Education as an instrument for transforming culture means it is a powerful tool that can be used to transform culture by shaping the beliefs, values, and attitudes of individuals and communities. It is a process that can help individuals to learn about their own culture and the cultures of others, and to develop a deeper understanding and appreciation of diversity.
Here are some ways in which education can be used as an instrument for transforming culture in detail:
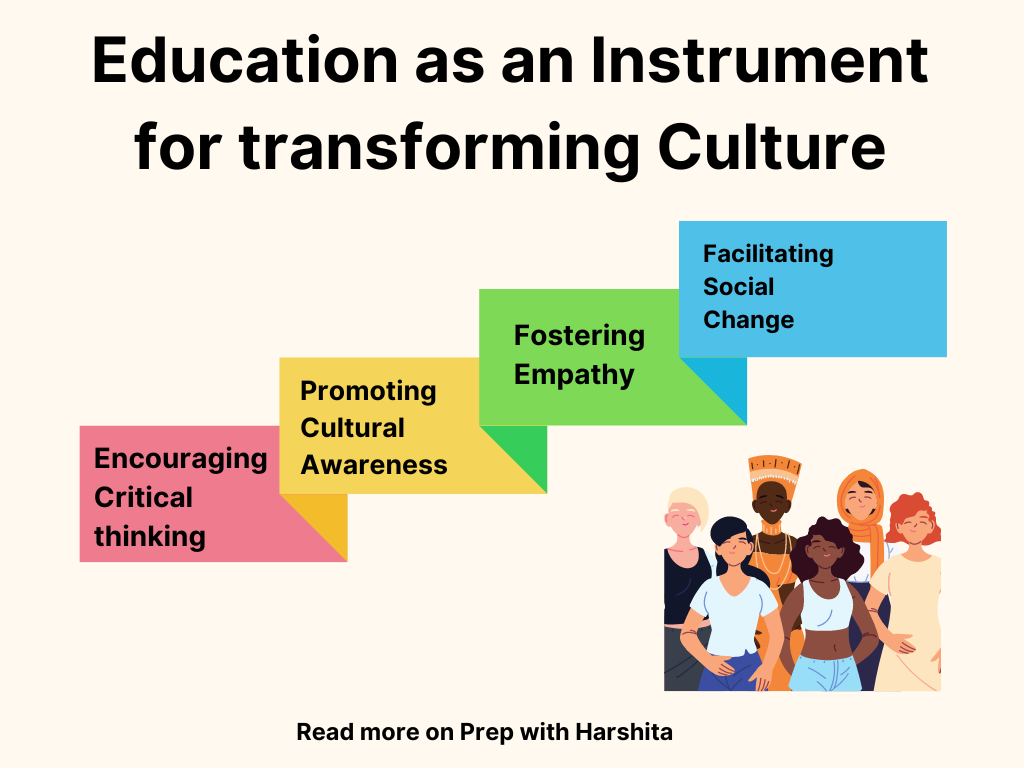
- Encouraging critical thinking:
Education can encourage critical thinking by challenging individuals to question their own beliefs and assumptions, and to examine different perspectives and points of view. Through education, individuals can learn to analyze information, evaluate arguments, and draw their own conclusions based on evidence. This can help individuals to develop a more open-minded and tolerant attitude towards different cultures, and to appreciate the value of diversity.
- Promoting cultural awareness:
Education can promote cultural awareness by providing individuals with opportunities to learn about their own culture and the cultures of others. Through education, individuals can gain a deeper understanding of the history, traditions, values, and customs of different cultures. This can help to break down stereotypes and prejudices, and to promote mutual understanding and respect.
- Fostering empathy:
Education can foster empathy by encouraging individuals to put themselves in the shoes of others, and to understand the experiences and perspectives of people from different cultural backgrounds. Through education, individuals can learn to appreciate the unique challenges and opportunities that are associated with different cultures. This can help to build bridges between different cultures and to promote a sense of shared humanity.
- Encouraging dialogue:
Education can encourage dialogue between individuals from different cultural backgrounds, and can provide a safe and respectful space for individuals to share their experiences and perspectives. Through education, individuals can learn to communicate effectively with people from different cultures, and to appreciate the richness and diversity of different ways of thinking and being. This can help to promote understanding and to break down barriers between different cultures.
- Facilitating social change:
Education can facilitate social change by empowering individuals to challenge cultural norms and practices that are discriminatory or oppressive. Through education, individuals can develop the skills and knowledge necessary to advocate for social justice and equality, and to promote positive change in their communities. This can help to create a more inclusive and just society, where everyone has the opportunity to thrive.
Also Read : Education as Manpower Planning
In conclusion, education is a powerful instrument for transforming culture by promoting critical thinking, cultural awareness, empathy, dialogue, and social change. Through education, individuals and communities can work towards creating a more inclusive, tolerant, and just society, where diversity is celebrated and everyone is valued.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita