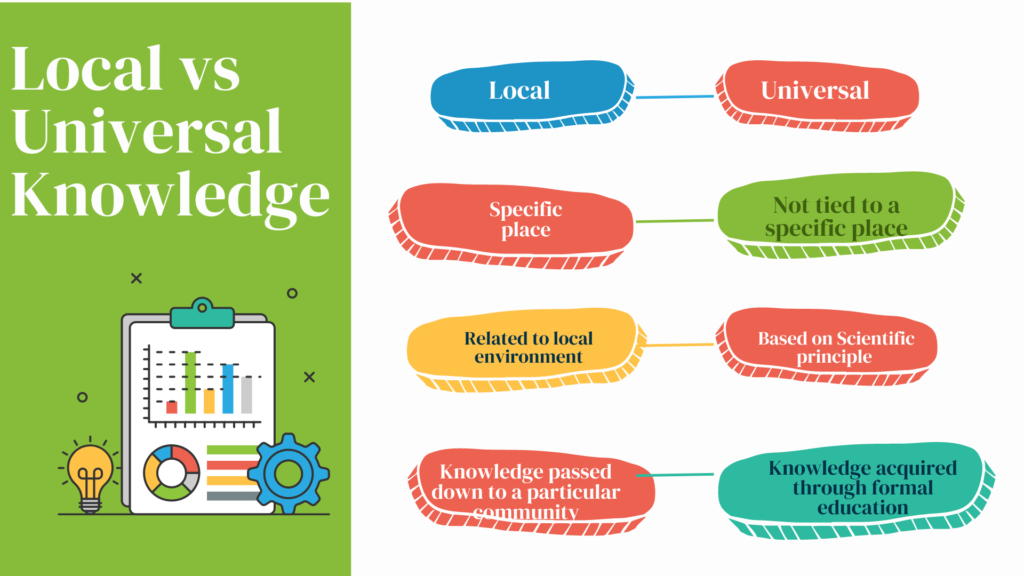
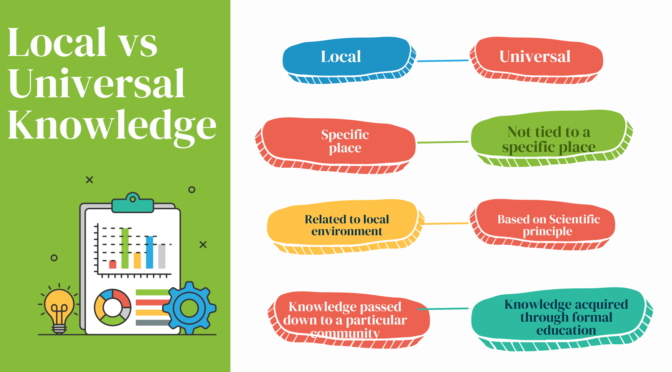
Local knowledge is the knowledge that is specific to a particular place, region, or culture. Local Knowledge includes traditional practices, beliefs, values, customs, and ways of life that have been developed and passed down over time within a particular community. Local knowledge is mostly practical in nature and closely related to the local environment, including the natural and human-made systems that support life in that area.
Local knowledge is specific to a particular place or culture, while universal knowledge is recognized as having value and validity across different regions and cultures.
Universal knowledge refers to knowledge that is not tied to any particular place or culture and is recognized as having value and validity across different regions and cultures. Universal knowledge typically includes scientific principles, mathematical concepts, and other forms of knowledge that are considered to be true and unchanging regardless of where they are studied. Universal knowledge is the result of proper scientific and systematic study and research which is considered to be objective and impartial.
Universal knowledge is considered to be true, valid, and relevant in all cultures and communities. It is based on scientific principles and evidence which is considered to be applicable and relevant in all societies and cultures. Universal knowledge is often acquired through formal education and is validated through research and experimentation.
Also Read: Contextual and Textual Knowledge