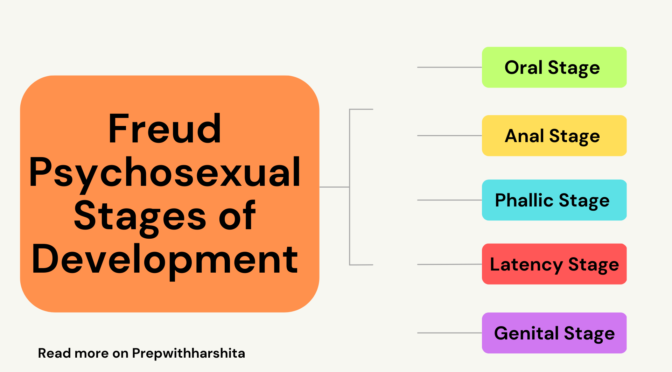
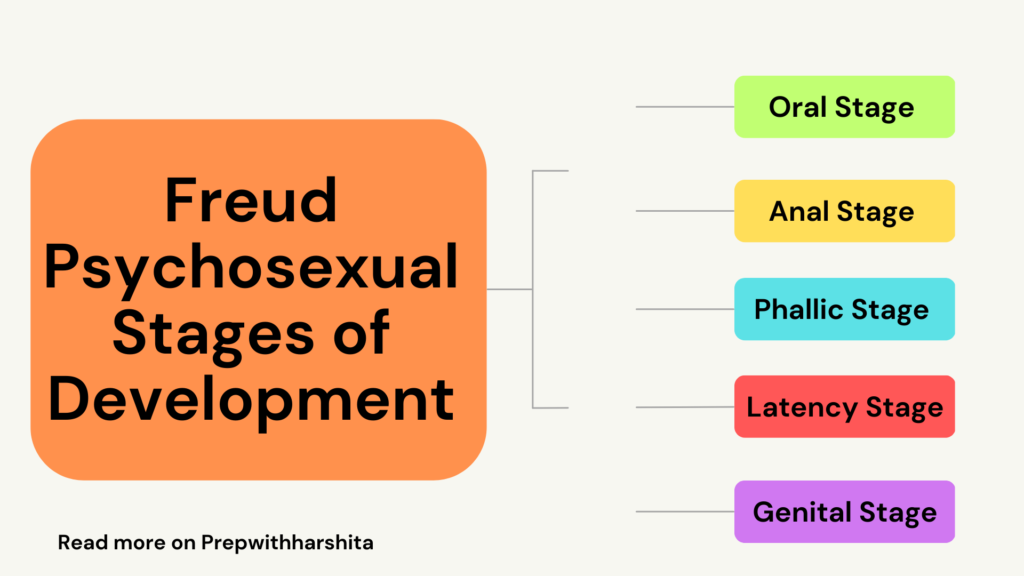
Sigmund Freud’s theory of psychosexual development is a theory that proposes that human development occurs in a series of stages, each of which is characterized by a particular conflict or crisis related to the expression of sexual and aggressive drives. According to Freud, the resolution of these conflicts determines the individual’s psychological and emotional health in adulthood.
The five stages of Freud’s theory of psychosexual development are:
- Oral Stage (birth to 18 months): In this stage, the infant’s primary source of pleasure and satisfaction comes from oral activities such as sucking, biting, and chewing. The main conflict in this stage is weaning, or the transition from breast or bottle feeding to solid foods.
- Anal Stage (18 months to 3 years): In this stage, the child’s focus shifts to the anal region and the elimination of waste. The main conflict in this stage is toilet training, which can lead to conflicts over issues of control and autonomy.
- Phallic Stage (3 to 6 years): In this stage, the child becomes more aware of their own gender identity and develops a strong attachment to the opposite-sex parent. This is known as the Oedipus complex for boys, and the Electra complex for girls.
- Latency Stage (6 years to puberty): In this stage, the child’s sexual and aggressive drives are largely dormant, and they focus on developing social and intellectual skills.
- Genital Stage (puberty to adulthood): In this stage, the individual’s sexual and aggressive drives are reactivated, and they seek out sexual relationships and intimate connections with others.
Freud believed that if a child experiences difficulties during any of these stages, it can lead to psychological and emotional problems in adulthood. For example, unresolved conflicts during the anal stage may lead to issues related to control, perfectionism, or messiness later in life. However, it’s important to note that Freud’s theory of psychosexual development is controversial and has been subject to criticism and debate in the field of psychology.
Also Read : Types of Evaluation
Also Read : Prep with Harshita