Health education is a process that aims to promote and improve the health and well-being of individuals, communities, and societies through the dissemination of knowledge, the development of essential skills, and the promotion of healthy behaviors and lifestyles.
It is an integral part of public health and healthcare systems and plays a crucial role in preventing diseases, promoting healthy behaviors, and empowering individuals to make informed decisions about their health.
Key concepts and principles of health education include:
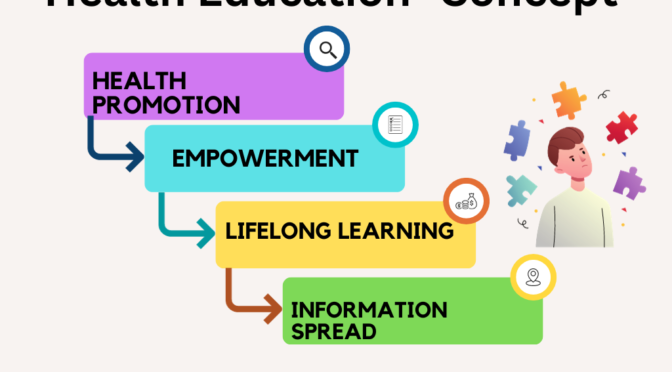
- Information Dissemination: Health education involves providing accurate and up-to-date information about various aspects of health, including nutrition, physical activity, disease prevention, mental health, sexual health, substance abuse, and more. This information empowers individuals to make informed choices about their health.
- Behavior Change: It seeks to influence and change unhealthy behaviors by promoting positive ones. This may involve teaching individuals how to quit smoking, adopt healthier eating habits, practice safe sex, or manage stress effectively.
- Health Promotion: It aims to promote health and prevent disease rather than just focusing on the treatment of illness. Health education encourages people to adopt a proactive approach to their health, emphasizing preventive measures such as vaccinations, screenings, and regular check-ups.
- Empowerment: It empowers individuals to take control of their own health and make informed decisions. It teaches them how to access reliable health information, assess risks, and develop self-care skills.
- Tailoring to Target Audience: Effective health education programs consider the specific needs, backgrounds, and cultural sensitivities of the target audience. Messages and interventions should be tailored to address the unique challenges and circumstances of different communities or populations.
- Communication Strategies: Effective communication is central to health education. It involves clear and concise messaging, using various communication channels such as media, social media, public speaking, and interpersonal communication.
- Community and School-Based Education: Health education can take place in schools, workplaces, healthcare settings, and communities. It may be part of formal curricula, workshops, awareness campaigns, or one-on-one counseling.
- Policy Advocacy: It can also involve advocating for policies that support healthy behaviors and environments, such as tobacco control laws, nutrition labeling, and public health regulations.
- Lifelong Learning: It is not limited to a specific age group or life stage. It should be a lifelong process, encouraging individuals to continuously seek knowledge and adapt their behaviors as they age and their health needs change.
Also Read: Interdisciplinary nature of Education
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita