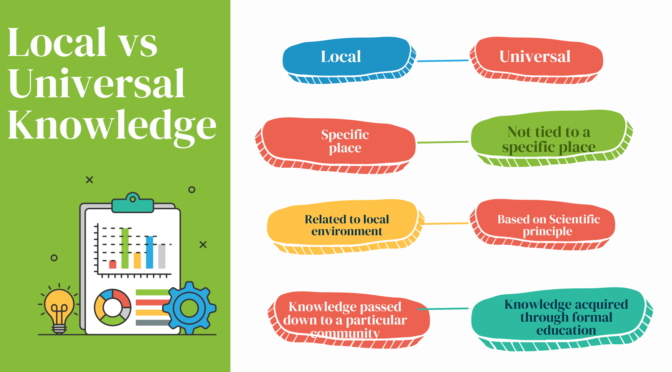
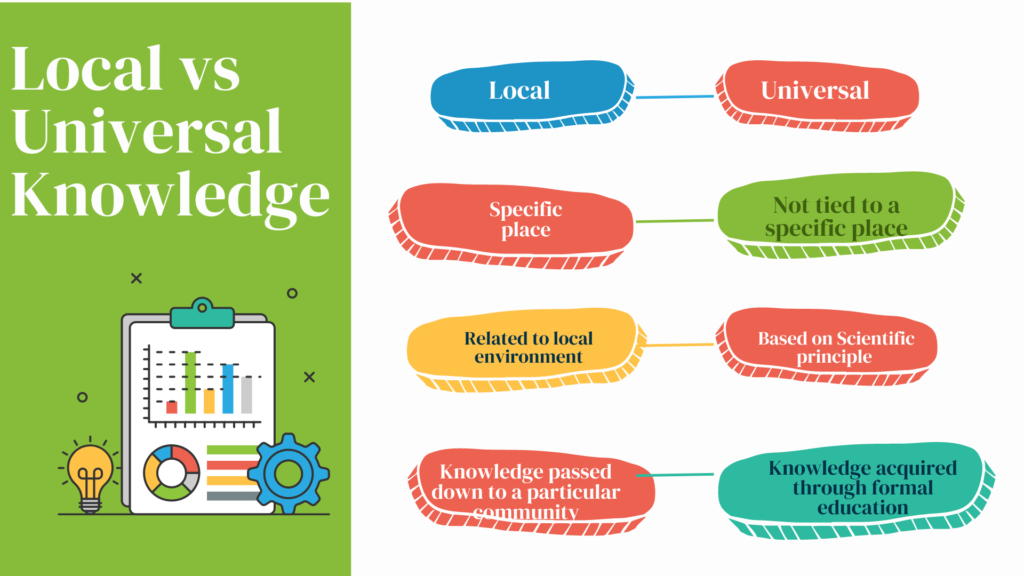
Contextual knowledge and textual knowledge are two types of knowledge that are important in understanding the information.
Textual knowledge refers to knowledge that is specifically stated or written down in text or language. It can include definitions, facts, theories, and other information that can be found in textbooks, articles, and other written materials.
On the other hand, contextual knowledge refers to the knowledge that is derived from the context or situation in which information is presented. It involves understanding the meaning and significance of information based on the broader context in which it is presented, including the social, cultural, historical, and personal factors that influence how information is interpreted.
For example, if someone reads the sentence “She wore a black dress to the funeral,” the textual knowledge would be the words themselves and their literal meaning. However, the contextual knowledge would involve understanding the cultural and social significance of wearing black to a funeral, as well as any personal or emotional factors that may be involved in the situation.
In summary, textual knowledge involves understanding the literal meaning of words and information, while contextual knowledge involves understanding the broader context in which information is presented and interpreted. Both types of knowledge are important in understanding and interpreting information accurately.
Also Read : Vedanta Philosophy

Also Visit : Prep with Harshita