Teacher autonomy and professional Independence refer to the degree to which teachers are able to make decisions about what and how to teach in their classroom without undue interference or control from external sources such as administrators or government officials.
Professional independence refers to the ability of teachers to exercise their professional judgment in matters related to teaching and learning, without being unduly influenced by external factors such as politics or market forces.
Both teacher autonomy and professional independence are important for the success of the education system. When teachers have a high degree of autonomy, they are more likely to be invested in their work and motivated to innovate and try new teaching methods. This can lead to improved student outcomes and a more engaging classroom environment.
Similarly, when teachers are able to exercise professional independence, they are better able to make decisions that are in the best interests of their students, rather than being swayed by external factors such as standardized testing or political pressure. This can lead to a more well-rounded education for students and better preparation for success in the real world.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita
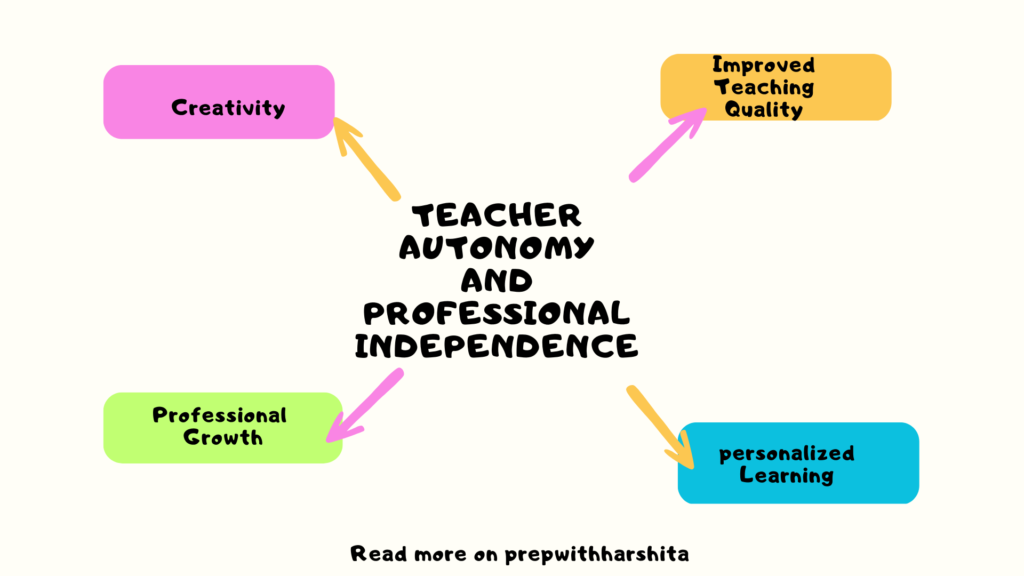
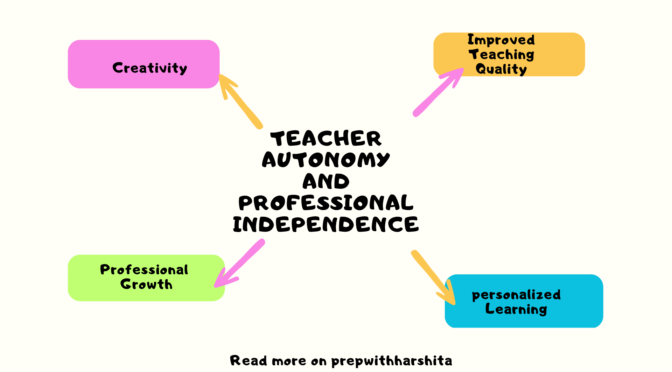
Teacher autonomy and professional independence are important for several reasons:
- Improved teaching quality: When teachers are given the freedom to make decisions about their classroom practices and teaching methods, they are more likely to be invested in their work and motivated to innovate. This can lead to improved teaching quality and better learning outcomes for students.
- Personalized learning: Teachers who have autonomy and independence are better able to personalize their teaching to meet the needs of individual students. They can adjust their teaching methods and materials to accommodate different learning styles, abilities, and interests.
- Professional growth: When teachers have autonomy and independence, they are more likely to engage in professional development and seek out opportunities to improve their skills and knowledge. This can lead to continuous improvement in teaching quality and better outcomes for students.
- Creativity and innovation: Teachers who have autonomy and independence are more likely to experiment with new teaching methods and approaches, which can lead to greater creativity and innovation in the classroom. This can help to engage students and make learning more exciting and relevant.
- Job satisfaction: Autonomy and independence can lead to increased job satisfaction among teachers. When teachers feel valued and trusted, they are more likely to be motivated and committed to their work. This can lead to lower teacher turnover rates and a more stable teaching workforce.
Overall, teacher autonomy and professional independence are important because they promote quality teaching, personalized learning, professional growth, creativity and innovation, and job satisfaction among teachers. This ultimately leads to better outcomes for students and a stronger education system.
Read Also: Aesthetics in Education