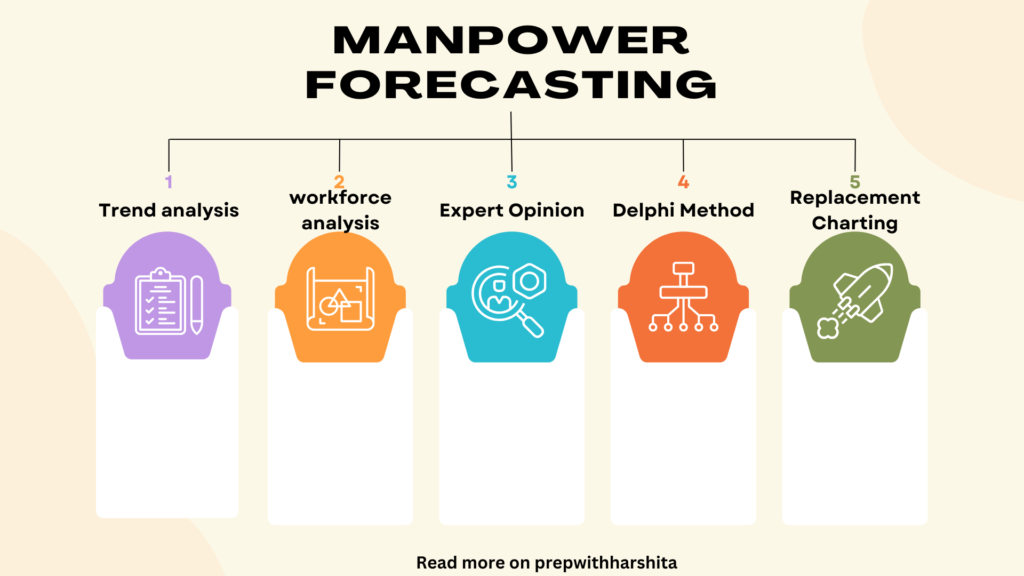
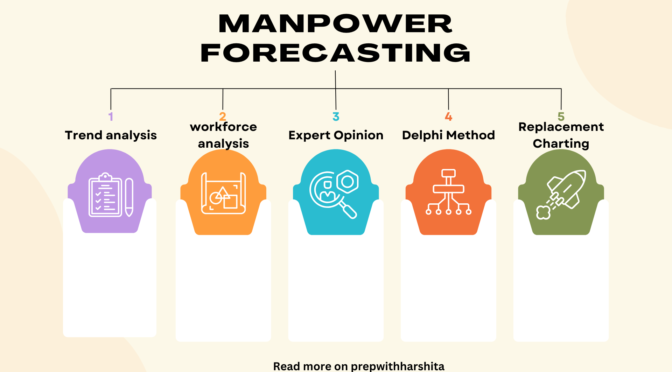
Manpower forecasting is the process of estimating the future workforce needs of an organization, based on a range of factors such as company growth projections, industry trends, and demographic changes. Here are some common techniques used for manpower forecasting:
- Trend analysis: This involves studying historical data on staffing levels, employee turnover rates, and other relevant factors to identify patterns and trends. This information can help in making predictions about future staffing needs.
- Workforce analytics: By analyzing employee data, such as performance ratings, skills, and demographics, organizations can identify gaps in the workforce and anticipate future hiring needs.
- Expert opinion: Gathering insights from managers and other subject matter experts can provide valuable information about industry trends and future business plans that can influence workforce needs.
- Workload analysis: Analyzing the workload and productivity levels of current employees can help determine if there is a need to hire additional staff or if current staff can be reallocated to more pressing needs.
- Scenario planning: This involves developing multiple scenarios based on various future scenarios, such as changes in technology or changes in the economy, to assess their impact on workforce needs.
- Replacement charting: This technique involves identifying critical positions within the organization and creating a list of potential candidates who could fill these roles in the future.
- Delphi method: This involves gathering expert opinions from a panel of industry experts anonymously, to ensure that personal biases do not influence the results.
Also Read: Cost Analysis in Education
Overall, the most effective manpower forecasting techniques will depend on the specific needs and goals of the organization, as well as the available data and resources.