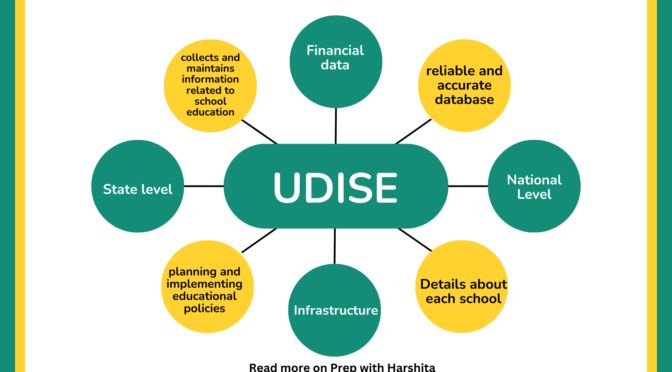
UDISE, which stands for Unified District Information System for Education, is a comprehensive database in India that collects and maintains information related to school education. It is managed by the Ministry of Education, Government of India. The primary objective of UDISE is to create a reliable and accurate database for educational planning and policy-making at both the state and national levels.
Here’s how UDISE operates at both levels:
State Level :
- Each state in India maintains its own UDISE database, which includes detailed information about schools, teachers, students, infrastructure, and various other educational indicators.
- The state-level UDISE data is crucial for the respective state governments to assess the status of education within their jurisdiction.
- It helps in planning and implementing educational policies, allocating resources, and monitoring the progress of educational initiatives at the state level.
National Level :
- The data collected at the state level is aggregated at the national level to create a comprehensive database that provides a panoramic view of the education system across the country.
- The national-level UDISE database is used by the Ministry of Education, Government of India, for formulating national-level policies, monitoring the overall progress of education, and making informed decisions related to education.
Key components of UDISE data include:
- School Information: Details about each school, including its location, type, management, etc.
- Teacher Information: Information about teachers, including their qualifications and experience.
- Student Enrollment: Data on the number of students enrolled in each class and other demographic details.
- Infrastructure: Information on the infrastructure and facilities available in schools, such as classrooms, laboratories, libraries, etc.
- Financial Data: Details about the financial aspects of education, including budget allocation and expenditure.
By maintaining and regularly updating the UDISE database, education authorities at both state and national levels can make data-driven decisions to enhance the quality of education and address challenges in the education system. The database also serves as a valuable resource for researchers, policymakers, and other stakeholders in the education sector.
Also Read: Nteq Model
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita