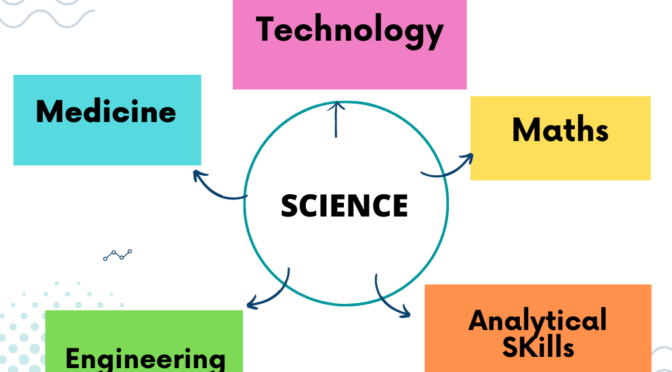
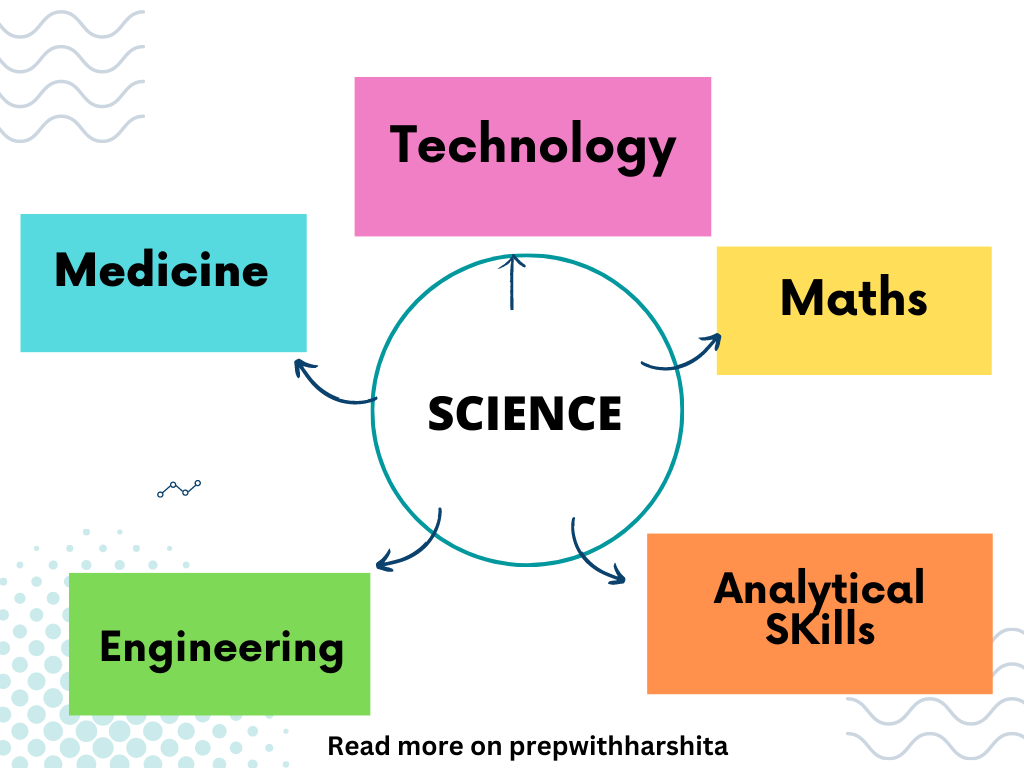
Science is a field of study that is closely connected to many other subjects, including mathematics, technology, engineering, and medicine. Correlation of Science with other Subjects is very vast.
Here are some examples of the correlation of Science with other subjects:
- Mathematics: Science and mathematics are closely linked, as science relies heavily on mathematical principles and equations. For example, physics is a branch of science that uses mathematical models to describe natural phenomena, and chemistry relies on mathematical equations to explain chemical reactions.
- Technology: Science and technology are also closely correlated, as many scientific discoveries have led to new technological advancements. For example, the development of the transistor, a key component of modern electronics, was based on the principles of quantum mechanics, a branch of physics.
- Engineering: Science and engineering are closely related, as engineers use scientific principles to design and build new products and systems. For example, biomedical engineers use knowledge of biology and chemistry to design medical devices and treatments.
- Medicine: Science and medicine are interconnected, as medical research relies on scientific discoveries and methods to develop new treatments and cures for diseases. For example, advances in genetics have led to new treatments for genetic disorders and cancer.
In general, science is a fundamental part of many other subjects, and its principles and methods are used across a wide range of fields.
Also Read : Herbarium
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita