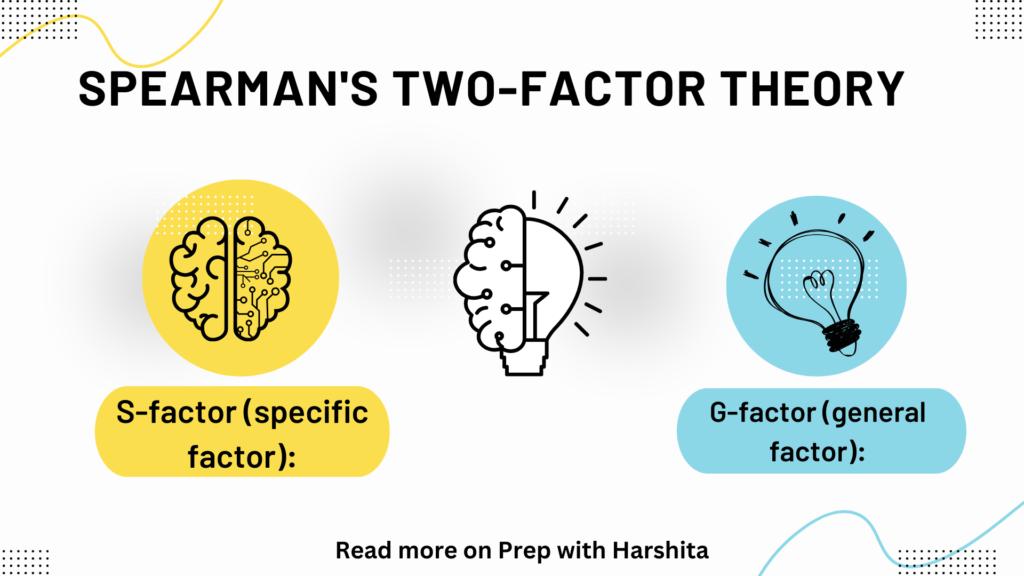
Spearman’s Two-Factor Theory of intelligence, which was proposed by British psychologist Charles Spearman in the early 20th century. This theory suggests that intelligence is composed of two factors: the general factor (g) and specific factors (s).
General Factor (g):
According to Spearman, there is a single, underlying general intelligence factor (g) that influences performance on all cognitive tasks. This general factor represents an individual’s overall cognitive ability and is responsible for the positive correlation observed between various intellectual tasks. In other words, people who perform well on one type of cognitive task are likely to perform well on others.
Also Read : Inquiry Teaching Model
Specific Factors (s):
In addition to the general factor, Spearman acknowledged that there are specific abilities (s) that are unique to particular tasks. These specific factors are not as pervasive or influential as the general factor but contribute to performance on specific types of cognitive tasks.
Spearman’s Two-Factor Theory has been influential in the history of intelligence research, and the general factor (g) is still considered by many as a key component of intelligence. However, contemporary theories of intelligence have expanded beyond Spearman’s model, incorporating multiple intelligences and considering other factors such as emotional intelligence. While the concept of a general factor remains, the understanding of intelligence has become more diverse over time.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita