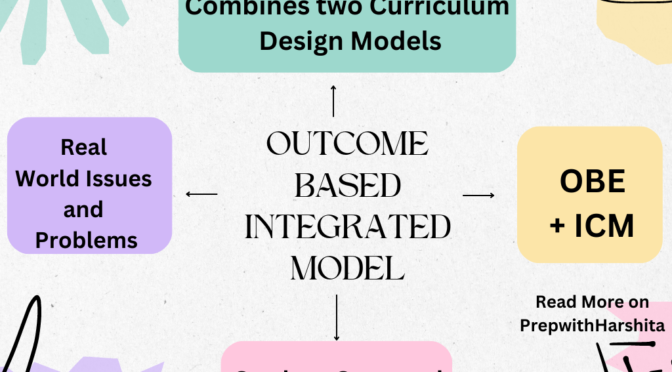
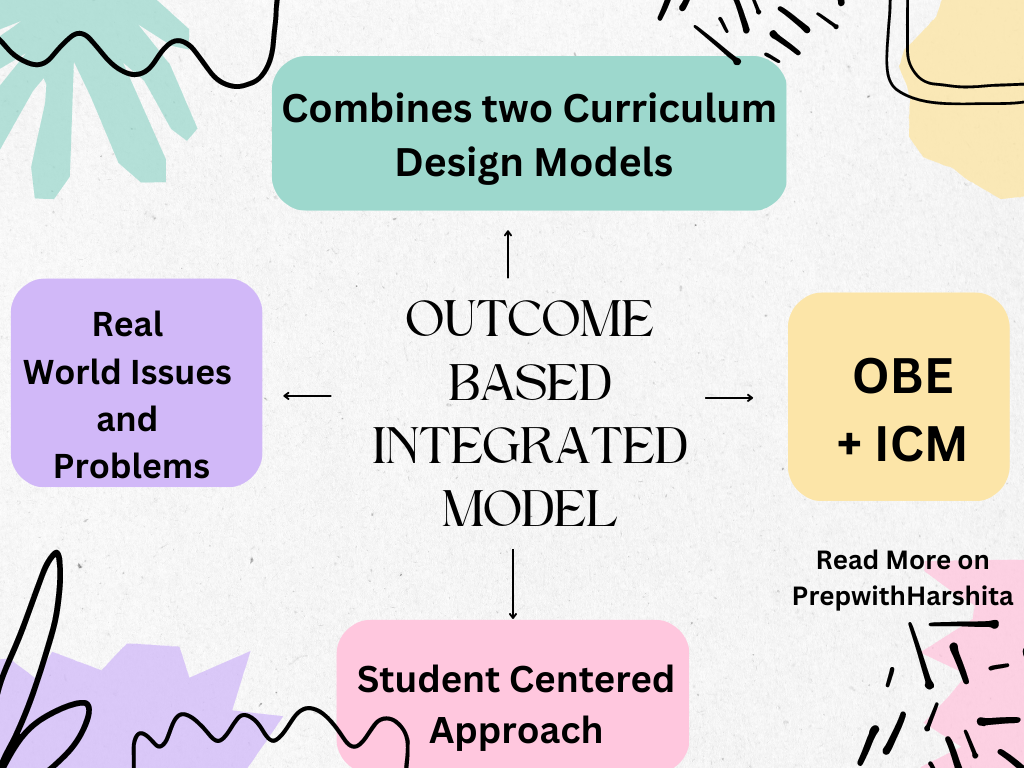
A core curriculum is a set of courses that all students are required to take in order to graduate from a particular school or program. These courses are typically considered to be essential for all students, regardless of their intended major or career path.
Core Curriculum :
- It vary from school to school, but they typically include courses in English, math, science, history, and social studies. Some schools also require courses in foreign languages, arts, or physical education.
- The purpose of a core curriculum is to provide students with a well-rounded education that will prepare them for college, careers, and civic life. By studying a variety of subjects, students can develop critical thinking skills, learn to communicate effectively and gain a better understanding of the world around them.
- In addition to the core curriculum, educational institutions may also offer elective courses or specialized tracks that allow students to explore specific interests or career paths. However, this curriculum remains the fundamental basis of education, providing students with essential knowledge and skills that are considered important for their overall intellectual and personal development.
- It’s worth noting that the specific subjects included in a core curriculum can vary across different educational systems and institutions. Some educational systems prioritize certain subjects more than others, depending on cultural, regional, or national priorities.
- Additionally, educational policies and curriculum frameworks may evolve over time to adapt to changing societal needs and educational trends.
Benefits of a core curriculum:
- Provides a well-rounded education
- Develops critical thinking skills
- Improves communication skills
- Increases knowledge of the world
- Prepares students for college and careers
- Promotes civic engagement
Features of Core Curriculum :
- Essential subjects: This includes fundamental subjects like mathematics, science, social studies, language arts, and foreign languages.
- Sequential structure: Subjects are taught in a logical progression, building upon previously learned concepts.
- Cross-disciplinary connections: It encourages making connections across different subjects to show their interconnectedness.
- Skill development: It focuses on developing essential skills like critical thinking, problem-solving, communication, and collaboration.
- Standards and learning objectives: It is guided by educational standards and learning objectives to ensure consistent and quality education.
- Flexibility and adaptability: It allows for flexibility to meet the needs of diverse learners, providing differentiated instruction and support.
- Regular assessment: It includes assessments to measure student progress and inform instructional decisions.
Also Read: Role of Teacher as Curriculum Maker

Also Visit: Prep with Harshita