Attitudinal Barrier and Facilitator in Inclusive Education are important factors. Attitudinal barriers refer to negative attitudes, beliefs, and prejudices that people may hold towards individuals with disabilities or differences. Inclusive education involves creating an environment where all learners, including those with disabilities, feel welcomed, respected, and valued.
However, attitudinal barriers can impede the success of inclusive education by creating a negative atmosphere for learners with disabilities.
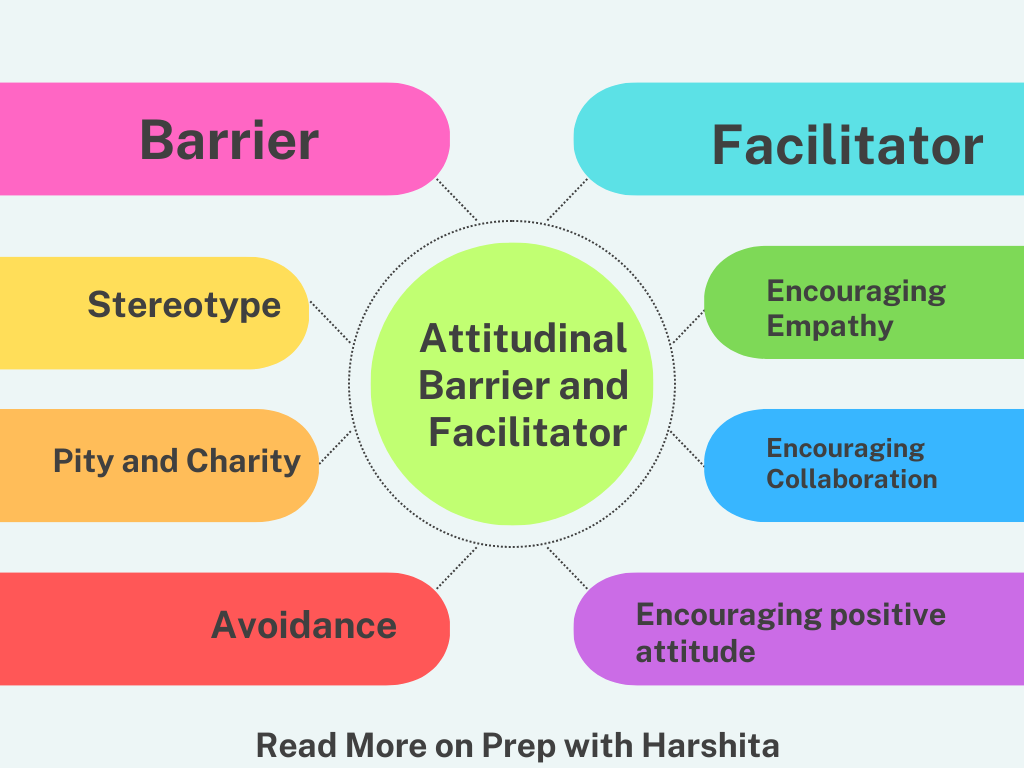
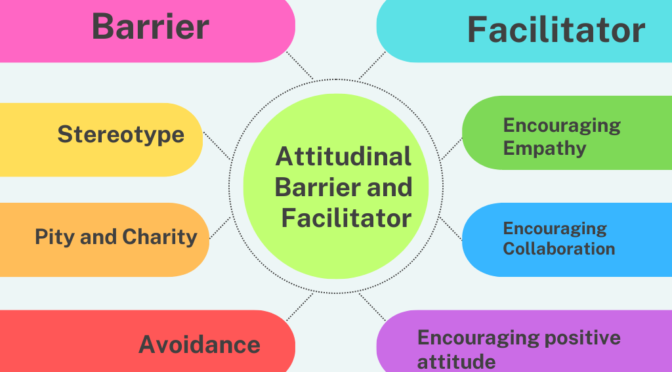
Attitudinal Barriers
Some examples of attitudinal barriers in inclusive education include:
- Stereotyping: The assumption that all learners with disabilities are the same or that they are not capable of achieving academic success.
- Pity and charity: A belief that learners with disabilities need to be pitied and helped, rather than recognized as equal members of the learning community.
- Fear and avoidance: The fear of interacting with learners with disabilities or the avoidance of engaging with them in educational activities.
- Stigmatization: The labeling of learners with disabilities as “different” or “abnormal,” which can lead to negative social attitudes and exclusion.
- Lack of knowledge: A lack of understanding about disabilities and how to support learners with disabilities in the classroom.
To overcome attitudinal barriers in inclusive education, it is essential to provide awareness and education for all stakeholders, including teachers, students, and parents. It is also important to create a positive and supportive learning environment that recognizes and celebrates the diversity of all learners. By breaking down attitudinal barriers, inclusive education can be successful and beneficial for all students.
Attitudinal Facilitator
An attitudinal facilitator in inclusive education is someone who works to promote positive attitudes towards learners with disabilities or differences in an educational setting. These individuals play an important role in creating a welcoming and inclusive environment for all learners, regardless of their abilities or differences.
Attitudinal facilitators in inclusive education can include teachers, school administrators, guidance counselors, and support staff. They work to promote positive attitudes towards learners with disabilities in a variety of ways, such as:
- Encouraging empathy and understanding: Attitudinal facilitators can encourage learners to empathize with and understand the challenges faced by their peers with disabilities.
- Celebrating diversity: They can promote a culture of diversity and inclusivity by celebrating the unique abilities and strengths of all learners.
- Providing education and training: Attitudinal facilitators can provide education and training to teachers and staff to increase their knowledge and understanding of disabilities and how to support learners with disabilities.
- Encouraging collaboration: They can encourage collaboration and teamwork among learners of all abilities to promote a sense of community and belonging.
- Modeling positive attitudes: Attitudinal facilitators can model positive attitudes towards learners with disabilities by treating them with respect and dignity and valuing their contributions to the learning community.
By serving as attitudinal facilitators in inclusive education, individuals can help to create a more inclusive and welcoming environment that supports the academic and social success of all learners.
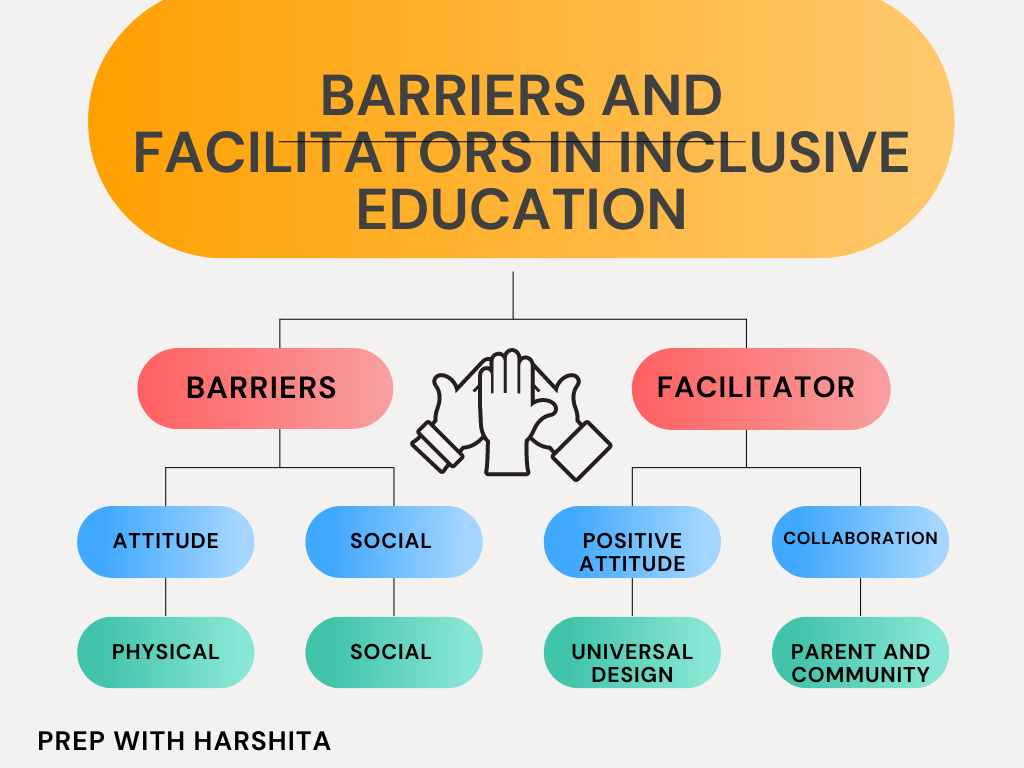
Also Read : Barriers and Facilitators in Inclusive Education