Curriculum development in science education is a process that involves several stages. Here are the key steps involved in developing a science curriculum:
- Identify learning goals: The first step in developing a science curriculum is to identify the learning goals for the course. This involves considering the key concepts, skills, and knowledge that students should acquire by the end of the course, as well as the learning outcomes that will be assessed.
- Design the curriculum framework: The next step is to design the curriculum framework, which provides an overview of the structure and content of the course. This includes selecting appropriate topics and organizing them into units, determining the scope and sequence of instruction, and identifying the instructional resources that will be used.
- Develop lesson plans: Once the curriculum framework has been established, the next step is to develop detailed lesson plans for each unit. This involves determining the instructional strategies that will be used to engage students, selecting appropriate materials and resources, and designing assessments to measure student learning.
- Implement the curriculum: After the curriculum has been developed, it is time to implement it in the classroom. This involves delivering the lessons and activities outlined in the curriculum framework, using the lesson plans developed during the planning stage.
- Evaluate and revise the curriculum: The final step in curriculum development is to evaluate the effectiveness of the curriculum and make revisions as needed. This involves assessing student learning outcomes, soliciting feedback from students and teachers, and making changes to the curriculum based on the results.
Also Read: Vivarium
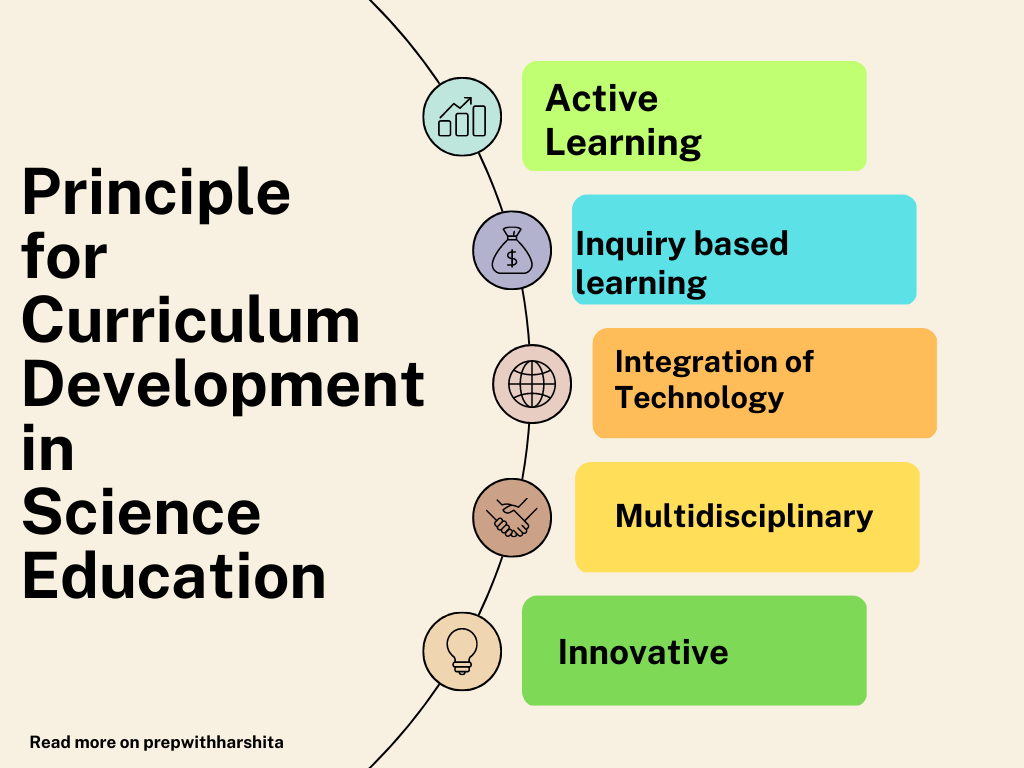
Principle for Curriculum Development in Science Education:
- Alignment with standards: Science curricula should align with national or state science standards to ensure that students are learning the key concepts and skills necessary for success in science. These standards provide a framework for developing curricula and assessments that reflect the expectations for student learning in science.
- Inquiry-based learning: Science curricula should incorporate inquiry-based learning, which allows students to engage in scientific investigations and develop critical thinking skills. This involves providing students with opportunities to explore scientific phenomena through hands-on activities, experiments, and investigations.
- Active learning: Science curricula should promote active learning, where students are actively engaged in the learning process rather than passively receiving information. This can involve a variety of instructional strategies, such as group work, discussions, and project-based learning.
- Integration of technology: Science curricula should integrate technology to enhance student learning and engagement. This can involve using simulations, virtual labs, and other digital tools to allow students to explore scientific concepts in new ways.
- Multidisciplinary approach: Science curricula should take a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating other subjects such as mathematics, engineering, and technology. This helps students to see the connections between different fields and to apply their scientific knowledge in real-world contexts.
- Equity and inclusion: Science curricula should be designed to promote equity and inclusion, providing opportunities for all students to engage in science learning regardless of their background or identity. This can involve incorporating diverse perspectives and experiences into the curriculum and creating a supportive and inclusive learning environment for all students.
Also Visit: Prep with Harshita