Conflict management in psychology refers to the process of resolving disagreements or disputes between individuals or groups in a constructive manner. It involves understanding the sources and nature of conflicts and employing strategies to prevent, manage or resolve conflicts.
Psychologists recognize that conflict is a natural and inevitable part of human interactions. It can arise from differences in values, goals, beliefs, personality, and culture. Conflict can also be caused by misunderstandings, communication breakdowns, or competing interests.
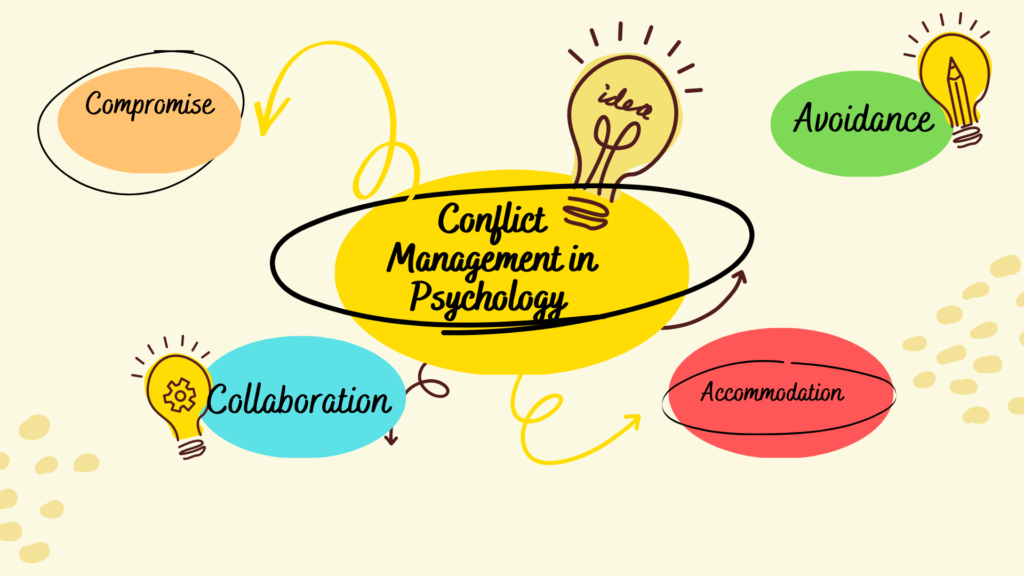
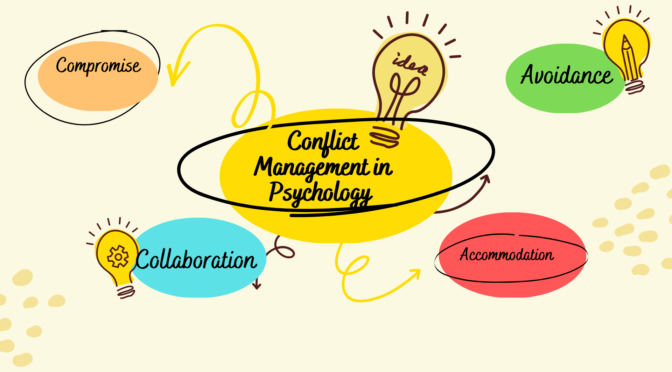
There are various approaches to conflict management in psychology. Some of the commonly used methods include:
- Collaborative problem-solving: This approach involves working together to identify the underlying issues and find mutually acceptable solutions.
- Compromise: In this approach, both parties make concessions and reach a middle ground that satisfies their interests.
- Avoidance: This approach involves ignoring or postponing the conflict until a later time when emotions are less intense.
- Accommodation: This approach involves one party giving in to the other to maintain harmony and preserve the relationship.
- Competitive: This approach involves seeking to win at all costs, which can lead to a win-lose situation.
Also read: Personality Assessment
Psychologists also emphasize the importance of effective communication, active listening, and empathy in conflict management. They may use techniques such as mediation, negotiation, or assertiveness training to help individuals or groups resolve conflicts. The ultimate goal of conflict management in psychology is to promote healthy relationships, enhance personal growth and reduce stress and negative emotions.