Science plays a crucial role in our lives and has many important benefits. Importance of Science is a vast topic.
Here are nine key points that highlight the importance of science:
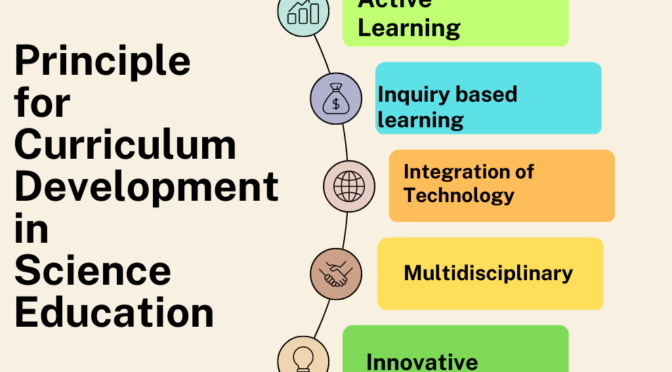
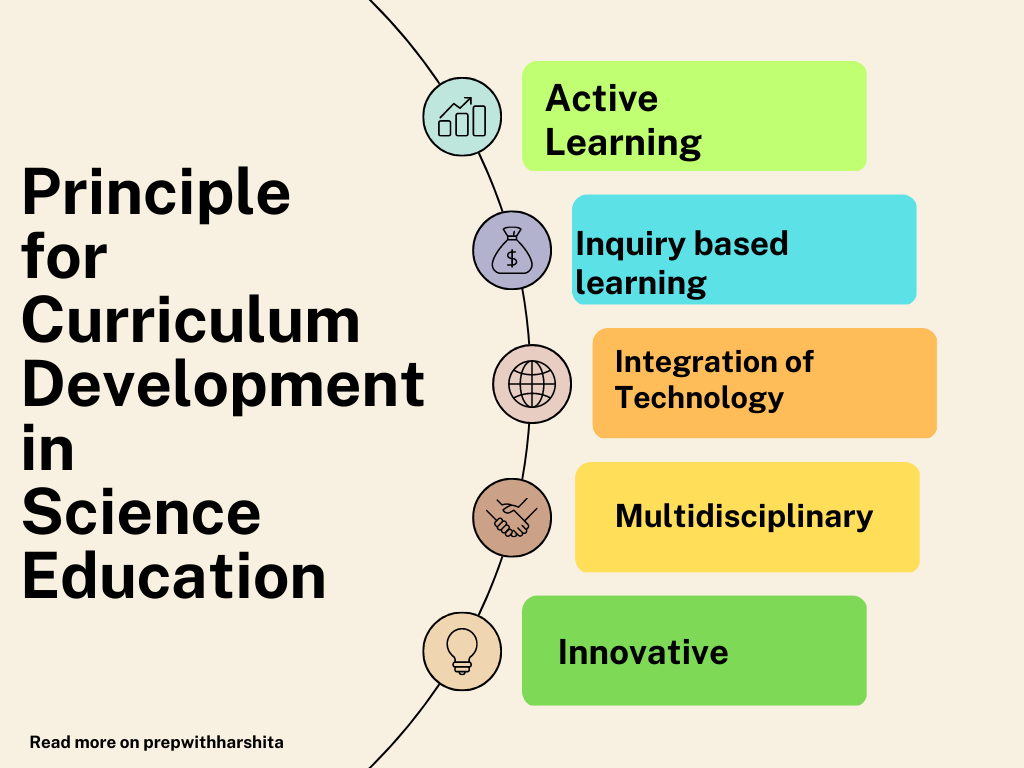
- Developing critical thinking skills: Science education teaches students to think critically, evaluate evidence, and draw conclusions based on empirical data. These skills are essential for making informed decisions and solving problems in many fields.
- Preparing students for the workforce: Science education provides students with the skills and knowledge they need to pursue careers in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) fields, which are in high demand in today’s job market.
- Enhancing scientific literacy: Science education helps students to develop a basic understanding of scientific concepts and principles, enabling them to better understand scientific issues that affect their daily lives.
- Fostering creativity and innovation: Science education encourages students to think creatively and develop innovative solutions to scientific problems. This mindset can be applied to many fields beyond science and can lead to new discoveries and breakthroughs.
- Addressing global challenges: Science education is essential for addressing global challenges such as climate change, pollution, and public health. By equipping students with the knowledge and skills to understand and address these issues, science education can help to create a more sustainable and equitable future for all.
- Advancing knowledge: Science is essential for advancing our knowledge and understanding of the natural world. By systematically observing and experimenting with the world around us, scientists can develop new theories and models that help us to explain how things work.
- Developing new technologies: Science is responsible for many of the technologies that have transformed our lives. From medicine and transportation to communication and entertainment, science has given us the tools we need to thrive in the modern world.
- Improving health: Science has helped us to understand the causes of many diseases and to develop treatments and cures that have saved countless lives. It has also contributed to public health initiatives like sanitation and vaccination programs.
- Solving environmental problems: Science is essential for addressing some of the most pressing environmental challenges we face, including climate change, pollution, and the depletion of natural resources. By understanding these problems and developing solutions, we can help to create a more sustainable future.
- Enhancing food security: Science has contributed to the development of new agricultural techniques and technologies that have increased food production and improved food quality. This has helped to feed a growing global population and reduce hunger and malnutrition.
- Fueling economic growth: Science and technology are major drivers of economic growth. By developing new products and services, creating jobs, and fueling innovation, science helps to create thriving economies and improve people’s lives.
- Promoting critical thinking: Science teaches us to think critically and question assumptions. By learning how to evaluate evidence and draw conclusions based on empirical data, we can make better decisions in our personal and professional lives.
- Inspiring curiosity and wonder: Science is a source of inspiration and wonder. From the smallest particles to the largest structures in the universe, science has revealed the beauty and complexity of the natural world and encouraged us to explore and discover more.
- Fostering international cooperation: Science is a global enterprise that transcends national boundaries and fosters international cooperation. By working together, scientists can share knowledge and resources, collaborate on research projects, and address global challenges that affect us all.
Also Visit : Prep with Harshita

Also Read : Meaning and Concept of Science