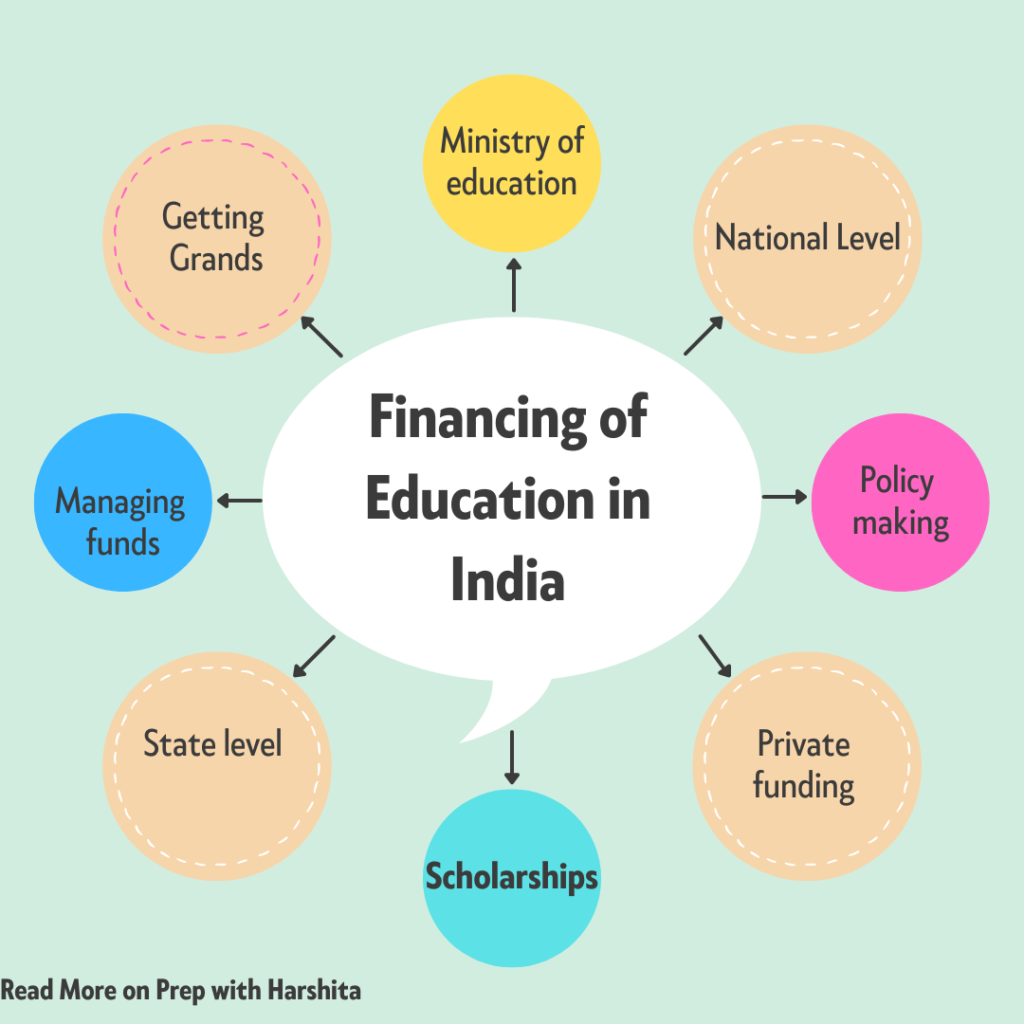
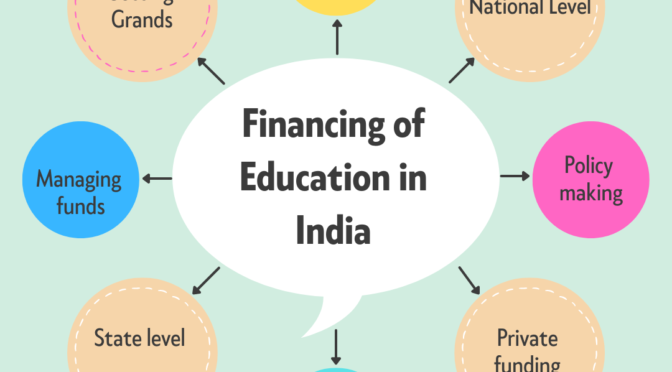
The financing of education in India involves a partnership between the central government and state governments.
Relation of Central and State Government
The central government is responsible for creating policies related to education and allocating funds to the states, while the state governments are responsible for implementing these policies and managing the funds.
The central government funds education through several schemes, such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA), and the centrally sponsored scheme of Teacher Education. These schemes provide financial assistance to states for various aspects of education, including primary education, secondary education, teacher training, and infrastructure development.
In addition to these schemes, the central government also provides funding to several autonomous institutions such as the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), and the National Institutes of Technology (NITs).
The state governments are responsible for financing and managing education at the state level, including primary, secondary, and higher education. They receive funding from the central government and also generate revenue through taxes and fees.
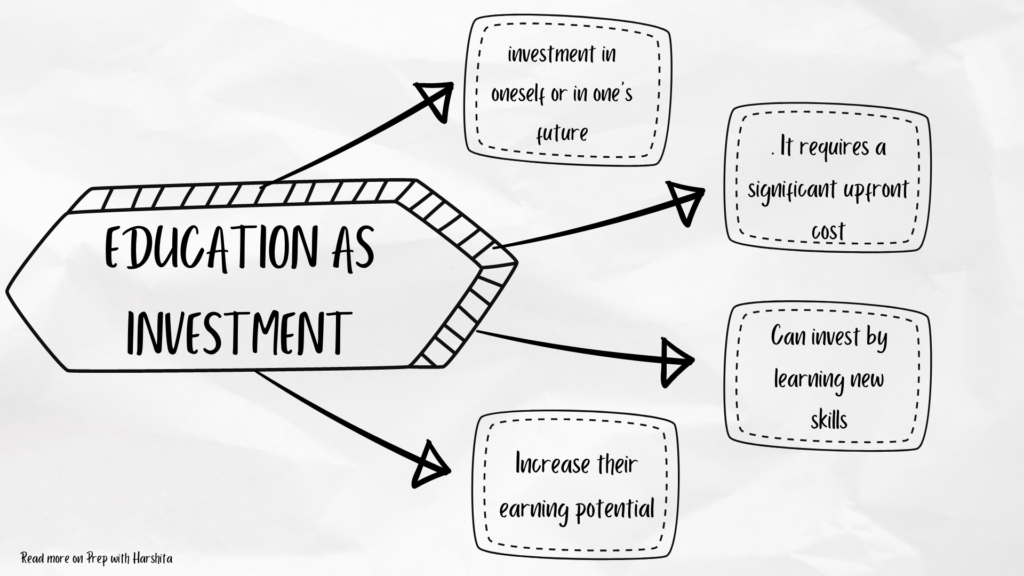
Also Read: Education as Investment
At National Level
- At the central level in India, the financing of education is primarily managed by the Ministry of Education, which is responsible for formulating policies related to education.
- They are also responsible for the allocation of funds to various education-related schemes and programs.
- The central government provides financial assistance to the states for various aspects of education, including primary education, secondary education, teacher training, and infrastructure development, through schemes like Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan (SSA), Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan (RMSA), and centrally sponsored schemes for teacher education, among others.
- The central government also provides funding to several autonomous institutions such as the Indian Institutes of Technology (IITs), Indian Institutes of Management (IIMs), and the National Institutes of Technology (NITs).
- Apart from these schemes and programs, the central government also provides scholarships and financial assistance to students belonging to economically weaker sections and other disadvantaged groups to ensure their access to quality education.
- The government has also introduced various initiatives like the Digital India campaign, Skill India Mission, and Atal Innovation Mission to promote innovation, digital literacy, and skill development among students.
- In addition to the Ministry of Education, the central government also provides funding to other ministries like the Ministry of Tribal Affairs, Ministry of Minority Affairs, and Ministry of Women and Child Development, which work towards providing education to marginalized and vulnerable sections of society.
At State Level
In India, the financing of education at the state level is primarily the responsibility of the state governments. Each state has its own education department and is responsible for funding and administering education within its boundaries.
The primary sources of funding for education at the state level in India include:
- State Budgets: The state governments allocate funds for education in their annual budgets. These funds are used to pay for the salaries of teachers, the construction of schools, the procurement of learning materials, and other related expenses.
- Grants from Central Government: The central government also provides grants to the state governments for education. These grants are provided through various schemes such as the Sarva Shiksha Abhiyan, Rashtriya Madhyamik Shiksha Abhiyan, and Mid-Day Meal Scheme.
- Loans from Financial Institutions: The state governments can also take loans from financial institutions such as the World Bank and Asian Development Bank to finance education.
- Private Funding: Private institutions such as non-profit organizations, philanthropic foundations, and corporate social responsibility initiatives also contribute towards the financing of education in India.
However, despite these sources of funding, there are still significant gaps in the availability and quality of education in many states of India, particularly in rural areas. In recent years, the government has taken steps to increase funding for education and improve access to education for marginalized communities.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita